Marine plant food, an often overlooked but incredibly nutritious and versatile dietary component, offers a wealth of health benefits and environmental advantages. From the depths of the ocean to our dinner plates, marine plants hold the key to unlocking a sustainable and nutrient-rich future.
Delving into the diverse types of marine plant food, we uncover the nutritional powerhouses of macroalgae, microalgae, and phytoplankton. These aquatic wonders provide an abundance of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, contributing significantly to overall health and well-being.
Types of Marine Plant Food
Marine plant food encompasses a diverse array of organisms that serve as a vital nutritional source for marine life. These organisms can be broadly classified into three main categories: macroalgae, microalgae, and phytoplankton.
Macroalgae
- Description:Large, multicellular algae that are visible to the naked eye.
- Examples:Seaweeds, kelp, and rockweed.
- Nutritional Value:Rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Microalgae
- Description:Microscopic, single-celled algae.
- Examples:Chlorella, spirulina, and diatoms.
- Nutritional Value:Excellent source of protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
Phytoplankton
- Description:Microscopic, free-floating algae that form the base of the marine food chain.
- Examples:Dinoflagellates, coccolithophores, and diatoms.
- Nutritional Value:High in chlorophyll, protein, and essential fatty acids.
Benefits of Marine Plant Food
Incorporating marine plant food into a diet offers numerous health benefits. Marine plants are a rich source of essential nutrients, contributing significantly to overall well-being.
The nutritional value of marine plants lies in their abundance of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients play crucial roles in maintaining bodily functions, preventing chronic diseases, and promoting overall health.
Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin C:Essential for immune system function, collagen production, and antioxidant protection.
- Vitamin K:Vital for blood clotting and bone health.
- Iron:Necessary for oxygen transport and red blood cell production.
- Calcium:Essential for strong bones and teeth.
- Magnesium:Involved in muscle function, nerve transmission, and energy production.
- Potassium:Regulates fluid balance and blood pressure.
Antioxidants
- Carotenoids:Protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Phycocyanin:A potent antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties.
- Polyphenols:Reduce oxidative stress and improve heart health.
By consuming marine plant food, individuals can reap the benefits of these essential nutrients, supporting optimal health and well-being.
Sources of Marine Plant Food
Marine plant food, derived from various sources, provides essential nutrients for the growth and well-being of marine organisms. These sources can be categorized into three primary methods: harvesting, cultivation, and supplements.
Harvesting
Harvesting involves the collection of marine plants directly from their natural habitats. This method has been practiced for centuries, with seaweeds, kelp, and algae being the most commonly harvested species. Harvesting can be done manually or through the use of specialized equipment, such as dredges or trawls.
Marine plant food, rich in nutrients, is a vital component for the health of our oceans. As we celebrate the festive season, we can’t help but think of food christmas baubles , a creative and edible way to add a touch of holiday cheer to our trees.
Just like marine plant food nourishes marine life, these festive treats bring joy to our homes during the holidays. And as we return to our marine plant food discussion, let’s remember that preserving the health of our oceans is crucial for the well-being of our planet.
The availability and sustainability of harvested marine plants depend on factors such as seasonality, environmental conditions, and conservation efforts.
Cultivation
Cultivation involves the controlled growth of marine plants in dedicated aquaculture systems. This method allows for the production of specific species under optimal conditions, ensuring consistent quality and supply. Marine plant cultivation is becoming increasingly popular as it offers a more sustainable alternative to harvesting, reduces the pressure on wild populations, and enables the production of high-value species.
Supplements
Marine plant supplements are concentrated extracts or powders derived from marine plants. These supplements are often used in aquaculture and home aquariums to provide additional nutrients or enhance the nutritional value of diets. Marine plant supplements can be derived from a variety of species, including seaweeds, kelp, and microalgae, and are available in various forms, such as flakes, pellets, or liquids.
Incorporation of Marine Plant Food into Diet
Marine plant food offers a wealth of nutritional benefits, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. Incorporating these nutrient-rich foods into your daily meals is relatively easy, and there are several methods to choose from. This guide provides an overview of effective ways to integrate marine plant food into your diet, along with suggested recipes, meal ideas, and serving recommendations.
The recommended daily intake of marine plant food varies depending on individual factors such as age, health status, and activity level. However, as a general guideline, it is recommended to consume at least two to three servings of marine plant food per week.
Methods for Incorporating Marine Plant Food into Diet
Here is a table summarizing various methods for incorporating marine plant food into your diet:
| Method | Examples |
|---|---|
| Salads | Add seaweed, wakame, or kelp to your salads for a boost of nutrients and flavor. |
| Soups and stews | Include kombu or other types of seaweed in soups and stews to enhance their nutritional value and add depth of flavor. |
| Stir-fries | Incorporate nori, hijiki, or other edible seaweeds into your stir-fries for a crunchy texture and a burst of umami. |
| Snacks | Snack on dried seaweed sheets, roasted seaweed snacks, or seaweed chips for a healthy and satisfying treat. |
| Sushi and rolls | Use seaweed as a wrapper for sushi and rolls, providing a nutritious and flavorful base for your favorite fillings. |
In addition to these methods, you can also find marine plant food in various processed products, such as seaweed-infused condiments, sauces, and seasonings. These products offer a convenient way to add a touch of marine plant goodness to your meals.
Meal Ideas and Serving Suggestions
Here are some meal ideas and serving suggestions to help you incorporate marine plant food into your diet:
- Seaweed salad: Combine seaweed, vegetables, and a light dressing for a refreshing and nutritious side dish.
- Miso soup: Add seaweed to your miso soup for a savory and umami-rich broth.
- Stir-fried vegetables with seaweed: Stir-fry your favorite vegetables with seaweed for a quick and healthy meal.
- Seaweed snacks: Enjoy seaweed snacks as a healthy alternative to chips or crackers.
- Sushi with seaweed wrapper: Make your own sushi or rolls using seaweed as the wrapper, filled with your preferred ingredients.
By following these simple tips, you can easily incorporate marine plant food into your diet and reap the numerous health benefits it has to offer.
Health Considerations
Consuming marine plant food generally poses minimal health risks, but certain considerations should be taken into account.
Marine plants are typically safe for consumption, but some species may contain toxins or contaminants that can cause adverse effects. It’s essential to obtain marine plant food from reputable sources and be aware of potential risks associated with specific species.
Potential Health Risks
- Toxins:Certain marine algae species, such as red tide algae, can produce toxins that cause neurological or gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Contaminants:Marine plants can accumulate heavy metals, such as mercury and lead, from polluted waters. Consuming large amounts of contaminated marine plants can lead to heavy metal toxicity.
- Allergies:Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to marine plants, particularly those with shellfish allergies.
Precautions
- Consume in moderation:Limit the consumption of marine plant food to recommended serving sizes to minimize the risk of heavy metal accumulation.
- Choose reputable sources:Obtain marine plant food from reliable suppliers who adhere to quality control measures to ensure the absence of toxins or contaminants.
- Be aware of specific species:Educate yourself about the potential risks associated with different marine plant species and avoid consuming those known to contain toxins.
Interactions with Medications or Supplements, Marine plant food
Marine plant food may interact with certain medications or supplements. For example, iodine-rich marine plants can interfere with the absorption of thyroid medications. Consult a healthcare professional before consuming marine plant food if you are taking any medications or supplements.
Future of Marine Plant Food
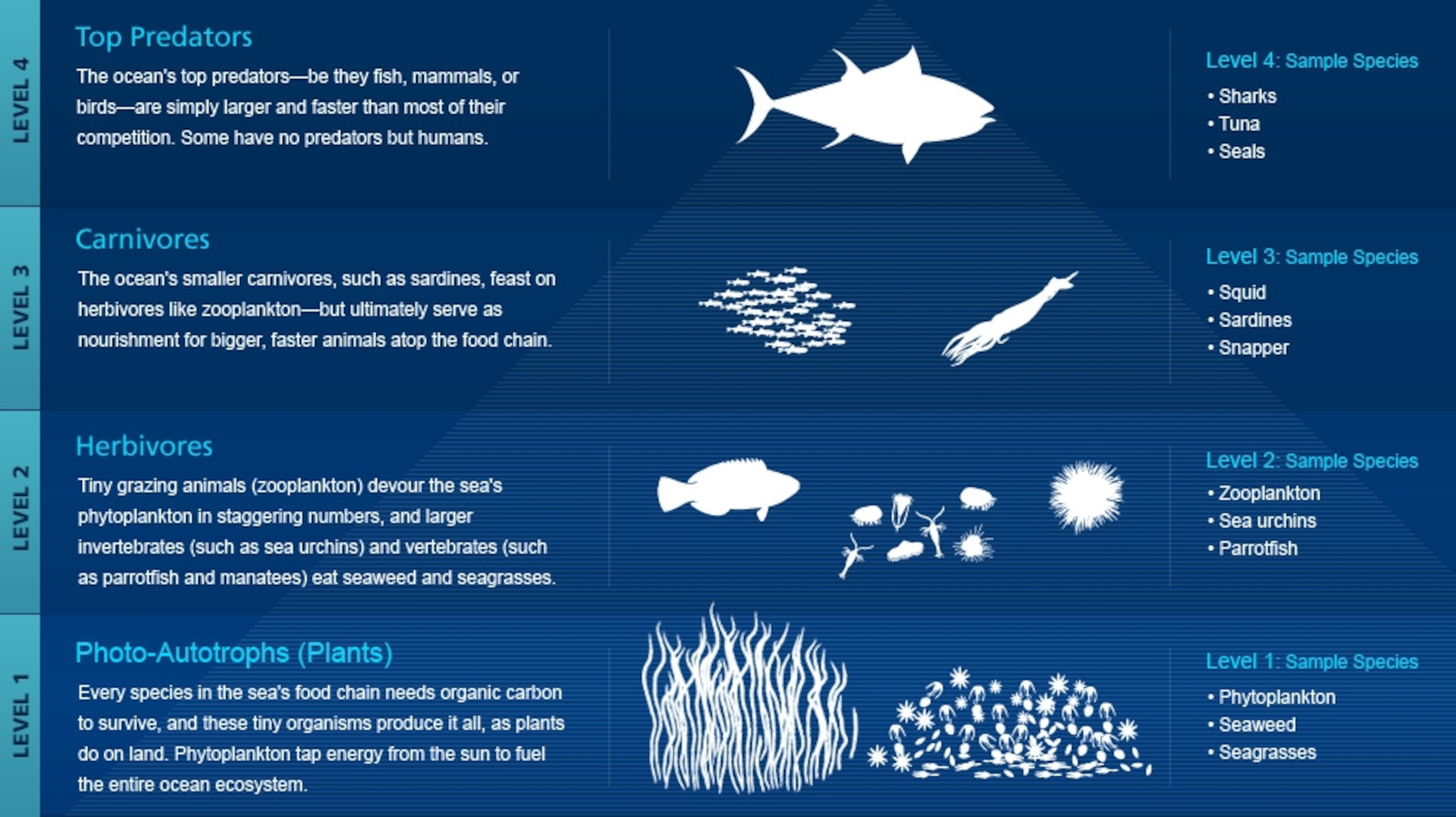
The future of marine plant food holds immense promise for sustainable food production and dietary innovation. As global populations continue to rise, marine plants emerge as a potential solution to meet the increasing demand for nutritious and environmentally friendly food sources.
One significant trend in the use of marine plant food is the growing recognition of their nutritional value. Research has demonstrated that marine plants are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Sustainable Food Source
Marine plants have the potential to be a sustainable food source due to their ability to grow in saltwater environments, which reduces the need for freshwater resources. They also have a high growth rate, allowing for efficient food production.
- Seaweed aquaculture is a promising method for cultivating marine plants on a large scale. This practice can help meet the growing demand for marine plant food while minimizing environmental impact.
- The use of marine plants in animal feed is another area of exploration. Incorporating marine plants into livestock diets can enhance the nutritional value of meat and dairy products.
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the production and utilization of marine plant food. These efforts include:
- Developing new cultivation techniques to increase yields and improve plant quality.
- Exploring innovative processing methods to preserve the nutritional value of marine plants.
- Investigating the potential of marine plants in the production of biofuels and other renewable energy sources.
Ultimate Conclusion
Incorporating marine plant food into our diets is not only beneficial for our health but also for the planet. As a sustainable and renewable resource, marine plants offer a promising solution to the challenges of food security and environmental degradation.
By embracing the culinary delights of seaweed salads, spirulina smoothies, and kelp-infused broths, we can harness the power of marine plants to nourish our bodies and protect our oceans.


