Raw food delivery route massachusetts presents a journey of vibrant health, a quest to connect with the purest essence of life’s nourishment. This path is not merely about delivering meals; it’s a dance of intention, a symphony of nature’s bounty brought directly to your doorstep. We shall delve into the intricate art of crafting efficient routes, safeguarding the sacredness of each ingredient, and weaving a tapestry of service that elevates the very act of eating.
From the bustling heart of Boston to the serene landscapes beyond, we will explore the landscape of demand, the dance of logistics, and the delicate balance of creating a service that embodies the principles of holistic well-being. This is more than just a business; it’s an opportunity to share the gifts of nature, one perfectly preserved, and beautifully presented meal at a time.
Market Overview: Raw Food Delivery in Massachusetts
The demand for raw food delivery services in Massachusetts is experiencing moderate growth, driven by increasing health consciousness and a growing interest in plant-based diets. This trend is influenced by the state’s relatively affluent population and its established culinary scene, which is open to innovative and health-focused food options. Regional variations exist, with higher demand observed in metropolitan areas like Boston and its surrounding suburbs, compared to more rural parts of the state.
Current Demand for Raw Food Delivery Services
The demand for raw food delivery in Massachusetts is concentrated in specific areas.
- Boston Metropolitan Area: This region, encompassing Boston and its adjacent suburbs, shows the highest demand. This is due to a dense population, higher disposable incomes, and a greater awareness of health and wellness trends. The presence of numerous universities and a young, health-conscious demographic further fuels this demand.
- Suburban Areas: Demand is also significant in affluent suburban communities like Newton, Brookline, and Wellesley. These areas are populated by individuals with higher incomes who prioritize healthy eating habits.
- Western Massachusetts: While demand is lower compared to the eastern part of the state, there is a growing interest in raw food in cities like Northampton and Amherst, which have a strong presence of health-conscious individuals and a more progressive lifestyle.
- Cape Cod and Islands: During the tourist season, there is a temporary surge in demand in the Cape Cod and Islands region. Visitors, particularly those from urban areas, seek healthy and convenient food options.
Demographics of Potential Customers
Potential customers for raw food delivery in Massachusetts exhibit distinct demographic characteristics.
- Age: The primary demographic consists of millennials (ages 25-40) and Gen X (ages 41-56), who are typically more informed about health and nutrition and are more likely to utilize online food delivery services. Baby Boomers (ages 57-75) also represent a segment, particularly those with specific health concerns or a strong interest in longevity.
- Income: The target market generally has a moderate to high income, allowing them to afford the typically higher prices associated with raw food and delivery fees. This includes professionals, entrepreneurs, and individuals with established careers.
- Lifestyle: Potential customers often lead active lifestyles and prioritize health and wellness. They may be fitness enthusiasts, yoga practitioners, or individuals interested in alternative medicine. They are also likely to be environmentally conscious and concerned about the sustainability of their food choices.
- Dietary Preferences: A significant portion of the customer base includes vegans, vegetarians, and individuals following specific diets such as paleo or gluten-free. Many customers are seeking raw food as a means of weight management, improved digestion, or enhanced energy levels.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape for raw food delivery in Massachusetts includes established players and emerging businesses.
- National Delivery Services: National food delivery platforms like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub offer access to some restaurants and vendors that provide raw or plant-based options, but they do not specialize in raw food. Their market share is significant due to their widespread availability and established user base.
- Specialized Raw Food Delivery Services: A few companies focus exclusively on raw food delivery, though their presence may be limited. These services often highlight the organic, locally sourced nature of their ingredients and offer customized meal plans. Their market share is smaller but growing due to their niche appeal. For example, a company called “Raw Revolution” (fictional) in Boston might focus exclusively on raw vegan meals, smoothies, and juices.
- Local Restaurants and Cafes: Many restaurants and cafes across Massachusetts that offer plant-based options may include raw dishes. These establishments often have a loyal local customer base. Their market share varies depending on their geographic location and marketing efforts.
- Health Food Stores: Some health food stores and co-ops may offer raw food options, either prepared in-store or through partnerships with local food vendors. These establishments cater to a health-conscious clientele and offer a complementary market for raw food delivery.
The success of raw food delivery services in Massachusetts depends on factors such as menu variety, ingredient sourcing, pricing, delivery efficiency, and effective marketing strategies.
Route Planning Fundamentals
Efficient route planning is crucial for the success of a raw food delivery service in Massachusetts. Minimizing travel time, optimizing fuel consumption, and ensuring timely deliveries are essential for customer satisfaction and profitability. This section Artikels a comprehensive route planning process, explores relevant software and tools, and details the steps involved in creating an effective delivery schedule.
Designing a Route Planning Process
A well-defined route planning process considers several factors to ensure efficient deliveries. The process involves several key steps, starting with order aggregation and ending with real-time adjustments.
- Order Aggregation and Batching: This involves collecting all delivery orders for a specific time period, usually a day or a specific delivery window. Orders are then batched together based on geographic proximity and delivery time constraints. This is a critical step as it groups orders logically. For instance, orders within a 15-mile radius of Boston, MA, might be grouped for a morning delivery window, while orders further west in the state could be grouped for afternoon deliveries.
- Geocoding and Address Verification: Accurate address geocoding is essential for route optimization. Each delivery address must be converted into precise geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). Address verification ensures that the addresses are valid and deliverable. Incorrect addresses can lead to delays and failed deliveries.
- Route Optimization: This is the core of the process. Route optimization algorithms, using specialized software, analyze the batched orders, considering factors such as distance, traffic conditions, delivery time windows, and vehicle capacity. The goal is to find the most efficient route that minimizes travel time and fuel consumption. The algorithm might recommend a route that prioritizes deliveries in areas with less traffic, even if it means a slightly longer overall distance.
- Vehicle Assignment: Based on the optimized routes and the capacity of each vehicle (e.g., refrigerated vans, electric vehicles), delivery orders are assigned to specific vehicles. The vehicle assignment process should consider the size and type of the raw food orders. A large order, for instance, might need a larger vehicle.
- Driver Dispatch and Navigation: Once the routes are optimized and vehicles are assigned, drivers are dispatched with the optimized routes and navigation instructions. The navigation system provides real-time traffic updates and re-routes the driver if necessary.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Adjustment: The delivery process requires constant monitoring. Real-time tracking of vehicle locations and delivery progress is essential. Unexpected delays, such as traffic congestion or delivery issues, require immediate adjustments to the route. This might involve re-routing a vehicle to avoid a heavily congested area or contacting a customer to reschedule a delivery.
Identifying Key Software and Tools for Route Optimization
Several software and tools can be used to optimize routes for a raw food delivery service, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The selection of the right tools depends on the size of the operation, the complexity of the routes, and the budget.
- Route Optimization Software: Dedicated route optimization software is the most efficient solution for businesses with multiple deliveries.
- Pros: Advanced algorithms, real-time traffic updates, integration with GPS devices, delivery time window management, driver performance tracking, and reporting features. Examples include Routific, Onfleet, and Circuit Route Planner.
- Cons: Can be expensive, may require training, and may not be suitable for very small operations.
- Mapping Software with Route Planning Features: Google Maps and Apple Maps offer basic route planning capabilities that can be useful for smaller delivery operations.
- Pros: Free or low cost, user-friendly interface, readily available on most devices, and real-time traffic information.
- Cons: Limited optimization capabilities, lack of advanced features such as delivery time window management, and may not be suitable for complex routes with multiple stops.
- Spreadsheet Software: Tools like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can be used for basic route planning and order management.
- Pros: Low cost, flexible for manual route planning, and can be used for order tracking and basic reporting.
- Cons: Manual process, time-consuming, limited optimization capabilities, and not scalable for larger delivery operations.
Organizing Steps for Creating a Delivery Schedule
Creating a delivery schedule that minimizes travel time and maximizes delivery capacity involves a series of organized steps. The following steps provide a structured approach to schedule creation.
- Order Collection and Data Input: Gather all customer orders, including delivery addresses, delivery time windows, order details, and any special instructions. This information should be accurately entered into a central system (e.g., a spreadsheet or order management software).
- Address Geocoding and Verification: Use a geocoding service or mapping software to convert delivery addresses into precise geographic coordinates. Verify that all addresses are valid and deliverable. Inaccurate addresses can cause delays and delivery failures.
- Delivery Time Window Definition: Determine the specific delivery time windows for each customer. This could be a 1-hour, 2-hour, or wider window, depending on the customer’s preference and the delivery service’s capabilities.
- Route Optimization with Software: Use route optimization software to create the most efficient routes. Input all the collected data, including order details, delivery time windows, and vehicle capacity. The software will generate optimized routes that minimize travel time, consider traffic conditions, and respect delivery time windows.
- Vehicle and Driver Assignment: Assign specific vehicles and drivers to each optimized route. Consider vehicle capacity, driver availability, and the type of raw food orders being delivered. Ensure that drivers have the necessary equipment, such as insulated bags or refrigerated compartments.
- Schedule Communication and Confirmation: Communicate the delivery schedule to the customers and drivers. Provide customers with estimated delivery times and tracking information. Drivers should receive detailed route instructions and any necessary support.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Adjustment: During the delivery process, monitor the progress of each delivery. Use real-time tracking to identify any delays or issues. Make necessary adjustments to the routes, such as re-routing vehicles or contacting customers to reschedule deliveries.
- Performance Analysis and Refinement: After each delivery cycle, analyze the performance of the delivery schedule. Review key metrics such as travel time, delivery time, and customer satisfaction. Use the data to identify areas for improvement and refine the route planning process for future deliveries.
Delivery Area Considerations
Establishing a well-defined and strategically planned delivery area is crucial for the success of a raw food delivery service. The goal is to maximize efficiency, minimize costs, and ensure customer satisfaction. This section focuses on determining the optimal delivery zone for a Boston-based operation, addressing logistical challenges, and outlining strategies for controlled expansion.
Optimal Delivery Area Determination
Defining the ideal delivery radius requires careful consideration of several factors. Population density, accessibility, and the potential customer base within each area are critical. Analyzing these elements allows for a data-driven decision, ensuring the delivery service reaches a viable market while maintaining operational feasibility.Population density is a significant factor. Areas with higher population concentrations generally offer a greater potential customer base within a smaller geographic footprint, leading to more efficient route planning and reduced delivery times.
For example, the city of Boston has varying population densities. Based on 2023 data, neighborhoods like Back Bay, South End, and Beacon Hill have significantly higher population densities compared to suburban areas further outside the city. These densely populated areas provide a concentrated customer base, making them ideal for initial delivery routes.Accessibility is also important. Areas with easy access, such as those near major highways and with readily available parking, are more efficient to serve.
Conversely, areas with limited access can increase delivery times and costs.
- Data Sources: Utilize publicly available data from sources like the US Census Bureau for population density, income levels, and demographic information. Also, use data from the Boston Transportation Department to assess traffic patterns, parking availability, and road conditions.
- Geographic Information System (GIS) Mapping: Employ GIS software to visually represent population density, customer locations, and potential delivery routes. This allows for the identification of high-potential areas and the visualization of delivery efficiency.
- Customer Survey: Conduct surveys to understand customer preferences, location, and willingness to pay for delivery services. This provides valuable insights into the demand for raw food delivery in different areas.
- Competitive Analysis: Research existing food delivery services in the Boston area to identify their delivery zones and understand the competitive landscape. This can help identify underserved areas or opportunities for differentiation.
Managing Deliveries in Areas with Limited Parking or Difficult Access
Delivering raw food to areas with challenging access, such as narrow streets, limited parking, or high traffic congestion, requires specialized strategies to maintain service quality and efficiency. This involves careful route planning, driver training, and utilizing appropriate delivery methods.Areas like the North End or Beacon Hill in Boston are known for their historic architecture, narrow streets, and limited parking. Successfully navigating these areas demands a proactive approach.
- Real-time Traffic and Parking Information: Integrate real-time traffic and parking data into route planning software. Applications such as Waze or Google Maps can provide live updates on traffic congestion, road closures, and parking availability, allowing drivers to adapt their routes and minimize delays.
- Designated Drop-off Zones: If possible, identify and utilize designated drop-off zones or loading areas. Contact local businesses or residential buildings to negotiate access to these areas.
- Driver Training: Provide drivers with comprehensive training on navigating difficult urban environments. This includes defensive driving techniques, parking etiquette, and strategies for dealing with traffic congestion.
- Delivery Vehicle Selection: Choose delivery vehicles that are well-suited for urban environments. Compact cars, scooters, or even electric bikes can be more maneuverable and efficient in areas with limited parking.
- Communication with Customers: Maintain clear and proactive communication with customers. Provide estimated delivery times and notify them of any potential delays due to traffic or parking challenges.
- Consider Alternative Delivery Methods: Explore the use of alternative delivery methods, such as walk-up deliveries, or partnerships with local businesses to act as pick-up points.
Strategies for Expanding the Delivery Area Over Time
Expanding the delivery area is a natural progression for a successful raw food delivery service. However, it must be managed strategically to maintain service quality and avoid overextending resources. Gradual, data-driven expansion is the key to sustainable growth.Expansion should be approached systematically, based on data analysis and customer demand. Expanding too quickly can lead to decreased service quality, increased costs, and potential operational challenges.
- Phase 1: Core Area Consolidation: Begin by establishing a strong presence in the initial delivery area. Focus on perfecting delivery routes, optimizing operations, and building a loyal customer base.
- Phase 2: Adjacent Area Expansion: Once the core area is established, gradually expand into adjacent areas. Analyze customer data and demand in these areas to ensure there is sufficient market potential.
- Phase 3: Data-Driven Expansion: Continuously monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as delivery times, customer satisfaction, and order volume. Use this data to identify areas with the greatest potential for expansion.
- Customer Feedback: Actively solicit customer feedback regarding the delivery service, including suggestions for expanding the delivery area.
- Marketing and Promotion: Implement targeted marketing campaigns to promote the raw food delivery service in new areas. This can include online advertising, social media promotions, and partnerships with local businesses.
- Scalable Infrastructure: Ensure that the delivery infrastructure, including vehicles, personnel, and technology, can scale to accommodate the expanded delivery area.
Vehicle and Equipment Selection
Choosing the right vehicle and equipment is paramount for a successful raw food delivery service in Massachusetts. It directly impacts food safety, operational efficiency, and ultimately, customer satisfaction. This section delves into the specifics of vehicle types, essential equipment, and vehicle maintenance to ensure a smooth and reliable delivery process.
Vehicle Types for Raw Food Delivery
Selecting the appropriate vehicle hinges on factors like delivery volume, route distance, and budget. Refrigeration capabilities and fuel efficiency are crucial considerations.
- Refrigerated Vans: These are the gold standard for raw food delivery. They come equipped with built-in refrigeration units, maintaining precise temperature control throughout the journey. They are ideal for larger delivery volumes and longer routes. The initial investment is higher, but they provide superior food safety. An example would be a Ford Transit or Mercedes-Benz Sprinter refrigerated van, which can maintain temperatures between 33°F and 40°F (0.5°C and 4.4°C), crucial for preventing bacterial growth in raw foods.
- Insulated Vans/Cargo Vans with Refrigeration Inserts: These offer a more cost-effective solution compared to fully refrigerated vans. They involve insulating a standard cargo van and utilizing portable refrigeration units or inserts. While the upfront cost is lower, temperature control might be less precise and require more active management.
- Fuel Efficiency Considerations: The choice of vehicle impacts fuel consumption, a significant operational cost. Consider hybrid or electric vehicles for reduced emissions and potential fuel savings, especially for urban routes. For instance, a Nissan e-NV200, a fully electric cargo van, can offer considerable savings on fuel and maintenance compared to a gasoline-powered van, especially within city limits with frequent stop-and-go driving.
- Trucks with Refrigerated Compartments: For larger-scale operations, trucks with refrigerated compartments might be necessary to accommodate substantial order volumes and delivery to multiple locations. These vehicles often have multiple compartments to maintain different temperature zones, a critical feature for various raw food types.
Essential Equipment for Food Safety
Maintaining the cold chain is non-negotiable for raw food delivery. This necessitates specific equipment to ensure food safety and quality.
- Temperature Monitoring Devices: These are indispensable for verifying that the cold chain remains unbroken.
- Digital Thermometers: Used to check the internal temperature of food items and the refrigerated compartment before and during deliveries.
- Data Loggers: These devices continuously record temperature readings throughout the delivery process, providing a record for quality assurance and regulatory compliance. They can be crucial in case of customer complaints or health inspections.
- Insulated Containers and Coolant Packs: These help maintain the desired temperature during transport. High-quality insulated containers and reusable coolant packs are vital for maintaining food at the correct temperature for extended periods, especially during the warmer months.
- Food-Grade Packaging: Utilizing food-grade containers and packaging materials prevents contamination and ensures the integrity of the raw food.
- Cleaning and Sanitizing Supplies: Maintaining a clean vehicle interior is essential. Disinfectant wipes, sanitizers, and cleaning solutions are necessary for regular cleaning and sanitization of the vehicle and equipment.
Vehicle Maintenance Checklist
Regular vehicle maintenance is critical for preventing breakdowns and ensuring reliable deliveries. A well-maintained vehicle reduces the risk of delays, spoilage, and customer dissatisfaction.
- Daily Checks:
- Inspect tires for pressure and wear.
- Check fluid levels (oil, coolant, windshield washer fluid).
- Verify the functionality of lights, signals, and brakes.
- Confirm the refrigeration unit is operating correctly and maintaining the set temperature.
- Weekly Checks:
- Clean and sanitize the vehicle’s interior, especially the cargo area.
- Inspect the refrigeration unit’s components (condenser, evaporator) for any issues.
- Check the condition of the coolant packs and replace them if necessary.
- Monthly/Periodic Maintenance:
- Change the engine oil and filter.
- Inspect and replace air filters.
- Check brake pads and rotors.
- Rotate tires.
- Conduct a comprehensive inspection of the refrigeration unit by a qualified technician.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, including dates, services performed, and any repairs. This helps track vehicle performance and identify potential issues proactively. This also assists in complying with any insurance requirements.
Food Safety and Handling Procedures
Maintaining the safety and integrity of raw food products is paramount for any delivery service. Adherence to stringent food safety and handling procedures is not only a legal requirement but also crucial for building customer trust and preventing potential health hazards. This section Artikels the specific regulations, standard operating procedures, and temperature control measures necessary for a successful and safe raw food delivery route in Massachusetts.
Food Safety Regulations in Massachusetts
Massachusetts, like all states, has specific regulations governing the handling and delivery of food, including raw products. These regulations are primarily enforced by the Massachusetts Department of Public Health (DPH). Understanding and complying with these regulations is essential to avoid penalties and ensure consumer safety.The key areas of focus include:
- Food Handler Training: All employees involved in handling food must undergo proper food handler training. This training covers topics such as personal hygiene, cross-contamination prevention, and safe food handling practices. Certification is often required. The training programs must adhere to the standards Artikeld in the Massachusetts Food Code.
- Permitting and Licensing: Businesses operating a food delivery service, especially those handling raw foods, must obtain the necessary permits and licenses from the local Board of Health. This typically involves an inspection of the facility, vehicles, and operational procedures to ensure compliance with food safety standards.
- Temperature Control: Maintaining proper temperature control is critical for raw food safety. The regulations specify temperature ranges for storage, transportation, and delivery of different types of raw foods. Refrigerated storage must be maintained at 41°F (5°C) or below. Frozen foods must be kept frozen.
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Procedures must be in place to prevent cross-contamination between raw and ready-to-eat foods. This includes separate storage areas, cutting boards, and utensils for raw meats, poultry, seafood, and produce. Thorough cleaning and sanitization are required.
- Labeling and Packaging: Raw food products must be properly labeled with information such as the name of the food, ingredients, net weight, and the name and address of the manufacturer or distributor. Packaging must be food-grade and designed to maintain the product’s integrity and prevent contamination during transport. Date marking for perishable foods is often required.
- Employee Health: Employees must be in good health and free from any communicable diseases that could be transmitted through food. The regulations often require employees to report any illnesses or symptoms to their supervisors.
- Record Keeping: Detailed records of food temperatures, cleaning and sanitization schedules, employee training, and inspections must be maintained. These records serve as proof of compliance and are essential during health inspections.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for Handling and Transporting Raw Food
Establishing and adhering to comprehensive Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) is crucial for ensuring the safety and quality of raw food products throughout the delivery process. These SOPs should be documented, readily available to all employees, and regularly reviewed and updated.Here’s a sample set of SOPs:
- Receiving and Inspection: Upon receiving raw food products from suppliers, immediately inspect them for signs of damage, spoilage, or temperature abuse. Verify that the products are within their expiration dates. Reject any products that do not meet the established quality standards. Record the temperature of refrigerated and frozen items upon arrival.
- Storage: Store raw food products in designated refrigerated or freezer units at the correct temperatures. Organize storage areas to prevent cross-contamination. Separate raw meats, poultry, and seafood from ready-to-eat foods. Use FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management to ensure that older products are used before newer ones.
- Preparation (If Applicable): If any preparation is done before delivery (e.g., portioning, packaging), do so in a clean and sanitized area, using separate equipment for raw and ready-to-eat foods. Wash hands thoroughly before and after handling raw foods. Use gloves when handling raw food products.
- Packaging: Package raw food products in food-grade containers or packaging materials designed to maintain temperature and prevent leaks. Use appropriate insulation, such as insulated bags or coolers, to maintain temperature during transport. Clearly label each package with the product name, any special handling instructions, and delivery information.
- Loading and Transport: Load the delivery vehicle in a manner that prevents cross-contamination. Place refrigerated and frozen items in insulated containers or coolers with ice packs or other cooling agents. Ensure that the delivery vehicle’s refrigeration system (if applicable) is functioning properly and maintaining the required temperature. Minimize the time that raw food products spend outside of temperature-controlled environments.
- Delivery: Deliver raw food products promptly to the customer. Advise customers to refrigerate raw food immediately upon receipt. If a customer is not available, follow pre-determined procedures for storing the food safely (e.g., leaving it in an insulated container with ice packs) or returning it to the facility.
- Cleaning and Sanitization: Regularly clean and sanitize all food preparation and storage areas, equipment, and utensils. Clean and sanitize the delivery vehicle daily. Use approved sanitizing agents and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Employee Hygiene: Enforce strict employee hygiene practices, including frequent handwashing, wearing clean uniforms, and reporting any illnesses. Provide employees with training on proper food handling techniques.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all food safety activities, including temperature logs, cleaning and sanitization schedules, employee training, and inspections. Keep these records readily available for review by health inspectors.
Temperature Control Measures for Raw Food Products
Maintaining the correct temperature is critical to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria in raw food products. Implementing effective temperature control measures is a fundamental aspect of raw food delivery safety.The following are crucial temperature control measures:
- Pre-Cooling: Before loading raw food products into the delivery vehicle, ensure that they are pre-chilled to the required temperature. This helps to maintain the cold chain during transport.
- Insulated Containers and Coolers: Use high-quality insulated containers, coolers, and bags to transport raw food products. The insulation helps to maintain the desired temperature and protects the products from external temperature fluctuations.
- Cooling Agents: Use sufficient cooling agents, such as ice packs, gel packs, or dry ice, to maintain the required temperature within the insulated containers. The amount of cooling agent needed will depend on the duration of the delivery route and the ambient temperature. For example, a delivery route expected to take two hours on a warm day might require several large ice packs per cooler, whereas a shorter route on a cooler day might require fewer.
- Temperature Monitoring: Use calibrated thermometers to monitor the temperature of raw food products during storage, transport, and delivery. Check the temperature of the products upon receiving them from suppliers, before loading them into the delivery vehicle, and periodically during the delivery process. Record the temperature readings in a log.
- Vehicle Temperature Control: If the delivery vehicle is equipped with a refrigeration system, ensure that it is functioning properly and maintaining the required temperature. Regularly check and maintain the refrigeration unit. If a refrigerated vehicle is not available, ensure that the delivery route is planned to minimize the time that raw food products spend outside of a temperature-controlled environment.
- Delivery Route Optimization: Plan delivery routes to minimize the time that raw food products spend in transit. Group deliveries by geographic proximity to reduce the total delivery time. Prioritize deliveries of highly perishable items.
- Customer Communication: Inform customers about the importance of refrigerating raw food products immediately upon receipt. Provide clear instructions on proper storage and handling. Consider providing a small insulated bag with ice packs to customers for their convenience.
Example: A raw meat delivery service in Boston uses refrigerated vans to transport its products. Each van is equipped with a digital temperature recorder that continuously monitors and logs the temperature of the cargo area. The service also provides customers with detailed instructions on how to safely handle and store the meat upon delivery. This demonstrates a proactive approach to temperature control and customer education.
Packaging and Presentation
Packaging and presentation are crucial elements for a successful raw food delivery service. They directly impact the food’s quality, safety, and the customer’s overall experience. Careful consideration of these factors helps to ensure food arrives fresh, visually appealing, and reflects the brand’s commitment to quality and sustainability.
Packaging Materials for Raw Food Delivery
Choosing the right packaging is essential for maintaining the integrity of raw foods. The materials must provide adequate insulation to regulate temperature, prevent leaks, and protect the food from physical damage during transit. Sustainability is also a key consideration, reflecting a commitment to environmentally friendly practices.
- Insulated Containers: These are fundamental for maintaining the temperature of raw food items. They are typically made from materials like:
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam: Provides excellent insulation but is not biodegradable. Often used for its cost-effectiveness and ability to maintain temperature over long distances.
- Recycled or recyclable cardboard boxes with insulated liners: Offer a balance of insulation and sustainability. Liners can be made from recycled materials or plant-based insulation.
- Reusable insulated bags: Offer a more sustainable option, often made from durable, insulated materials that can be easily cleaned and reused by the customer.
- Secondary Packaging: This layer directly holds the food and protects it from contamination.
- BPA-free, food-grade plastic containers: Lightweight, leak-proof, and suitable for a wide range of raw food items. They are easy to clean and can often be recycled.
- Compostable containers: Made from plant-based materials like cornstarch or sugarcane. They offer an eco-friendly alternative but may not be suitable for all foods, especially those with high moisture content.
- Glass jars: Ideal for items like smoothies or dressings. They provide excellent preservation and are reusable, but they are heavier and more prone to breakage than plastic.
- Cooling Elements: Essential for maintaining the cold chain.
- Reusable ice packs: Filled with a non-toxic gel and can be frozen repeatedly. They are a cost-effective and sustainable option.
- Dry ice: Provides very low temperatures, suitable for highly perishable items. Requires careful handling due to safety concerns and can potentially freeze food if in direct contact.
- Sustainable Materials: Minimize environmental impact.
- Recycled paper and cardboard: Used for boxes, labels, and cushioning.
- Plant-based films and wraps: For wrapping individual items.
- Biodegradable tape: To seal boxes and containers.
Packaging Examples for Different Raw Food Items
The packaging strategy should be tailored to the specific characteristics of each raw food item. This ensures optimal preservation of freshness, texture, and visual appeal.
- Smoothies and Juices:
- Packaged in airtight glass bottles or BPA-free plastic bottles to prevent leaks and maintain freshness.
- Bottles are placed in an insulated container with ice packs to keep them cold.
- Optional: A decorative label with the ingredients and nutritional information adds a premium touch.
- Salads:
- Packaged in clear, compartmentalized containers to keep ingredients separate and prevent sogginess.
- Dressing is placed in a separate, small container to be added just before consumption.
- Insulated container with ice packs to maintain freshness of the greens.
- Raw Desserts (e.g., cheesecakes, energy balls):
- Placed in individual, aesthetically pleasing containers to preserve their shape and presentation.
- Containers are placed in a box with cushioning material to prevent damage during transit.
- Optional: A decorative paper band around the container adds a touch of elegance.
- Prepared Meals (e.g., veggie bowls, wraps):
- Packaged in containers that are microwave-safe (if applicable) and leak-proof.
- Containers are placed in an insulated bag or box with ice packs.
- Optional: Include a small card with reheating instructions, if necessary.
Enhancing the Presentation of Delivered Raw Food
The presentation of the delivered raw food contributes significantly to the customer’s satisfaction. Creating a positive unboxing experience reinforces the brand’s image and encourages repeat business.
- Attractive Packaging Design:
- Use a consistent brand aesthetic, including logo, colors, and fonts.
- Choose packaging that is visually appealing and reflects the quality of the food.
- Consider the use of sustainable and eco-friendly materials.
- Personalized Touches:
- Include a handwritten note thanking the customer for their order.
- Offer a small sample of a new product or a special discount for their next order.
- Add a card with information about the ingredients and nutritional benefits of the food.
- Visual Appeal:
- Arrange the food in an aesthetically pleasing way within the container.
- Use garnishes (e.g., fresh herbs, edible flowers) to enhance the presentation of salads and prepared meals.
- Ensure the packaging is clean and free of any blemishes or imperfections.
- Clear and Concise Labeling:
- Include the name of the dish, ingredients, and any allergens.
- Provide clear instructions for storage and reheating (if applicable).
- Add a “best by” or “use by” date to ensure food safety.
Customer Service and Communication
Exceptional customer service and clear communication are vital for the success of a raw food delivery business in Massachusetts. Customers, often health-conscious and discerning, expect prompt, courteous service and accurate information regarding their orders. Establishing a robust system for handling inquiries, addressing complaints, and providing timely updates builds trust and fosters customer loyalty, leading to positive reviews and repeat business.
Handling Customer Inquiries and Complaints
A well-defined process for managing customer interactions is crucial. This ensures consistent and professional responses, regardless of the issue.To efficiently handle inquiries and complaints, implement the following steps:
- Centralized Communication Channels: Establish a primary method for customer contact, such as a dedicated phone line, email address, or online chat system. This streamlines communication and prevents messages from being missed.
- Trained Customer Service Representatives: Equip customer service representatives with thorough product knowledge, delivery procedures, and company policies. They should be empowered to resolve common issues independently.
- Prompt Response Times: Set targets for response times to inquiries and complaints. Aim for a quick turnaround to demonstrate responsiveness and attentiveness. Consider:
Responding to initial inquiries within 1 hour during business hours and within 24 hours outside of business hours.
- Complaint Logging and Tracking: Implement a system for logging and tracking all customer complaints. This allows for monitoring of trends, identification of recurring problems, and evaluation of the effectiveness of resolution efforts.
- Standardized Complaint Resolution Procedures: Develop clear, pre-defined procedures for addressing common complaints, such as incorrect orders, damaged products, or late deliveries. Empower representatives to offer solutions like refunds, replacements, or discounts.
- Escalation Protocols: Establish a clear escalation path for complex or unresolved issues. Ensure that representatives know when and how to involve supervisors or managers.
- Documentation of Resolutions: Maintain detailed records of all complaint resolutions, including the nature of the complaint, the solution offered, and the outcome. This information is valuable for future reference and continuous improvement.
Communicating Delivery Updates and Potential Delays
Proactive communication regarding delivery status and potential delays is essential for managing customer expectations and minimizing dissatisfaction. Transparency builds trust and allows customers to plan accordingly.To effectively communicate delivery updates and potential delays, implement these strategies:
- Order Confirmation and Delivery Time Estimates: Immediately after an order is placed, send a confirmation email or text message that includes a clear estimated delivery window.
- Automated Delivery Updates: Implement an automated system that sends customers real-time updates on the status of their delivery. This could include notifications when the order is prepared, dispatched, and out for delivery.
Consider using SMS or email to send updates at key milestones, such as “Order is being prepared,” “Order is out for delivery,” and “Order has been delivered.”
- Proactive Communication of Delays: If a delay is anticipated (e.g., due to traffic, weather, or unforeseen circumstances), notify customers immediately. Provide a revised delivery time estimate and, if appropriate, offer an apology or compensation, such as a discount on a future order.
Example: “Due to unexpected heavy traffic, your delivery is estimated to arrive between 7:00 PM and 7:30 PM. We apologize for any inconvenience and are offering a 10% discount on your next order.”
- Personalized Communication: For significant delays or complex situations, consider contacting customers directly via phone to provide a personalized explanation and resolution.
- Clear Contact Information: Provide customers with readily accessible contact information, such as a phone number or email address, so they can easily reach out with questions or concerns.
- Delivery Tracking Features: If possible, integrate a delivery tracking feature into your system, allowing customers to monitor the location of their delivery in real-time.
Collecting and Utilizing Customer Feedback
Gathering customer feedback is a critical component of continuous improvement. Feedback provides valuable insights into customer satisfaction, identifies areas for improvement, and helps tailor services to better meet customer needs.Design a system for collecting and using customer feedback through these methods:
- Post-Delivery Surveys: Send automated surveys to customers shortly after delivery. Keep the surveys brief and focused, asking specific questions about the ordering process, delivery experience, product quality, and overall satisfaction.
Example questions: “How satisfied were you with the delivery time?” “How would you rate the quality of the raw food?” “Would you order from us again?”
- Online Reviews and Ratings: Encourage customers to leave reviews and ratings on platforms such as Google, Yelp, and Facebook. Actively monitor these reviews and respond to both positive and negative feedback.
- Feedback Forms: Include a feedback form on your website or within your delivery packaging. Make it easy for customers to provide comments, suggestions, and report any issues.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitor social media channels for mentions of your business and respond to any comments or questions.
- Customer Interviews: Conduct occasional customer interviews or focus groups to gather more in-depth feedback and understand customer perspectives.
- Analyzing Feedback Data: Regularly analyze all customer feedback to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
Utilize data analytics tools to track key metrics, such as customer satisfaction scores, complaint rates, and common issues.
- Implementing Changes Based on Feedback: Use the feedback to make changes to your delivery services. This could involve modifying delivery routes, improving food packaging, refining customer service procedures, or updating menu offerings. Communicate these changes to customers to demonstrate that their feedback is valued.
Technology Integration
In today’s competitive landscape, leveraging technology is crucial for the success of any raw food delivery service. Implementing the right tools can streamline operations, enhance customer experience, and improve overall efficiency. This section delves into the core technological requirements, focusing on delivery management software, payment processing, and online ordering systems.
Delivery Management Software Features
Selecting the right delivery management software is paramount for optimizing route planning, order management, and driver coordination. The software should offer a robust set of features to handle the complexities of raw food delivery.
- Route Optimization: The software must automatically optimize delivery routes based on factors such as order location, delivery time windows, and vehicle capacity. This minimizes travel time, reduces fuel consumption, and ensures timely deliveries. For example, the software could integrate with real-time traffic data to avoid congestion.
- Order Management: This feature should allow for seamless order intake, tracking, and modification. It needs to integrate with the online ordering system and POS system. It should also provide real-time order status updates to both the business and the customer.
- Driver Management: Driver tracking, communication, and performance monitoring are critical. The software should allow dispatchers to assign orders to drivers, monitor their location in real-time, and communicate with them via in-app messaging. It should also include features for managing driver schedules and performance metrics.
- Customer Communication: Automated notifications are essential. The software should send customers order confirmation, delivery updates (e.g., “your order is out for delivery”), and estimated time of arrival (ETA) notifications via SMS or email. This keeps customers informed and reduces inquiries.
- Reporting and Analytics: The software should provide comprehensive reports on key performance indicators (KPIs), such as delivery times, driver performance, and customer satisfaction. This data helps to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions. For instance, analyzing delivery times can reveal patterns in traffic congestion or driver inefficiencies.
- Inventory Management Integration: To ensure raw ingredients are available, the software should be able to integrate with the inventory system. It should be able to automatically deduct ingredients based on the orders.
Payment Processing Options
Choosing the right payment processing solution is vital for providing a seamless and secure checkout experience for customers.
- Credit and Debit Card Processing: This is a standard requirement. The payment gateway should support major credit and debit cards (Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover) and offer secure transaction processing, including fraud protection.
- Mobile Payment Options: Integrating with mobile payment platforms like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay provides customers with convenient and contactless payment options, which are increasingly popular.
- Digital Wallets: Supporting digital wallets like PayPal and Venmo offers additional flexibility and appeal to a wider customer base.
- Subscription Payments: For recurring orders, the payment processor should facilitate recurring billing and subscription management.
- Security and PCI Compliance: The payment processor must be PCI DSS compliant to protect sensitive customer data. This involves implementing robust security measures to prevent data breaches and fraud.
A recommended solution for a raw food delivery service is to use a payment processor that offers a combination of the above features. Options such as Stripe or Square are good choices because they offer competitive rates, a user-friendly interface, and robust security features. These platforms also support integration with various e-commerce platforms and delivery management software. For instance, Stripe provides detailed transaction data and fraud protection tools.
Online Ordering and Tracking Integration
Seamless online ordering and tracking capabilities are crucial for customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. This involves integrating the online ordering system with the delivery management software and providing customers with real-time order updates.
- User-Friendly Online Ordering System: The online ordering platform should be easy to navigate and provide a visually appealing presentation of the raw food menu. The platform should include clear descriptions, images, and nutritional information for each item.
- Real-Time Order Tracking: Integrating the online ordering system with the delivery management software allows customers to track their orders in real-time. This can be achieved through a map view showing the driver’s location and estimated time of arrival.
- Order Customization: Customers should be able to customize their orders, specifying preferences, dietary restrictions, and any special instructions. This can be integrated directly into the online ordering platform.
- Automated Notifications: Implement automated email and SMS notifications to keep customers informed about their order status. Notifications should include order confirmation, preparation updates, dispatch information, and delivery ETA.
- Integration with Delivery Management Software: The online ordering system needs to seamlessly integrate with the delivery management software to ensure that orders are automatically routed to the appropriate drivers. This integration should include the transfer of customer information, order details, and delivery instructions.
- Mobile Optimization: The online ordering system should be fully optimized for mobile devices, as many customers will place orders using their smartphones or tablets. This ensures a smooth and user-friendly experience across all devices.
For example, a raw food delivery service could use a platform like Shopify or WooCommerce to build its online store and then integrate it with a delivery management software like Onfleet or Routific. The customer places an order on the Shopify website, which is then automatically routed to the Onfleet platform. The customer receives notifications throughout the delivery process, including a real-time map showing the driver’s location.
This integration provides a seamless and transparent experience for both the business and the customer.
Cost Analysis and Pricing Strategies
Understanding the financial aspects of your raw food delivery service is crucial for long-term sustainability. This section delves into a detailed cost breakdown, explores effective pricing strategies, and Artikels promotional tactics to maximize profitability and customer acquisition. Careful financial planning and strategic pricing are essential for a successful business venture.
Cost Breakdown of Running a Raw Food Delivery Service
Operating a raw food delivery service involves various costs, which can be categorized for easier management. Accurately assessing these costs is fundamental to determine profitability and set competitive prices.
- Vehicle Expenses: This encompasses all costs associated with the vehicle used for deliveries.
- Purchase/Lease: The initial investment in a vehicle, whether bought or leased. Lease payments are typically a fixed monthly expense.
- Fuel: Gasoline or electricity costs, which fluctuate depending on fuel prices and vehicle efficiency. For example, a delivery route covering 100 miles per day, with a vehicle averaging 25 miles per gallon and gasoline at $4.00 per gallon, would incur a daily fuel cost of $16.
00.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Regular servicing, unexpected repairs, and tire replacements are ongoing costs. Budgeting a percentage of the vehicle’s value annually (e.g., 2-3%) can help estimate these costs.
- Insurance: Commercial vehicle insurance, which is typically more expensive than personal auto insurance.
- Registration and Licensing: Annual fees for vehicle registration and any required commercial licenses.
- Food Costs: The expenses directly related to procuring raw ingredients.
- Ingredient Sourcing: Costs of buying fresh, organic, and locally sourced produce, which may vary based on seasonal availability and supplier pricing.
- Waste: The cost of ingredients that spoil before being used. Minimizing waste through careful inventory management and portion control is essential.
- Packaging: Costs of containers, labels, and any other packaging materials required to maintain the freshness and safety of the food.
- Labor Costs: Payments for individuals involved in food preparation, packaging, delivery, and customer service.
- Salaries/Wages: Payments to employees, including any benefits such as health insurance or paid time off.
- Payroll Taxes: Employer contributions for social security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance.
- Contractor Fees: Payments to independent contractors, such as delivery drivers, if they are not employees.
- Operational Expenses: Costs associated with running the business, including rent, utilities, and marketing.
- Rent/Mortgage: The cost of a commercial kitchen or office space, if applicable.
- Utilities: Electricity, water, and internet costs.
- Marketing and Advertising: Expenses for online advertising, social media marketing, and promotional materials.
- Software and Technology: Costs for point-of-sale systems, delivery management software, and website hosting.
- Insurance: General liability insurance to protect against accidents or claims.
Pricing Strategy Considerations
Setting the right prices is a balancing act between covering costs, maximizing profit, and remaining competitive. A well-defined pricing strategy considers both the cost of goods sold (COGS) and the perceived value by the customer.
- Cost-Plus Pricing: This method involves calculating the total cost of producing a meal (including food, labor, and overhead) and adding a markup to determine the selling price.
Selling Price = Cost + Markup (as a percentage of cost)
For example, if the cost to prepare a raw food meal is $10 and the desired markup is 50%, the selling price would be $15.
- Value-Based Pricing: This strategy sets prices based on the perceived value of the product to the customer. Factors include the quality of ingredients, the convenience of delivery, and the health benefits of raw food. Consider the price of similar offerings from competitors, but focus on the unique benefits your service provides.
- Competitive Pricing: This involves monitoring the prices of competitors and adjusting your prices accordingly. If competitors offer similar products at lower prices, you may need to lower your prices or emphasize your unique selling points. Conversely, if your service provides superior quality or convenience, you may be able to charge a premium.
- Dynamic Pricing: This strategy involves adjusting prices based on demand, time of day, or other factors. For example, you could offer higher prices during peak delivery times or offer discounts during slower periods.
Discount and Promotion Strategies
Attracting new customers and retaining existing ones requires a combination of attractive pricing and strategic promotions. These strategies should be designed to drive sales, build customer loyalty, and increase brand awareness.
- Introductory Discounts: Offer a discount on the first order to entice new customers to try your service. This could be a percentage off, free delivery, or a complimentary item. For example, “Get 20% off your first order with code WELCOME20!”
- Loyalty Programs: Reward repeat customers with discounts, free items, or exclusive offers. This can encourage customer retention and foster a sense of appreciation. A common example is a “Buy 10 meals, get one free” program.
- Referral Programs: Encourage existing customers to refer new customers by offering rewards to both parties. This can be an effective way to expand your customer base through word-of-mouth marketing. For instance, “Refer a friend and you both get $10 off your next order!”
- Seasonal Promotions: Offer special promotions tied to holidays or seasonal ingredients. This can create excitement and generate increased sales. A “Summer Detox Special” or a “Thanksgiving Raw Feast” are examples.
- Bundle Deals: Offer discounts on multiple items purchased together. This encourages customers to buy more and can increase average order value. For example, “Get a smoothie and a salad for 15% off.”
- Flash Sales: Create a sense of urgency by offering limited-time discounts. This can drive immediate sales and generate excitement. “24-hour flash sale: 30% off all entrees!”
- Partnerships: Collaborate with complementary businesses, such as gyms, yoga studios, or health food stores, to cross-promote your services and reach new customers. For instance, a joint promotion with a local yoga studio offering a discount on raw food deliveries to their members.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial for any food delivery business, and raw food presents unique challenges due to its perishable nature and food safety requirements. Adhering to all applicable regulations ensures consumer safety, protects your business from liability, and builds trust with your customer base. Understanding and complying with these regulations is a continuous process, requiring vigilance and adaptation to evolving standards.
Licenses and Permits for Raw Food Delivery in Massachusetts
Operating a raw food delivery service in Massachusetts necessitates several licenses and permits to ensure legal compliance. These requirements can vary slightly depending on the specific municipality, so it’s essential to check with both the state and local authorities.
Further details about mill creek community food bank is accessible to provide you additional insights.
- Food Establishment Permit: This is the foundational permit, required for any business that handles, prepares, or sells food. The Massachusetts Department of Public Health (DPH) oversees this permit. The specific requirements, including inspections and sanitation standards, will depend on the scale and scope of your operation. For instance, a home-based business might have different requirements compared to a commercial kitchen.
- Food Handler’s Permit (or Food Safety Certification): While not a permit
-per se*, this is a mandatory requirement for anyone involved in food handling. It ensures that employees have the knowledge and skills to safely handle food, preventing contamination and illness. Several organizations offer accredited food safety training programs, and the certification typically needs to be renewed periodically. - Business Certificate (Doing Business As – DBA): If you’re operating under a name different from your legal business name, you’ll need a DBA certificate from the city or town where your business is located.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): If you plan to hire employees, you’ll need an EIN from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This is used for tax purposes.
- Local Permits: Depending on your location, you may need additional permits from your city or town, such as zoning permits or permits related to operating a vehicle for commercial purposes. Some municipalities require permits for food delivery services, especially if using a vehicle.
Insurance Requirements for a Food Delivery Business
Adequate insurance coverage is paramount for protecting your business from financial risks. Food delivery services face unique liabilities, including potential foodborne illnesses, accidents involving delivery vehicles, and property damage.
- General Liability Insurance: This protects your business from claims of bodily injury or property damage caused by your operations. For example, if a delivery person slips and falls on a customer’s property, general liability insurance can cover the resulting medical expenses and legal fees.
- Product Liability Insurance: This covers claims related to the food products you deliver. If a customer becomes ill from consuming your raw food, product liability insurance can help cover medical expenses, legal fees, and potential settlements.
- Commercial Auto Insurance: If you use vehicles for deliveries, commercial auto insurance is essential. It covers accidents involving your delivery vehicles, including property damage, bodily injury, and medical expenses. This is often more comprehensive than personal auto insurance, as it covers business-related activities.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: If you have employees, workers’ compensation insurance is required by law in Massachusetts. It covers medical expenses and lost wages for employees who are injured on the job.
- Cyber Liability Insurance: With the increasing reliance on technology for order processing and customer data, cyber liability insurance is becoming increasingly important. It protects your business from data breaches, cyberattacks, and associated liabilities.
Resources for Staying Updated on Changes in Food Safety Regulations
Food safety regulations are constantly evolving to address new challenges and advancements in food science. Staying informed is crucial for maintaining compliance and protecting your customers.
- Massachusetts Department of Public Health (DPH): The DPH website is the primary source for information on food safety regulations in Massachusetts. They provide updates on new regulations, guidance documents, and contact information for questions.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA sets national standards for food safety. Their website offers a wealth of information, including regulations, guidelines, and recalls. Staying informed about federal regulations is also important, as they often influence state regulations.
- Local Boards of Health: Your local board of health is another crucial resource. They can provide information on local regulations, inspections, and any specific requirements for your business.
- Industry Associations: Organizations like the National Restaurant Association (NRA) and the Massachusetts Restaurant Association (MRA) often provide resources, training, and updates on food safety regulations for their members. These associations frequently host workshops and seminars on relevant topics.
- Food Safety Training Providers: Several organizations offer food safety training and certification programs. These programs often provide updates on current regulations and best practices.
- Legal Counsel: Consulting with an attorney specializing in food law can be beneficial, especially if you have complex legal questions or need assistance navigating regulatory requirements.
Marketing and Promotion
Promoting a raw food delivery service in Massachusetts requires a multifaceted marketing plan designed to reach health-conscious consumers, busy professionals, and anyone seeking convenient access to nutritious meals. The plan should emphasize the benefits of raw food, highlight the convenience of delivery, and build a strong brand identity that resonates with the target audience.
Marketing Plan for Raw Food Delivery
A comprehensive marketing plan should encompass various strategies to build brand awareness, generate leads, and drive sales.
- Define Target Audience: Identify specific demographics, psychographics, and geographic locations within Massachusetts. This includes understanding their dietary preferences, lifestyle, and online behavior. For instance, target areas with a higher concentration of health-conscious individuals, such as areas near yoga studios, fitness centers, and farmers’ markets.
- Develop Brand Identity: Create a unique brand name, logo, and visual identity that reflects the values of the raw food delivery service. The brand should communicate freshness, health, and convenience. The color palette should evoke feelings of naturalness and purity.
- Establish Online Presence: Build a professional website with online ordering capabilities, detailed menu descriptions, nutritional information, and customer testimonials. Ensure the website is mobile-friendly and optimized for search engines ().
- Implement Content Marketing: Create valuable content, such as blog posts, articles, recipes, and videos, related to raw food, healthy eating, and the benefits of a raw food diet. Share this content on the website and social media platforms to attract and engage potential customers.
- Utilize Social Media Marketing: Develop a strong social media presence on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Pinterest to showcase the food, share recipes, run contests, and engage with followers.
- Employ Email Marketing: Build an email list and send regular newsletters with special offers, new menu items, and healthy eating tips. Segment the email list based on customer preferences to personalize communications.
- Consider Local Partnerships: Collaborate with local businesses, such as health food stores, gyms, and wellness centers, to cross-promote the raw food delivery service. Offer samples, discounts, or joint marketing campaigns.
- Offer Promotions and Discounts: Provide introductory discounts, loyalty programs, and seasonal promotions to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
- Monitor and Analyze Results: Track key marketing metrics, such as website traffic, social media engagement, and sales, to measure the effectiveness of the marketing efforts. Make adjustments to the marketing plan as needed based on the data.
Effective Use of Social Media Platforms
Social media is a powerful tool for reaching potential customers and building brand awareness. Each platform offers unique opportunities to connect with the target audience.
- Instagram: Instagram is ideal for showcasing the visual appeal of raw food. Post high-quality photos and videos of the food, highlighting its freshness and vibrant colors. Use relevant hashtags, such as #rawfood, #rawvegan, #healthyfood, and #massachusettsfood, to increase visibility. Run contests and giveaways to engage followers and attract new ones.
- Facebook: Facebook is a good platform for building a community and sharing informative content. Create a Facebook page for the raw food delivery service and post recipes, articles about the benefits of raw food, and customer testimonials. Run targeted Facebook ads to reach specific demographics in Massachusetts. Consider hosting live Q&A sessions with a nutritionist or raw food expert.
- Pinterest: Pinterest is a visual search engine that can drive traffic to the website. Create visually appealing boards featuring recipes, food photography, and healthy eating tips. Include links back to the website to encourage purchases.
- TikTok: TikTok is effective for reaching a younger audience. Create short, engaging videos showcasing the preparation of raw food dishes, the delivery process, and customer testimonials. Use trending sounds and hashtags to increase visibility.
- Engage with Followers: Respond promptly to comments and messages, and encourage customer reviews and feedback. Run polls and quizzes to gather insights and build a loyal following.
- Collaborate with Influencers: Partner with health and wellness influencers in Massachusetts to promote the raw food delivery service to their followers. Send influencers complimentary meals in exchange for reviews and social media posts.
Referral Program for Customer Loyalty
A referral program can be an effective way to incentivize customer loyalty and acquire new customers through word-of-mouth marketing.
- Program Design: Design a simple and easy-to-understand referral program. Offer a reward to both the referrer (existing customer) and the referred customer (new customer). For example, offer a discount on their next order, a free item, or a credit towards future purchases.
- Incentives: Determine the value of the incentives. Consider offering a higher reward for the referrer to encourage more referrals. Make sure the incentives are attractive and align with the customer’s preferences.
- Program Promotion: Promote the referral program prominently on the website, in email newsletters, and on social media platforms. Make it easy for customers to share their referral link or code.
- Tracking and Management: Implement a system to track referrals and manage the rewards. Use a referral program software or a manual tracking system. Ensure that the rewards are delivered promptly and accurately.
- Example Program Structure:
- Referrer Reward: Receive a $10 discount on their next order for each successful referral.
- Referred Customer Reward: Receive a 15% discount on their first order.
The program should be simple: Customers receive a unique referral code. They share this code with friends. When a friend uses the code, both the referrer and the friend receive their respective discounts.
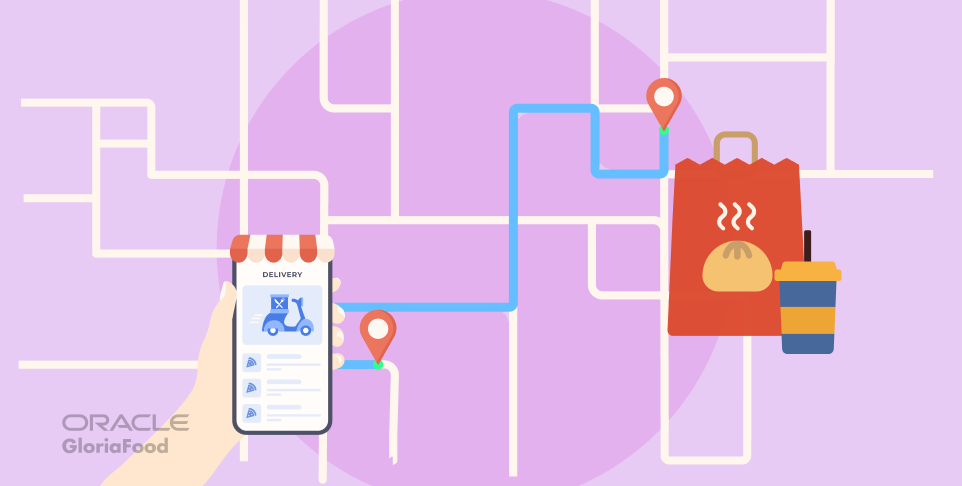
Delivery Route Optimization Techniques
Optimizing delivery routes is crucial for the profitability and efficiency of a raw food delivery service in Massachusetts. This involves leveraging technology and strategic planning to minimize travel time, fuel costs, and delivery delays. A well-optimized route translates to fresher food for customers and a more sustainable business model.
Using Mapping Software to Optimize Delivery Routes
Mapping software is an indispensable tool for route optimization. These applications utilize algorithms to calculate the most efficient routes based on factors such as distance, traffic, and delivery time windows.To demonstrate, consider the following steps and examples:
- Inputting Delivery Locations: The first step involves entering all delivery addresses into the mapping software. For example, a delivery route might include addresses in Boston, Cambridge, and Somerville.
- Route Calculation: The software, such as Google Maps, MapQuest, or dedicated route optimization software like Circuit or Route4Me, then calculates the optimal route, considering factors like one-way streets and road closures. The software prioritizes minimizing travel time and distance.
- Time Window Optimization: If customers have specified delivery time windows (e.g., between 10 AM and 12 PM), the software adjusts the route to accommodate these constraints. For instance, a delivery scheduled for 11 AM in Cambridge would be prioritized to ensure timely arrival.
- Multi-Stop Route Planning: For services with multiple deliveries, the software arranges the stops in the most efficient order. It calculates the shortest overall travel time while adhering to delivery time windows.
- Real-time Tracking and Adjustments: Many software platforms offer real-time tracking, allowing drivers to monitor their progress and make on-the-fly adjustments if needed. For instance, if traffic is unexpectedly heavy on a particular road, the driver can reroute using the software’s suggestions.
Accounting for Traffic Conditions and Other Delays When Planning Routes
Traffic and unforeseen delays are unavoidable realities in Massachusetts, especially in urban areas. Effective route planning requires incorporating these factors to ensure timely deliveries.The following strategies are crucial:
- Real-Time Traffic Data Integration: Mapping software utilizes real-time traffic data to identify congested areas. For example, Google Maps and Waze provide live traffic updates, allowing drivers to avoid areas with heavy traffic.
- Time Buffers: Incorporating buffer time into delivery schedules is essential. For instance, if a delivery is estimated to take 30 minutes, an additional 15-20 minutes might be added to the schedule to account for potential delays.
- Alternative Route Planning: Always having alternative routes planned is important. If a major highway is congested, the driver can quickly switch to a secondary route. The mapping software can automatically suggest alternative routes based on current traffic conditions.
- Weather Considerations: Weather conditions, particularly in New England, can significantly impact travel times. During heavy rain or snow, travel times should be increased. Monitoring weather forecasts and adjusting routes accordingly helps ensure timely deliveries.
- Incident Awareness: Be aware of potential incidents, such as accidents or road closures. Utilize traffic apps or local news sources to stay informed and reroute as necessary.
Creating a Schedule for Reviewing and Adjusting Delivery Routes to Improve Efficiency
Continuous improvement is vital. A regular review and adjustment schedule is necessary to refine delivery routes and enhance efficiency.The following steps are suggested:
- Weekly Route Performance Review: Every week, analyze the previous week’s delivery data. This involves examining delivery times, fuel consumption, and customer feedback related to delivery timeliness.
- Data Analysis: Identify recurring patterns and bottlenecks in delivery routes. For example, consistently late deliveries to a specific area might indicate a need for route adjustments or the addition of delivery personnel.
- Customer Feedback Integration: Regularly solicit feedback from customers regarding delivery experiences. Customer comments can highlight areas for improvement, such as difficult-to-access locations or delivery time preferences.
- Software Updates: Regularly update the mapping software and route optimization tools to ensure the most current data and algorithms are used.
- Monthly Route Optimization Meetings: Conduct monthly meetings to review the data and implement necessary adjustments. This might involve modifying the route, adjusting delivery time windows, or re-evaluating staffing levels.
- Quarterly Performance Evaluations: Perform a more comprehensive quarterly evaluation of delivery performance. Analyze key metrics such as delivery cost per order, customer satisfaction scores, and overall profitability.
Building a Delivery Team
As a raw food delivery service, your delivery team is the face of your business. They are the last point of contact with your customers and play a critical role in ensuring customer satisfaction and brand reputation. Building a strong, reliable, and well-trained delivery team is essential for success.
Identifying Key Qualities for Delivery Personnel
Finding the right people is paramount. Beyond basic qualifications, certain qualities are essential for raw food delivery personnel. These qualities contribute to the smooth operation and positive customer experiences.
- Reliability and Punctuality: Delivery personnel must be dependable and arrive on time for their shifts and deliveries. This ensures customers receive their orders within the promised timeframe.
- Strong Communication Skills: Effective communication is crucial for interacting with customers, confirming deliveries, and resolving any issues that may arise. This includes both verbal and written communication skills.
- Attention to Detail: Accuracy in handling orders, verifying addresses, and ensuring the correct items are delivered is critical to minimize errors and maintain customer satisfaction.
- Customer Service Orientation: Delivery personnel should be friendly, courteous, and able to handle customer inquiries or complaints professionally. This contributes to a positive brand image.
- Physical Stamina: The job requires physical activity, including lifting, carrying, and potentially navigating stairs or uneven terrain.
- Knowledge of Route Navigation: Proficiency in using GPS and navigation tools, and a basic understanding of the delivery area, is important for efficient route completion.
- Adaptability and Problem-Solving: The ability to adapt to unexpected situations, such as traffic delays or incorrect addresses, and find solutions quickly is a valuable asset.
- Commitment to Food Safety: A strong understanding of food safety practices, including proper handling, storage, and transportation of raw food, is non-negotiable.
Designing a Training Program for Delivery Staff
A comprehensive training program is vital to equip delivery staff with the knowledge and skills necessary to perform their duties effectively and safely. This program should cover key aspects of the job.
- Food Safety Training: This is a crucial element of the training program.
- Customer Service Training: This component focuses on building positive customer interactions. The training should cover effective communication techniques, handling customer inquiries and complaints, and creating a positive delivery experience.
- Route Navigation Training: Training on using GPS devices, mapping software, and route optimization techniques is important for efficient deliveries. This includes understanding traffic patterns, identifying potential delays, and planning alternative routes.
- Product Knowledge: Delivery staff should have a basic understanding of the raw food products offered, including ingredients, preparation methods, and potential allergens. This allows them to answer customer questions and provide helpful information.
- Company Policies and Procedures: Ensure all staff are familiar with company policies, including dress code, punctuality expectations, delivery protocols, and incident reporting procedures.
- Vehicle and Equipment Training: Proper operation and maintenance of delivery vehicles and equipment, such as insulated bags or containers, is essential.
Training should cover the principles of food safety, including proper handling, storage, and transportation of raw food products to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity.
It should also include temperature control protocols, cross-contamination prevention, and personal hygiene standards. Regular refresher courses and assessments should be conducted to reinforce food safety practices.
Role-playing scenarios can be used to practice different customer interactions and develop problem-solving skills.
Emphasize the importance of being polite, respectful, and professional in all interactions.
Include practical exercises, such as simulating delivery routes, to reinforce navigation skills.
Also, provide information on how to handle address changes or incorrect delivery information.
Managing and Motivating a Delivery Team
Effective management and motivation are key to ensuring high performance and employee satisfaction. A well-managed team is more likely to be productive, reliable, and committed to providing excellent service.
- Clear Expectations and Performance Standards: Set clear expectations for delivery performance, including delivery times, customer service standards, and food safety protocols.
- Regular Communication and Team Meetings: Maintain open communication channels with the delivery team through regular meetings, emails, and instant messaging.
- Incentives and Recognition Programs: Implement incentive programs to reward high-performing delivery staff.
- Fair Compensation and Benefits: Offer competitive wages and benefits to attract and retain qualified delivery personnel.
- Opportunities for Professional Development: Provide opportunities for professional development and advancement.
- Create a Positive Work Environment: Foster a positive and supportive work environment where employees feel valued and respected.
- Provide the Right Tools and Resources: Equip delivery staff with the necessary tools and resources to perform their jobs effectively.
- Lead by Example: Managers and supervisors should lead by example, demonstrating the desired behaviors and work ethic.
Use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), such as on-time delivery rates, customer satisfaction scores, and error rates, to measure and track performance.
Provide regular feedback and performance reviews to identify areas for improvement.
Use these communication channels to share updates, address concerns, and provide feedback.
Encourage team members to share ideas and suggestions.
Offer bonuses for achieving delivery targets, positive customer feedback, or exceptional performance.
Recognize and reward outstanding employees through employee of the month programs or other forms of recognition.
Consider providing health insurance, paid time off, and other benefits to improve employee satisfaction.
Ensure that compensation is fair and consistent with the demands of the job.
Offer training courses to enhance their skills and knowledge, and create career paths within the company.
This demonstrates a commitment to their growth and development.
Encourage teamwork, collaboration, and open communication.
Address any issues or conflicts promptly and fairly.
This includes reliable vehicles, GPS devices, insulated bags, and appropriate uniforms.
Ensure that equipment is well-maintained and readily available.
Show respect for employees, communicate effectively, and be committed to customer satisfaction.
This sets a positive tone for the entire team.
Addressing Challenges and Risks: Raw Food Delivery Route Massachusetts
Raw food delivery presents unique challenges, primarily centered on food safety and maintaining product integrity. These challenges, if not addressed proactively, can lead to spoilage, contamination, and ultimately, customer dissatisfaction and financial losses. A robust risk management strategy is therefore essential for the success and sustainability of a raw food delivery business in Massachusetts.
Potential Risks Associated with Raw Food Delivery
Raw food, by its nature, is highly perishable and susceptible to spoilage and contamination. This section identifies the major risks inherent in the delivery process.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Maintaining the cold chain is critical. Exposure to even brief periods of elevated temperatures can accelerate spoilage and bacterial growth, particularly for items like raw meat, fish, and certain fruits and vegetables. This is a significant risk during transit, especially in Massachusetts’ varying climate.
- Cross-Contamination: Raw foods can easily contaminate other items, including surfaces, equipment, and even other delivered food. This is a serious food safety hazard that can lead to illness. Improper handling and storage practices are primary contributors to cross-contamination.
- Packaging Failures: Inadequate packaging can lead to leaks, spills, and exposure to contaminants. Packaging must be robust enough to withstand handling during transport and maintain the desired temperature. Damaged packaging also affects product presentation, impacting customer satisfaction.
- Delivery Delays: Unexpected delays, whether due to traffic, vehicle breakdowns, or route inefficiencies, can compromise food quality and safety. Delays increase the time raw food is outside of optimal temperature ranges, increasing the risk of spoilage.
- Contamination from External Sources: Delivery vehicles and personnel can be sources of contamination if hygiene standards are not strictly enforced. Exposure to allergens, cleaning chemicals, or other environmental contaminants is a risk.
- Equipment Malfunctions: Refrigeration units in vehicles or storage facilities can fail, leading to rapid spoilage of the raw food. Backup systems and regular maintenance are essential to minimize this risk.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks and Handling Unexpected Issues
Proactive measures and a well-defined response plan are essential to mitigate the identified risks. This section Artikels strategies for risk reduction and managing unforeseen circumstances.
- Temperature Control: Implement a robust cold chain management system. Use insulated containers with appropriate ice packs or dry ice. Monitor temperatures throughout the delivery process using temperature loggers. Ensure delivery vehicles have reliable refrigeration systems and regular maintenance. Train delivery personnel on proper temperature handling procedures.
- Strict Hygiene Protocols: Enforce rigorous hygiene standards for all personnel involved in food handling and delivery. This includes frequent handwashing, the use of clean gloves, and proper sanitation of all equipment and surfaces. Implement a comprehensive cleaning and sanitizing schedule for vehicles and storage areas.
- Proper Packaging: Utilize high-quality, leak-proof, and insulated packaging materials. Consider using packaging designed to maintain specific temperature ranges. Clearly label packages with handling instructions and “Keep Refrigerated” warnings. Choose packaging materials that are sustainable and environmentally friendly where possible.
- Efficient Route Planning and Monitoring: Optimize delivery routes to minimize travel time. Use real-time tracking technology to monitor delivery progress and identify potential delays. Communicate proactively with customers about any delays. Consider offering delivery windows to provide flexibility.
- Contamination Prevention: Establish separate storage areas for raw and cooked foods, and for allergens if applicable. Train personnel on cross-contamination prevention techniques. Implement a policy of thorough cleaning and sanitizing of all surfaces and equipment after each use. Inspect delivery vehicles regularly for cleanliness.
- Supplier Partnerships: Establish relationships with reliable food suppliers who adhere to high food safety standards. Verify supplier certifications and conduct regular audits to ensure compliance. Implement a system for tracking product recalls and communicating them to customers.
- Customer Communication: Provide clear instructions to customers on how to handle and store their raw food deliveries upon receipt. Include information about recommended storage temperatures and shelf life. Address customer concerns promptly and professionally.
Contingency Plan for Vehicle Breakdowns and Disruptions
A contingency plan is crucial to address unexpected events that can disrupt the delivery schedule. This section Artikels a plan to handle vehicle breakdowns and other potential disruptions.
- Vehicle Backup Plan: Maintain a backup vehicle ready for immediate use in case of a breakdown. This backup vehicle should be equipped with the necessary refrigeration and temperature control capabilities.
- Emergency Contact List: Create a readily accessible list of emergency contacts, including vehicle repair services, towing companies, and food safety authorities.
- Communication Protocol: Establish a clear communication protocol for notifying customers about delays or changes to the delivery schedule. Use text messages, emails, and phone calls to keep customers informed.
- Alternative Delivery Options: If a vehicle breakdown or other disruption prevents delivery, explore alternative options such as:
- Arranging for a temporary replacement vehicle.
- Offering customers the option to reschedule their delivery.
- Providing a partial refund or discount.
- Utilizing a third-party delivery service, if available.
- Temperature Control during Disruptions: If a vehicle breakdown occurs, immediately transfer the raw food to a refrigerated environment, such as a backup vehicle or a temporary storage facility. Utilize ice packs or dry ice to maintain the cold chain during the transfer.
- Employee Training: Train all delivery personnel on the contingency plan, including how to respond to vehicle breakdowns, how to communicate with customers, and how to maintain food safety during disruptions. Conduct regular drills to ensure preparedness.
- Insurance Coverage: Ensure adequate insurance coverage to protect against financial losses resulting from vehicle breakdowns, spoilage, and other unforeseen events. Review insurance policies regularly to ensure they meet the business’s needs.
Future Trends and Innovations
The raw food delivery landscape is constantly evolving, driven by shifts in consumer preferences, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and convenience. Businesses that proactively adapt to these trends and embrace innovation will be best positioned for long-term success in the Massachusetts market. This section explores emerging trends, technological advancements, and expansion strategies that can propel raw food delivery services forward.
Emerging Trends in the Raw Food Industry
Several key trends are reshaping the raw food industry, directly influencing the demand and operational aspects of delivery services. Understanding these trends is crucial for strategic planning.* Increased Demand for Plant-Based and Vegan Options: The popularity of plant-based diets continues to surge. Raw food delivery services should focus on providing diverse and creative vegan and plant-based meals to cater to this growing segment.
This includes incorporating ingredients like jackfruit, tempeh, and a wide variety of nuts, seeds, and vegetables.* Focus on Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing: Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their food choices. Sourcing locally-grown, organic ingredients, minimizing packaging waste, and utilizing eco-friendly delivery methods (e.g., electric vehicles, bicycles) are becoming essential for attracting and retaining customers.* Emphasis on Transparency and Traceability: Consumers want to know where their food comes from and how it is produced.
Providing detailed information about ingredients, sourcing practices, and preparation methods builds trust and enhances brand loyalty. This can be achieved through online platforms, detailed ingredient lists, and partnerships with local farms and suppliers.* Growth of Personalized Nutrition: Customized meal plans based on individual dietary needs and preferences are gaining popularity. Raw food delivery services can leverage technology to offer personalized menus, allowing customers to specify allergies, intolerances, and health goals.* Integration of Functional Foods and Superfoods: Consumers are seeking foods with added health benefits.
Incorporating superfoods like spirulina, chlorella, goji berries, and adaptogens into raw food offerings can enhance their nutritional value and appeal.
Innovative Technologies for Raw Food Delivery, Raw food delivery route massachusetts
Technological advancements offer significant opportunities to improve the efficiency, convenience, and customer experience of raw food delivery.* Advanced Route Optimization Software: Utilizing sophisticated route optimization software can significantly reduce delivery times and fuel costs. These systems consider factors like traffic conditions, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity to determine the most efficient routes.* Real-time Order Tracking and Notifications: Providing customers with real-time order tracking and delivery updates enhances transparency and improves the customer experience.
This can be achieved through mobile apps, SMS notifications, and interactive maps.* Smart Packaging Solutions: Innovative packaging solutions can help maintain the freshness and temperature of raw food during delivery. Examples include insulated containers, temperature-controlled packaging, and biodegradable materials.* Inventory Management Systems: Implementing robust inventory management systems helps to minimize food waste and ensure that ingredients are always available.
These systems can track inventory levels, predict demand, and automate ordering processes.* AI-Powered Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots can handle common customer inquiries, such as order status updates and menu information, freeing up human customer service representatives to handle more complex issues.* Contactless Delivery Options: Offering contactless delivery options, such as drop-off at the doorstep or designated pick-up locations, can enhance safety and convenience, especially in the wake of public health concerns.
Expanding the Raw Food Delivery Business
Strategic expansion can significantly increase revenue streams and market reach for a raw food delivery service.* Offering Meal Kits: Providing pre-portioned meal kits with all the necessary ingredients and instructions allows customers to prepare raw food meals at home. This option caters to customers who enjoy cooking but want to save time on meal planning and grocery shopping.* Catering Services for Events and Businesses: Expanding into catering services can generate significant revenue, particularly for corporate events, office lunches, and private gatherings.
This requires developing a separate catering menu, managing logistics, and providing excellent customer service.* Subscription Services: Implementing a subscription model, where customers receive regular deliveries of raw food meals, encourages customer loyalty and provides a predictable revenue stream. Offering different subscription tiers based on meal frequency, portion sizes, and dietary preferences can attract a wider customer base.* Partnerships with Health and Wellness Centers: Collaborating with health and wellness centers, yoga studios, and gyms can provide access to a new customer base and increase brand visibility.
This can involve offering exclusive discounts, sponsoring events, or providing catering services.* Expansion into Retail Space (Hybrid Model): Establishing a small retail space in a strategic location, such as a health food store or a busy urban area, can enhance brand visibility and offer customers a place to pick up orders or purchase raw food products. This hybrid model can combine the convenience of delivery with the added touchpoint of a physical store.* Developing a Line of Raw Food Products: Creating and selling raw food products, such as smoothies, juices, snacks, or desserts, can provide additional revenue streams and complement the existing delivery service.
This can include offering these products through the delivery service, at a retail location, or through partnerships with other businesses.
Wrap-Up
As we conclude our exploration of raw food delivery route massachusetts, remember that this endeavor transcends the ordinary. It’s a commitment to vitality, a celebration of the body’s inherent wisdom, and a testament to the power of conscious choices. By optimizing routes, prioritizing safety, and embracing the spirit of service, we can build a network of nourishment that elevates the well-being of all.
Let the delivery of raw food be a daily reminder of the connection between the earth, the body, and the soul.


