Food stuck in gums, a common yet often overlooked oral health concern, can lead to a range of issues. From the immediate discomfort of a lodged piece of popcorn to the potential for long-term gum inflammation and infection, understanding the causes, impacts, and solutions is key. This comprehensive guide dives into the intricacies of food impaction, providing actionable insights for maintaining healthy gums.
This guide will explore various aspects of food impaction, including identifying the problem, its impact on oral health, home remedies and prevention strategies, professional help and treatments, dietary considerations, and essential visual aids to aid your understanding.
Identifying the Problem
Food particles lodged in the gums, a common oral health concern, can range from minor inconveniences to more serious issues if left unaddressed. Understanding the nature of these particles, the foods most prone to causing them, and the mechanisms behind their entrapment is crucial for effective preventative measures and appropriate solutions. This section delves into the intricacies of food impaction in the gums.
Description of Food Particles Lodged in Gums
Food particles lodged in the gums are small bits of undigested food, typically of varying sizes and shapes, that become trapped between the gum line and the teeth. These particles can range from tiny crumbs to larger pieces of food, depending on the type of food consumed and the individual’s oral hygiene practices. The trapped particles can lead to irritation, discomfort, and potentially more serious issues if not removed promptly.
Types of Food Commonly Causing Impaction
Certain foods, due to their texture, size, or consistency, are more likely to become lodged in the gums. These include, but are not limited to, popcorn kernels, fibrous vegetables (like carrots and celery), sticky sweets (like caramels and gummy candies), and hard, crunchy foods (like nuts and chips). The texture and shape of the food significantly influence its propensity to get stuck.
Mechanisms of Food Particle Entrapment
Food particles can become lodged in the gums due to several factors. Improper chewing techniques can lead to incompletely broken-down food pieces being propelled towards the gum line. Poor oral hygiene, such as insufficient brushing and flossing, allows food particles to accumulate around the gum line, increasing the risk of entrapment. The shape and size of the teeth, as well as the presence of dental irregularities (like gaps or crowding), can also contribute to food impaction.
Potential Causes of Food Impaction in Gums
Several factors can contribute to food getting lodged in the gums. Insufficient oral hygiene is a significant cause. Poor chewing habits, such as inadequate mastication or hurried eating, also contribute to food impaction. Certain dental conditions, like gum recession or malocclusion, can increase the likelihood of food particles becoming trapped. In addition, certain dietary choices, as mentioned earlier, also play a crucial role in this issue.
Table: Food, Size/Shape, and Lodging Locations
| Food Type | Typical Size/Shape | Common Lodging Locations in Gums |
|---|---|---|
| Popcorn Kernels | Small, irregular shapes, often with sharp edges | Between gum line and teeth, especially in interdental spaces |
| Carrots | Long, cylindrical, with fibrous texture | Along the gum line, particularly around molars and premolars |
| Caramels | Soft, sticky, and irregular shapes, often elongated | Around the gum line and interdental areas, prone to adhering to teeth and gums |
| Nuts | Varying shapes and sizes, often hard and brittle | Between gum line and teeth, especially around molars, can also get lodged on gum tissue |
Impact on Oral Health
Food impaction, the lodging of food particles between teeth and gums, can have significant immediate and long-term consequences for oral health. Neglecting these impacted particles can escalate into more serious issues, impacting the overall well-being of the mouth. Understanding these implications is crucial for maintaining a healthy oral cavity.Impacted food creates an environment conducive to bacterial growth. These bacteria, multiplying rapidly in the confined spaces, trigger inflammation and potentially lead to infections.
This initial irritation can escalate, affecting the supporting structures of the teeth and contributing to more extensive oral health problems. The nature of the food itself plays a critical role in the severity of the impaction and the resultant oral health complications.
Immediate Effects of Food Impaction
The immediate effect of food impaction is often localized discomfort and irritation. Individuals may experience pain, tenderness, and swelling around the impacted area. These symptoms can vary depending on the type and amount of food lodged. Furthermore, the presence of food debris can lead to an unpleasant taste and odor, negatively impacting oral hygiene.
Long-Term Effects of Food Impaction
Persistent food impaction can result in more severe and long-lasting oral health problems. Inflammation of the gums, known as gingivitis, is a common consequence. This inflammation, if left untreated, can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced gum disease that damages the tissues and bone supporting the teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss.
Correlation with Gum Inflammation and Infection
Food impaction provides an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. The trapped food particles act as a source of nutrients for these microorganisms, allowing them to multiply rapidly. This bacterial overgrowth leads to inflammation, and if not managed, can escalate into a gum infection. The infection can spread to surrounding tissues, causing further damage and discomfort. The specific type of bacteria involved, as well as the individual’s immune response, can influence the severity of the infection.
Role of Different Food Types
The type of food consumed significantly influences the risk of impaction and its subsequent effects. Hard, crunchy foods, like nuts and seeds, are more likely to get lodged between teeth, increasing the chance of impaction. Sticky foods, like caramel or certain candies, can also adhere to teeth and gums, creating a breeding ground for bacteria. Conversely, soft, easily chewed foods pose a lower risk of impaction.
However, even soft foods can become impacted if not properly removed after consumption.
Table: Food Types, Impaction Consequences, and Oral Health Risks
| Food Type | Potential Impaction Consequences | Associated Oral Health Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Hard, Crunchy Foods (e.g., nuts, seeds, chips) | Increased risk of lodging between teeth, creating a site for bacterial buildup. | High risk of gingivitis, possible periodontitis development if not addressed promptly. |
| Sticky Foods (e.g., caramel, gum, certain candies) | Adherence to teeth and gums, creating a favorable environment for bacterial growth. | Increased risk of gingivitis, potential for cavities, and delayed plaque removal. |
| Fibrous Foods (e.g., raw vegetables, certain fruits) | Potential for lodging between teeth and gums, increasing bacterial accumulation. | Increased risk of gingivitis and plaque buildup, potentially accelerating periodontitis. |
| Soft Foods (e.g., mashed potatoes, yogurt) | Lower risk of impaction compared to hard or sticky foods. | Still susceptible to impaction if not thoroughly cleaned. |
Home Remedies and Prevention
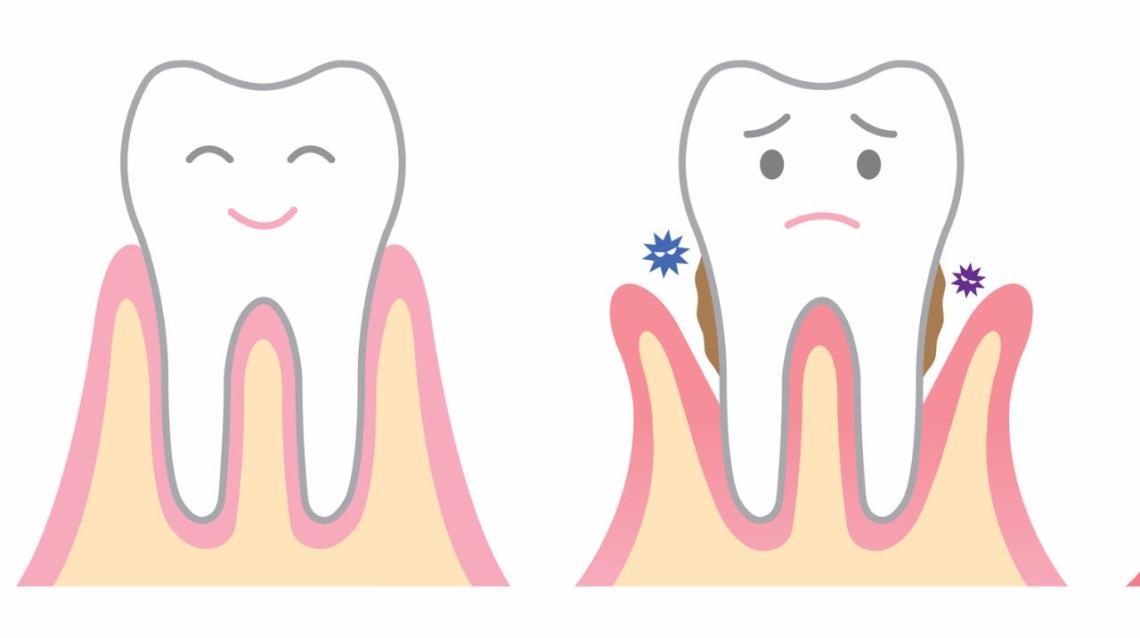
Food impaction in the gums can be a frustrating and sometimes painful experience. Fortunately, several home remedies and preventative measures can help remove these particles and prevent future issues. Understanding how to effectively clean the gum line and employing proper oral hygiene techniques are crucial in maintaining healthy gums and preventing food from becoming lodged.
Effective Home Remedies for Removing Food Particles
Several simple home remedies can help dislodge food particles from the gums. Gentle rinsing with warm salt water is a common and effective method. The salt helps to reduce inflammation and clean the area. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle, circular motions can also dislodge food. For stubborn particles, a toothpick or interdental brush can be carefully used, but extreme caution is needed to avoid injury.
Avoid using sharp objects, as these can damage the gums.
Proper Use of Oral Hygiene Tools
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is paramount in preventing food impaction. A soft-bristled toothbrush is essential for cleaning the gum line. Brushing should be done gently in a circular motion, focusing on the gum line and the areas where food particles tend to accumulate. Using an interdental brush can help clean between teeth and along the gum line, ensuring that food particles are not trapped.
Rinsing with mouthwash can also help remove food debris and freshen breath.
Methods of Oral Hygiene to Prevent Food Impaction
Several methods can effectively prevent food from becoming lodged in the gums. Regular brushing and flossing are crucial for removing plaque and food particles. Brushing twice a day for two minutes each time, and flossing daily, helps maintain a clean oral environment. Using an interdental brush or other specialized tools can target areas where food tends to get trapped.
Chewing sugar-free gum can stimulate saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and neutralize acids.
Table of Home Remedies
| Home Remedy | Application | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Warm Salt Water Rinse | Swish a mixture of warm water and salt in your mouth for 30 seconds. | Good for reducing inflammation and cleaning the area. |
| Gentle Toothbrushing | Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle, circular motions to dislodge food particles. | Effective for removing loose food particles. |
| Interdental Brush | Use an interdental brush to clean between teeth and along the gum line. | Excellent for removing food particles in hard-to-reach areas, but use with caution. |
| Mouthwash | Rinse with a fluoride mouthwash to help remove debris and freshen breath. | Helps remove food particles and freshen breath. |
Procedure for Cleaning the Gum Line to Avoid Impaction
A systematic approach to cleaning the gum line is essential.
- Thorough Brushing: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle circular motions, focusing on the gum line.
- Flossing: Carefully floss between teeth to remove any trapped food particles.
- Interdental Cleaning: Use an interdental brush to clean between teeth and along the gum line.
- Rinsing: Rinse your mouth with warm salt water or a fluoride mouthwash.
- Post-Meal Care: Rinse or brush immediately after meals to remove any food particles before they can become lodged.
Professional Help and Treatments
Food impaction, while often manageable at home, can sometimes necessitate professional intervention. Ignoring persistent or severe impaction can lead to complications, including infection and damage to surrounding tissues. Understanding when and how to seek professional help is crucial for maintaining oral health.Professional dental care is essential for addressing severe food impaction that cannot be removed by home remedies.
Dentists possess the expertise and tools to effectively remove impacted food particles, preventing further complications and promoting a healthy oral environment.
When Professional Help Is Necessary
Persistent pain, swelling, or discomfort around the impacted food are strong indicators that professional intervention is needed. Similarly, if the food is deeply embedded or lodged in a difficult-to-reach area, a dentist can effectively remove it. The inability to dislodge the food after repeated attempts at home remedies also suggests the need for professional help. A dentist can also address the underlying causes of the impaction, such as gum disease or tooth decay, which may make it difficult to remove the food on your own.
Dental Procedures for Severe Food Impaction
Various dental procedures are employed to remove impacted food, tailored to the specific location and severity of the impaction. These procedures range from simple cleaning techniques to more complex procedures.
- Dental Floss and Interdental Brush Use: A dentist might use dental floss or interdental brushes to carefully remove food lodged between teeth or in tight spaces. This is a routine procedure often performed in conjunction with other techniques to address the underlying cause of the impaction.
- Scaling and Root Planing: If gum disease or inflammation is contributing to the impaction, scaling and root planing procedures are employed to remove plaque and tartar buildup, allowing for easier access and removal of the impacted food. This procedure is crucial in addressing the root cause of recurrent impaction problems.
- Surgical Intervention (in rare cases): In extreme cases where food is deeply embedded or there are concerns about infection, surgical intervention might be necessary. This involves careful removal of the impacted food and any damaged tissue, followed by proper wound care and antibiotics to prevent complications.
The Dentist’s Role
A dentist plays a critical role in addressing food impaction, encompassing both immediate removal and long-term preventive measures. They assess the severity of the impaction, determine the appropriate treatment approach, and provide necessary follow-up care to prevent recurrence. A thorough examination is crucial to determine the root cause of the impaction and address any underlying oral health issues.
Professional Cleaning Procedure, Food stuck in gums
A professional cleaning procedure involves several steps, ensuring the removal of impacted food without causing further damage. The specific steps may vary based on the severity of the impaction.
- Examination and Assessment: The dentist thoroughly examines the affected area to determine the location and extent of the impaction, assessing any contributing factors like gum disease or tooth decay.
- Removal of Impacted Food: Using specialized instruments, the dentist carefully removes the impacted food particles. This may involve the use of dental tools like scalers, explorers, or curettes, depending on the situation.
- Cleaning and Polishing: The affected area is thoroughly cleaned to remove any remaining food debris or plaque. Polishing ensures a smooth surface, preventing future impaction.
- Follow-up and Preventive Measures: The dentist provides post-procedure instructions and preventive measures, such as recommending oral hygiene practices and regular check-ups to minimize the risk of future impaction.
Dental Procedures: Benefits and Risks
| Procedure | Benefits | Potential Risks ||—|—|—|| Dental Floss and Interdental Brush Use | Simple, cost-effective method to remove small impactions. | Can be ineffective for deep impactions, potential for gum irritation if not used properly. || Scaling and Root Planing | Addresses underlying gum disease, reduces inflammation, improves oral health. | Potential for discomfort during procedure, rare risk of infection.
|| Surgical Intervention | Removes deeply impacted food, addresses potential infection. | Higher risk of complications compared to other procedures, potential for scarring. |
Dietary Considerations
Proper dietary habits play a crucial role in preventing food particles from becoming lodged in the gums. By understanding the relationship between food textures and eating habits, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of impaction. Careful selection and preparation of food, coupled with mindful chewing techniques, are key strategies in maintaining gum health.Modifying eating habits and selecting appropriate foods can dramatically reduce the incidence of food impaction.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about chow chow dog food.
A shift towards more conscious consumption patterns can minimize the likelihood of food particles becoming trapped between gum tissue and teeth.
Dietary Tips to Minimize Food Impaction
Careful consideration of food texture and consistency is essential in preventing food impaction. Soft, easily digestible foods are generally less likely to get lodged between teeth and gums. This principle is particularly relevant for individuals prone to impaction.
- Choose soft foods over hard or crunchy ones. Examples include cooked vegetables, mashed potatoes, and yogurt. These are more easily broken down during chewing, reducing the risk of small pieces becoming lodged.
- Avoid overly sticky foods that tend to cling to teeth and gums. Sticky candies, certain types of bread, and some fruits (like overly ripe grapes) can contribute to impaction.
- Cut food into smaller, manageable pieces before eating. This helps in more efficient chewing and reduces the likelihood of large pieces becoming lodged in hard-to-reach areas.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Water helps to rinse away food particles and aids in the mechanical breakdown of food during chewing.
Modifying Eating Habits to Reduce Impaction
Consciously modifying eating habits can significantly lower the incidence of food impaction. This includes adjusting the pace and manner of eating.
- Eat slowly and chew thoroughly. Thorough chewing breaks down food into smaller particles, preventing them from getting lodged between teeth and gums. Focus on each bite and the process of chewing before swallowing.
- Avoid eating large bites. Large bites increase the risk of food getting lodged between teeth and gums due to the increased likelihood of incomplete chewing.
- Take your time between bites. This allows your mouth to prepare for the next bite, promoting thorough chewing.
- Use utensils effectively. Employing appropriate utensils can help in controlling the size of food portions and facilitating thorough chewing.
Relationship Between Food Textures and Gum Impaction
Different food textures have varying potential to cause impaction. Hard, crunchy, or sticky foods are more likely to become lodged compared to soft, easily digestible foods.
| Food Type | Texture | Potential for Impaction |
|---|---|---|
| Hard candy | Hard, sticky | High |
| Popcorn kernels | Hard, crunchy | High |
| Dried fruit | Hard, chewy, sticky | High |
| Steamed vegetables | Soft, tender | Low |
| Smoothie | Smooth, liquidy | Low |
Importance of Thorough Chewing
Thorough chewing is paramount in preventing food impaction. It breaks down food into smaller particles, making it easier to swallow and reducing the risk of food getting lodged between teeth and gums.
Thorough chewing is essential to prevent food impaction.
Proper chewing is a fundamental oral hygiene practice that minimizes the risk of food particles becoming trapped in hard-to-reach areas. It promotes the effective breakdown of food, aiding digestion and minimizing the chance of food particles getting stuck between teeth and gums. This habit also reduces the risk of discomfort and potential oral health issues.
Illustrations and Visual Aids
Visual aids are crucial in understanding and addressing food impaction in the gums. Clear illustrations can effectively communicate the location, nature, and prevention of this common oral health issue. They aid in comprehension, making complex concepts easier to grasp, and thus facilitating better preventive measures.Visual representations of impacted food particles and appropriate hygiene practices provide practical guidance for individuals seeking to maintain optimal oral health.
This section will showcase detailed illustrations designed to enhance understanding and promote effective self-care.
Gum Line Illustration
A detailed illustration of the gum line should highlight the various areas where food particles frequently become lodged. The image should clearly depict the junction between the gums and teeth, emphasizing the intricate contours and crevices where food can accumulate. This illustration should show different types of teeth (incisors, canines, premolars, molars) and their corresponding gum line features. Areas prone to food impaction, like the grooves of molars and the spaces between teeth, should be specifically marked.
Food Type Illustration
A visual representation of various food types should demonstrate their potential for causing gum impaction. This graphic can feature different categories of foods, such as crunchy vegetables, sticky sweets, and fibrous fruits. For each food type, the illustration should show the specific physical characteristics that contribute to impaction, such as the texture, size, and shape. Examples might include a close-up of a piece of popcorn lodged between molars, or a sticky piece of caramel near the gum line.
Proper Oral Hygiene Graphic
A graphic depicting the process of proper oral hygiene to prevent impaction should illustrate the crucial steps in maintaining a clean mouth. This could be a step-by-step sequence, demonstrating the use of a toothbrush, dental floss, and mouthwash. The illustration should visually guide the viewer through the process, emphasizing the importance of thorough brushing, flossing between teeth, and reaching all surfaces of the teeth.
The graphic should highlight the importance of consistent, proper brushing technique, and not just the visual act of brushing.
Dental Floss Illustration
The illustration should demonstrate the effective use of dental floss to remove food from between teeth. It should show the correct technique, including how to guide the floss between the teeth, and how to carefully slide it up and down against each tooth surface to remove any trapped food particles. Different angles of floss use should be included to demonstrate the application to various tooth positions.
The illustration should emphasize the importance of gentle, careful movement to avoid damaging gums.
Interdental Brush Illustration
An illustration on the use of interdental brushes for removing food particles should demonstrate the proper insertion and use of these brushes. The illustration should show how to select an appropriate brush size for specific spaces between teeth, how to angle the brush, and how to move it effectively to dislodge food. Different angles and brush positions should be included to show the effectiveness in various interdental areas.
The illustration should also include a guide to brush selection, size, and appropriate pressure to prevent injury to gums or teeth.
Epilogue: Food Stuck In Gums
In conclusion, addressing food impaction requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing proper oral hygiene techniques, mindful dietary choices, and prompt professional intervention when needed. By understanding the various factors contributing to food impaction and employing the recommended solutions, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of oral health problems and maintain healthy, vibrant gums.


