Food truck vent – it’s the unsung hero of the street food game. Forget the fancy sauces and the banging tunes, if your ventilation’s knackered, your whole operation’s gonna stink. We’re talkin’ health hazards, greasy fires, and a vibe that’s more “dodgy kebab shop” than “legit street eats.” So, listen up, ’cause we’re breakin’ down everything you need to know to keep your food truck smelling sweet and your customers happy.
This ain’t just about getting rid of the smoke, either. We’re diving deep into the different types of vents, from the basic exhaust hoods to the fancy grease extraction systems. We’ll be lookin’ at the gubbins that make ’em tick, the calculations you need to get the right size, and the rules you gotta follow to keep the authorities off your back.
Plus, we’ll be talkin’ maintenance – ’cause a dirty vent is a recipe for disaster. Basically, this is the A-Z of keeping your food truck smelling like success, not a burnt-out chippy.
Food Truck Venting
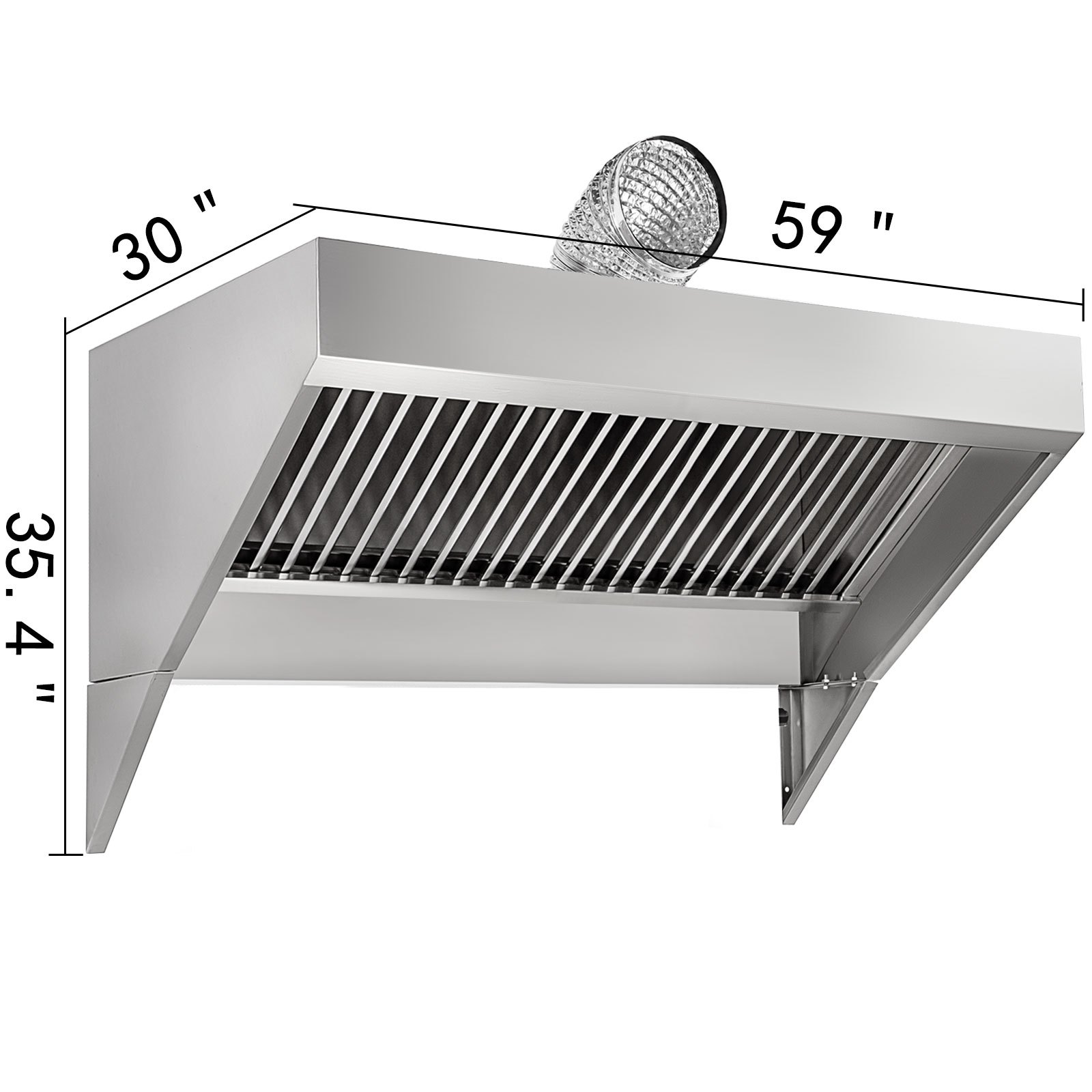
Proper ventilation is the unsung hero of a successful food truck operation, often overlooked but critically important. It’s the invisible system that keeps your food truck not only compliant with health and safety regulations but also a comfortable and efficient place to work. Investing in a good ventilation system is an investment in the long-term health of your staff, the longevity of your equipment, and the overall success of your mobile food business.
Overview of Food Truck Ventilation Importance
The importance of a well-designed and maintained ventilation system in a food truck cannot be overstated. It directly impacts the air quality inside the truck, the safety of your staff, and the efficiency of your cooking operations. Without effective ventilation, your food truck can quickly become an unpleasant and even dangerous environment.
Primary Functions of a Food Truck Vent
The primary functions of a food truck vent are multifaceted, encompassing health, safety, and operational efficiency. A well-functioning vent system works tirelessly to maintain a safe and productive workspace.
- Air Quality Control: Food truck vents remove smoke, grease, odors, and excessive heat generated during cooking. This prevents the buildup of harmful pollutants and ensures a cleaner, more breathable environment for food truck staff.
- Grease and Smoke Removal: Efficient vents capture grease-laden air, preventing grease buildup on surfaces and equipment. This reduces the risk of fire hazards and makes cleaning easier. They also remove smoke, which can irritate eyes and lungs.
- Temperature Regulation: Vents help regulate the temperature inside the food truck, keeping it cooler and more comfortable, especially during peak cooking hours. This is particularly important in hot climates.
- Odor Control: Vents eliminate food odors, preventing them from lingering and potentially affecting food quality or attracting pests.
- Fire Safety: Proper ventilation reduces the risk of fire by removing grease and smoke, two primary contributors to food truck fires. It also helps to prevent the buildup of flammable vapors.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many local and state health codes mandate specific ventilation requirements for food trucks. Failure to comply can result in fines or even closure of your business.
- Equipment Protection: By removing grease and heat, vents help protect your cooking equipment from damage and extend its lifespan.
Common Problems from Inadequate Food Truck Venting
Inadequate ventilation in a food truck leads to a host of problems, impacting everything from employee health to business operations. These issues highlight the critical need for a robust and well-maintained ventilation system.
- Health Hazards: Poor ventilation exposes employees to smoke, grease, and harmful fumes, potentially leading to respiratory problems, eye irritation, and other health issues.
- Fire Hazards: Grease buildup in the hood and ductwork increases the risk of fire, potentially causing significant damage to the truck and endangering lives.
- Unpleasant Working Conditions: Excessive heat, smoke, and odors create an uncomfortable and unpleasant working environment, which can decrease employee morale and productivity.
- Equipment Damage: Grease and heat can damage cooking equipment, leading to premature wear and tear, reducing equipment lifespan, and increasing maintenance costs.
- Reduced Food Quality: Lingering odors can affect the taste and quality of food.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Failure to meet ventilation requirements can result in fines, business closure, and legal issues.
- Increased Cleaning Costs: Inadequate ventilation leads to grease buildup, requiring more frequent and intensive cleaning of the truck and equipment.
- Customer Discomfort: Poor ventilation can result in unpleasant odors escaping the truck, potentially impacting the customer experience.
Types of Food Truck Vents
Food truck ventilation is crucial for removing smoke, grease, odors, and heat generated during cooking. Selecting the right ventilation system is vital for ensuring a safe and comfortable working environment, complying with health codes, and preventing fire hazards. Several types of ventilation systems are available, each with its own characteristics and suitability for different food truck setups.
Exhaust Hoods, Food truck vent
Exhaust hoods are the most fundamental component of a food truck ventilation system. They capture and remove cooking fumes, smoke, and grease-laden air from the cooking area. They are typically installed directly above cooking appliances like stoves, grills, and fryers.
- Types of Exhaust Hoods: There are primarily two types: wall-mounted and island hoods. Wall-mounted hoods are attached to the wall, while island hoods are designed for use above cooking equipment that is not against a wall.
- Functionality: Exhaust hoods work by drawing air upwards through a filter system. These filters capture grease particles, preventing them from entering the exhaust ductwork and potentially causing a fire.
- Importance of Airflow: The effectiveness of an exhaust hood is measured by its airflow capacity, typically expressed in cubic feet per minute (CFM). The CFM rating must be adequate to handle the volume of smoke and fumes produced by the cooking equipment.
Makeup Air Units
Makeup air units (MAUs) are often paired with exhaust hoods to replace the air that is removed by the hood. This is essential for maintaining a balanced air pressure within the food truck, preventing negative pressure that can make it difficult to open doors, and drawing in unconditioned air from outside.
- Purpose: MAUs supply conditioned or unconditioned air into the food truck. This can help regulate the temperature and improve the overall working environment.
- Conditioning Options: Some MAUs include heating and cooling capabilities, which are particularly useful in extreme climates.
- Integration: The MAU should be sized appropriately to match the CFM rating of the exhaust hood. If the MAU delivers less air than the hood extracts, negative pressure will persist. If the MAU delivers more air, positive pressure will be created.
Grease Extraction Systems
Grease extraction systems are designed to remove grease particles from the air before it is exhausted outside. This is particularly important for preventing grease buildup in the ductwork and on the roof of the food truck, which can pose a fire hazard.
- Filtration Methods: Grease extraction systems often utilize a series of filters, including baffle filters, mesh filters, and electrostatic precipitators (ESPs). Baffle filters are commonly used as a first stage, while ESPs are highly effective at removing fine grease particles.
- Importance of Maintenance: Regular cleaning and maintenance of grease extraction systems are crucial for their effectiveness and safety. Filters must be cleaned or replaced regularly to prevent grease buildup.
- Regulations: Local health codes and fire safety regulations often mandate the use of grease extraction systems.
Comparison of Food Truck Vent Systems
Choosing the right ventilation system involves careful consideration of factors like cost, effectiveness, and space requirements. The following table provides a comparison of the main types of food truck vent systems:
| Feature | Exhaust Hoods | Makeup Air Units | Grease Extraction Systems | Typical Costs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Function | Captures and removes smoke, grease, and odors from the cooking area. | Replaces air exhausted by the hood, maintaining air pressure and temperature control. | Removes grease particles from the air before it is exhausted. | |
| Pros | Essential for removing cooking fumes and smoke. Relatively straightforward to install. | Improves air quality and comfort. Can be integrated with heating and cooling. | Reduces fire hazards. Improves air quality. Can help extend the life of ductwork. | |
| Cons | Does not address air replacement. Can be ineffective without proper CFM rating. | Adds to the complexity and cost of the system. Requires additional space. | Adds to the initial cost and ongoing maintenance requirements. | |
| Typical Costs | $500 – $3,000 (depending on size and features) | $1,000 – $5,000 (depending on features like heating/cooling) | $1,000 – $5,000 (depending on the type and size) |
Ventilation System Components
Maintaining a functional and efficient ventilation system is paramount for any food truck operation. It’s not merely about removing smoke; it’s about creating a safe and comfortable working environment, complying with health regulations, and preventing fire hazards. A well-designed system ensures the longevity of equipment and the well-being of staff.
Exhaust Fans
Exhaust fans are the heart of the ventilation system, responsible for drawing contaminated air out of the food truck. They are typically roof-mounted or integrated into the hood system. The selection of the correct exhaust fan is critical and depends on the volume of air that needs to be removed, often measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM).
- Function: The primary function is to extract smoke, grease-laden vapors, heat, and odors produced during cooking.
- Types: There are various types, including upblast and downblast fans. Upblast fans discharge air vertically, while downblast fans discharge air horizontally. The choice depends on the food truck’s design and local regulations.
- Considerations: Factors to consider when choosing an exhaust fan include CFM rating, motor horsepower, noise levels, and energy efficiency. Higher CFM ratings are needed for operations with high-volume cooking or multiple appliances.
Filters
Filters are essential components designed to capture grease and particulate matter before they enter the ductwork and exhaust fan. They protect the fan and other components from becoming clogged and potentially failing, which would reduce the efficiency of the system and become a fire hazard.
- Types: Common types include baffle filters, mesh filters, and grease-extracting filters. Baffle filters are the most prevalent in food trucks, known for their effectiveness in trapping grease.
- Function: They remove grease particles from the air, preventing them from accumulating in the ductwork and on the exhaust fan. This reduces the risk of fire and maintains airflow efficiency.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning or replacement of filters is crucial for optimal performance. Clogged filters reduce airflow and can lead to poor ventilation and increased fire risk. The frequency of cleaning depends on cooking volume and the type of food prepared.
Ductwork
Ductwork serves as the pathway for conveying the extracted air from the hood to the exhaust fan and out of the food truck. Proper design and installation of ductwork are vital for efficient ventilation and fire safety.
- Materials: Ductwork is typically constructed from stainless steel or galvanized steel due to their durability and resistance to grease and heat.
- Design: The ductwork should be designed to minimize bends and turns to reduce airflow resistance. Smooth interior surfaces also help prevent grease buildup.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning of ductwork is essential to remove accumulated grease, which poses a significant fire hazard. Professional cleaning services are often recommended to ensure thorough cleaning and compliance with fire codes.
Grease Traps
Grease traps, also known as grease interceptors, are specifically designed to capture and remove grease and oil from the exhaust air stream. They are critical in preventing grease from entering the external environment and sewer systems.
- Location: Grease traps are typically located within the hood or ductwork system, often close to the filters.
- Function: They collect grease particles, preventing them from entering the ductwork and potentially causing fire hazards or environmental contamination.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential for grease trap effectiveness. Grease must be removed and disposed of properly, typically by a licensed waste hauler.
Diagram of a Standard Food Truck Ventilation System
A standard food truck ventilation system comprises a series of interconnected components working in unison. The illustration below describes the general layout.
Description of the Diagram:
The diagram illustrates a cross-section of a food truck’s interior, focusing on the ventilation system.
- The Hood: The diagram shows a large stainless-steel hood positioned above the cooking appliances (e.g., a grill, deep fryer, and stovetop). The hood is designed to capture smoke, grease, and fumes generated during cooking. It has integrated baffle filters to remove grease.
- Filters: Positioned within the hood, the diagram highlights baffle filters. These are angled metal plates that capture grease particles as the air passes through them.
- Ductwork: Ductwork, represented by a series of connected metal pipes, runs from the hood upwards to the roof. The ductwork is shown as a smooth, clean passage.
- Exhaust Fan: At the top of the ductwork, on the roof of the food truck, the exhaust fan is depicted. It is a large, box-shaped unit that draws air from the hood through the ductwork and expels it outside the truck.
- Grease Trap: A grease trap is located within the ductwork. This component is designed to collect any remaining grease particles that may have passed through the filters.
- Make-Up Air: Though not always present, the diagram suggests the potential of make-up air systems, usually placed at the base of the hood to provide fresh air to the cooking area, compensating for the air extracted by the exhaust system.
The diagram shows the flow of air: from the cooking appliances, up through the hood, through the filters, through the ductwork, through the exhaust fan, and out of the truck.
Ventilation System Sizing and Calculations
Sizing a food truck ventilation system is crucial for ensuring a safe, comfortable, and compliant cooking environment. It’s a balancing act, considering factors from the heat generated by your equipment to the physical dimensions of your truck. Proper sizing prevents excessive energy consumption and minimizes potential fire hazards, creating a more efficient and pleasant workspace.
Factors Influencing Ventilation System Sizing
Several factors contribute to determining the appropriate size of a food truck ventilation system. Understanding these elements allows for a tailored design that meets specific needs.
- Cooking Equipment: The type and quantity of cooking appliances are primary determinants. High-heat equipment, such as deep fryers and charbroilers, require significantly more ventilation than lower-heat appliances, like microwaves or warming ovens. The BTU (British Thermal Units) rating of each appliance is critical for calculations.
- Menu: The type of cuisine influences ventilation needs. For instance, a menu heavily featuring fried foods generates more grease and smoke, necessitating a more robust system compared to a menu primarily based on salads and sandwiches.
- Truck Dimensions: The overall size of the food truck plays a role. A smaller truck will require a smaller ventilation system, assuming the same equipment, compared to a larger one. The height of the truck’s ceiling and the location of the cooking equipment also influence the system design.
- Local Codes and Regulations: Building codes and fire safety regulations vary by location. These codes dictate minimum airflow requirements, hood sizes, and other specifications that must be adhered to for compliance.
Calculating Required Airflow (CFM) for a Food Truck
Determining the required airflow, measured in Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM), is a critical step in sizing a ventilation system. This calculation involves assessing the heat load generated by the cooking equipment.
- Determine the Total BTU Input: Calculate the total BTU input for all cooking appliances. This information is usually found on the appliance’s data plate. Add up the BTU ratings of all appliances that will be used simultaneously. For example, if you have a fryer (50,000 BTU) and a griddle (30,000 BTU), the total input is 80,000 BTU.
- Apply a CFM Calculation Method: Several methods can be used. A common method is based on the type of equipment. Some examples are:
- General Rule of Thumb: A basic estimate suggests 100 CFM per linear foot of hood for light-duty cooking (e.g., sandwich making).
- Specific Appliance Based Calculations: More accurate calculations are often based on the type of equipment and its BTU rating. A common formula uses a multiplier based on equipment type:
- For electric appliances, multiply the total wattage by 3.1 CFM per 1000 BTU.
- For gas appliances, multiply the total BTU by a factor, usually between 4 and 6 CFM per 100 BTU. The exact factor depends on the equipment and local regulations.
- Account for Make-Up Air: Ensure the system includes make-up air to replace the air exhausted by the hood. This prevents negative pressure inside the truck, which can hinder the ventilation process and potentially draw in fumes. Make-up air requirements are usually calculated as a percentage of the exhaust air.
- Factor in Local Codes: Always check and adhere to local codes and regulations, as these often dictate minimum CFM requirements or specific calculation methods.
For example, let’s say a food truck has a gas range (40,000 BTU) and a charbroiler (60,000 BTU). Using a factor of 5 CFM per 100 BTU for gas appliances:
(40,000 BTU / 100)
- 5 CFM + (60,000 BTU / 100)
- 5 CFM = 2,000 CFM + 3,000 CFM = 5,000 CFM.
This calculation provides an estimate of the required exhaust airflow.
Calculating Necessary Vent Hood Size
Vent hood size is directly related to the cooking equipment it serves. The hood must effectively capture and remove smoke, grease, and odors generated by the appliances.
- Determine Equipment Coverage: The hood should extend beyond the cooking equipment to capture rising contaminants. A general rule is to extend the hood at least 6 inches beyond the cooking surface on all sides.
- Consider Hood Type: Different hood types (wall-mounted, island, etc.) have varying capture efficiencies. The hood type affects the necessary size.
- Use a Formula for Hood Size: The hood size is usually calculated by measuring the length and width of the cooking equipment and adding the recommended overhang.
- Length of Hood: The total length is calculated by adding the length of the cooking appliances plus the overhang on each side. For instance, if a griddle is 48 inches long, and the overhang is 6 inches on each side, the hood length should be 60 inches (48 + 6 + 6).
- Width of Hood: The width is calculated similarly. It is based on the depth of the cooking equipment plus the overhang.
- Consult Local Codes: Local codes specify minimum hood sizes and other requirements. Always verify these before finalizing the design.
For instance, a food truck with a 36-inch-wide griddle and a 24-inch-wide fryer would need a hood that covers both. Assuming an overhang of 6 inches on each side: The length of the hood should be the combined length of the griddle and fryer plus the overhang. The width should cover the deepest appliance plus the overhang.
Installation and Maintenance: Food Truck Vent
Proper installation and consistent maintenance are crucial for the efficient and safe operation of a food truck ventilation system. Neglecting these aspects can lead to poor air quality, fire hazards, and reduced equipment lifespan. Adhering to a strict schedule and following best practices ensures the longevity and optimal performance of the system, protecting both the food truck and its occupants.
Installation Steps
The installation of a food truck ventilation system requires careful planning and execution to ensure compliance with local codes and regulations. A well-installed system is critical for safety and operational efficiency.
- Site Assessment and Planning: Before beginning, assess the food truck’s layout and available space. Determine the optimal placement for the hood, exhaust fan, and make-up air system, considering potential obstructions and accessibility for maintenance. Review local building codes and fire safety regulations to ensure compliance with all relevant standards.
- Hood Installation: Mount the kitchen hood securely to the ceiling, ensuring it is level and properly sealed to prevent air leakage. Connect the hood to the ductwork, using appropriate connectors and sealing materials to create an airtight seal. Consider the hood’s dimensions and capacity relative to the cooking equipment.
- Ductwork Installation: Install the ductwork, ensuring it is constructed from fire-rated materials, such as stainless steel. Route the ductwork through the roof or side of the truck, following the shortest and most direct path possible to minimize friction and maximize airflow. Support the ductwork properly to prevent sagging and ensure structural integrity.
- Exhaust Fan Installation: Mount the exhaust fan securely on the roof or side of the truck, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Connect the fan to the ductwork, ensuring a tight and secure connection. Ensure the fan’s electrical connections are properly wired and grounded.
- Make-Up Air System Installation (If Applicable): Install the make-up air system, if required, to replace the air exhausted by the hood. Connect the system to a fresh air source, ensuring proper filtration to remove contaminants. Properly integrate the make-up air system with the exhaust fan to maintain balanced airflow.
- Grease Trap Installation: Install the grease trap according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Connect the trap to the hood’s exhaust system and ensure it is easily accessible for cleaning and maintenance. Place the grease trap in a location that complies with local regulations.
- Electrical Connections: Ensure all electrical connections are made by a qualified electrician and comply with local electrical codes. Properly wire the exhaust fan, make-up air system, and any other electrical components. Provide appropriate overcurrent protection for the system.
- System Testing and Inspection: After installation, test the ventilation system to ensure it is operating correctly. Check the airflow, ensure there are no leaks, and verify that all components are functioning properly. Schedule a final inspection with the local authorities to confirm compliance with all regulations.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule is essential for keeping a food truck ventilation system operating safely and efficiently. This includes regular cleaning, inspections, and filter replacements.
- Filter Cleaning: Clean or replace filters regularly, depending on the type of filter used. For mesh filters, cleaning should be done at least weekly, or more frequently if cooking produces high grease levels. Use a degreasing solution and hot water. For baffle filters, clean them monthly or as needed.
- Grease Trap Cleaning: Clean the grease trap frequently, typically every one to three months, or as specified by local regulations. The frequency depends on the volume of cooking and grease production. Remove and dispose of the collected grease properly, in accordance with local waste disposal guidelines.
- Fan Inspection: Inspect the exhaust fan and make-up air fan (if applicable) at least quarterly. Check for any signs of wear, damage, or imbalance. Lubricate the fan bearings as needed. Ensure the fan blades are clean and free of grease buildup.
- Ductwork Inspection: Inspect the ductwork at least annually for grease buildup, leaks, and other damage. Professional cleaning may be required periodically, especially if grease accumulation is significant. Check for any signs of corrosion or deterioration.
- Belt and Motor Inspection: For belt-driven fans, inspect the belts for wear and tear and replace them as needed. Check the motor for proper operation and lubrication. Ensure that all electrical connections are secure and free of corrosion.
- System Performance Testing: Periodically test the system’s airflow and performance to ensure it meets the required standards. Professional testing may be necessary to verify airflow rates and identify any potential issues.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Food truck ventilation systems can encounter various issues that can impact their performance and safety. Prompt troubleshooting and repair are critical to maintaining a safe and efficient operation.
- Poor Ventilation: If the hood isn’t effectively removing smoke and odors, check the following:
- Blocked Filters: Clean or replace dirty filters.
- Fan Malfunction: Inspect the fan motor and blades. Replace or repair the fan if necessary.
- Ductwork Obstruction: Inspect the ductwork for grease buildup or other obstructions. Clean the ductwork if needed.
- Insufficient Airflow: Verify that the fan is the correct size and that the system is properly balanced.
- Grease Buildup: Excessive grease accumulation poses a fire hazard. Address it by:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean filters, hoods, and ductwork frequently.
- Grease Trap Maintenance: Empty the grease trap regularly.
- Professional Cleaning: Consider professional duct cleaning as needed.
- Fan Noise: Unusual noises indicate potential problems. Investigate by:
- Loose Components: Tighten any loose screws or bolts.
- Worn Bearings: Lubricate or replace worn fan bearings.
- Blade Obstruction: Remove any obstructions from the fan blades.
- Electrical Issues: Electrical problems can be dangerous. Resolve them by:
- Blown Fuses or Tripped Breakers: Replace fuses or reset breakers.
- Wiring Problems: Have a qualified electrician inspect and repair any wiring issues.
- Motor Failure: Replace the fan motor if it fails.
- Code Violations: Ensure compliance by:
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections to identify potential violations.
- Professional Advice: Consult with professionals to ensure the system meets all current codes.
Regulations and Compliance
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for food truck owners. Compliance ensures the safety of your staff and customers, protects your business from potential fines, and contributes to the overall well-being of the community. Understanding and adhering to local and national regulations concerning ventilation systems is not just a legal obligation; it’s a fundamental aspect of responsible food truck operation.
Local and National Regulations
Food truck ventilation systems are subject to a web of regulations designed to prevent fires, ensure air quality, and safeguard public health. These regulations vary by location, making it essential to research the specific requirements in your operating area.The primary regulatory bodies involved include:
- Fire Codes: Fire codes, often based on the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards, dictate the design, installation, and maintenance of ventilation systems to minimize fire hazards. These codes specify requirements for grease duct construction, fire suppression systems, and regular inspections. For example, NFPA 96, Standard for Ventilation Control and Fire Protection of Commercial Cooking Operations, is a key reference.
- Health Department Requirements: Health departments focus on ensuring food safety and preventing the spread of disease. Their regulations often address air quality within the food truck, including the removal of smoke, odors, and grease particles. They may specify the type of filters required and the frequency of filter cleaning or replacement.
- Building Codes: Building codes, enforced at the local level, often influence the construction and alteration of food trucks, including the installation of ventilation systems. These codes may address structural integrity, electrical wiring, and other safety aspects related to the ventilation system.
- Air Quality Regulations: Local air quality regulations, such as those enforced by air quality management districts, may limit the amount of pollutants emitted by food trucks. This could influence the type of filtration system required to reduce smoke and odor emissions.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines, operational shutdowns, and even legal action. It’s a significant risk that can severely impact a food truck business.
Permits and Inspections
Obtaining the necessary permits and undergoing regular inspections are integral parts of legal and safe food truck operation. These processes ensure that your ventilation system meets all required standards and operates effectively.The permitting process typically involves:
- Ventilation System Plans: Detailed plans of your ventilation system, including specifications for all components, are usually required for permit application. These plans must demonstrate compliance with relevant codes and regulations.
- Permit Application: The application process involves submitting the plans and other required documentation to the relevant local authorities, such as the fire marshal or health department.
- Permit Fees: Fees vary depending on the location and the complexity of the system.
- Inspection: After installation, your ventilation system will undergo inspections to verify compliance with the approved plans and regulations. These inspections are conducted by qualified inspectors.
Regular inspections are typically required to ensure the ongoing safe and effective operation of your ventilation system. These inspections might include:
- Grease Duct Inspection: Inspections of grease ducts to check for grease buildup and ensure they are properly cleaned.
- Filter Inspection: Inspections of filters to verify they are clean and functioning correctly.
- Fire Suppression System Inspection: Inspection of the fire suppression system to ensure it is in good working order.
- Equipment Inspection: General inspection of all components of the ventilation system, including fans, motors, and controls.
The frequency of inspections varies depending on local regulations. Non-compliance with inspection requirements can lead to fines and operational restrictions.
Investigate the pros of accepting asian food owasso in your business strategies.
Grease Management and Fire Prevention
Effective grease management is critical for preventing fires in food trucks. Grease buildup in ventilation systems is a major fire hazard. Complying with grease management regulations is not just a matter of following the law; it is a critical component of fire safety.Key aspects of grease management include:
- Regular Cleaning: Grease ducts, hoods, and filters must be cleaned regularly to prevent grease buildup. The frequency of cleaning depends on the volume of cooking and the type of food prepared. Many jurisdictions require professional cleaning services for grease ducts.
- Proper Filtration: Using appropriate filters to capture grease particles before they enter the ventilation system is crucial. These filters should be cleaned or replaced as needed.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Installing and maintaining a fire suppression system, such as an automatic sprinkler system, is essential for quickly extinguishing fires that may start in the cooking area or ventilation system.
- Employee Training: Training staff on fire safety procedures, including how to use fire extinguishers and report fires, is crucial.
Ignoring grease management regulations can have devastating consequences. A grease fire can quickly spread through a food truck, causing significant damage, injuries, and even fatalities.
“Preventing fires is not just about complying with regulations; it is about protecting lives, preserving property, and ensuring the sustainability of your business.”
Grease Management and Fire Safety
Maintaining a safe and hygienic food truck environment is paramount, and a significant aspect of this involves effective grease management and stringent fire safety protocols. Neglecting these areas can lead to serious consequences, including fire hazards, health code violations, and potential business closure. Proper handling of grease and adherence to fire safety regulations are not just about compliance; they are about protecting your staff, your customers, and your investment.
Role of Grease Traps and Grease Extraction Systems
Grease traps and grease extraction systems are critical components in preventing fires and upholding hygiene standards within a food truck’s ventilation system. They work in tandem to remove grease and other contaminants from the exhaust stream, minimizing the risk of fire and preventing the build-up of harmful substances.Grease traps, also known as grease interceptors, are typically located in the kitchen area and are designed to capture grease, oil, and fats (FOG) before they enter the wastewater system.
They operate on the principle of density: FOG is less dense than water and floats to the top, where it is trapped. This prevents FOG from clogging pipes and entering the municipal sewer system, which can lead to environmental damage and costly fines. The effectiveness of a grease trap depends on its size and design, with larger traps generally capable of handling higher volumes of wastewater.Grease extraction systems, on the other hand, are integrated within the ventilation system itself, typically consisting of a hood, filters, and an exhaust fan.
Their primary function is to remove grease-laden vapors from the air generated during cooking. These systems are designed to capture grease particles before they can accumulate in the ductwork and on the exhaust fan, which are major fire hazards. Different types of filters are used, including baffle filters, mesh filters, and electrostatic precipitators, each with varying levels of efficiency in grease removal.
Baffle filters, for example, are commonly used because of their ability to separate grease through changes in airflow direction.
Best Practices for Grease Trap Cleaning and Disposal
Proper cleaning and disposal of grease from grease traps are essential for maintaining hygiene and preventing environmental hazards. Neglecting these practices can lead to odors, blocked drains, and potential health code violations.Regular cleaning is the cornerstone of effective grease trap management. The frequency of cleaning depends on the size of the grease trap, the volume of food prepared, and the types of food cooked.
A general guideline is to clean the trap when it is approximately 25% full of grease and solids. Failure to do so can reduce the trap’s efficiency and increase the risk of overflows.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the grease trap for any signs of damage, leaks, or excessive build-up of grease and solids.
- Frequency: Establish a cleaning schedule based on the food truck’s usage and the size of the grease trap. Consider weekly or bi-weekly cleaning for high-volume operations.
- Professional Services: Hire a licensed professional to clean the grease trap. They have the equipment and expertise to safely remove and dispose of the grease.
- Proper Disposal: Ensure the grease is disposed of properly. Most municipalities have specific regulations regarding grease disposal. Grease can often be recycled or used for biofuel production. Never pour grease down the drain, as this can lead to significant environmental problems.
- Record Keeping: Maintain records of all grease trap cleaning activities, including the date, time, and the name of the service provider. This documentation is crucial for compliance with health and environmental regulations.
Fire Safety Measures for the Vent System
Implementing robust fire safety measures within the food truck’s vent system is non-negotiable. Cooking operations, especially those involving high heat and grease, inherently pose fire risks. The vent system, being directly involved in the cooking process, requires careful attention to minimize these risks.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the entire vent system, including the hood, filters, ductwork, and exhaust fan. Look for grease build-up, damage, and any other potential fire hazards.
- Professional Cleaning: Schedule professional cleaning of the vent system at least every three to six months, or more frequently depending on the volume and type of cooking. Professional cleaning removes grease and other flammable materials that can fuel a fire.
- Fire Suppression System: Install an automatic fire suppression system within the hood. These systems are designed to detect and extinguish fires quickly, minimizing damage and protecting personnel. A common system uses a chemical agent that is specifically designed to suppress grease fires.
- Filter Maintenance: Regularly clean or replace the filters in the hood. Dirty filters can reduce airflow and increase the risk of grease accumulation.
- Exhaust Fan Operation: Ensure the exhaust fan is operating correctly and at the proper speed. A malfunctioning fan can lead to inadequate ventilation and increased fire risk.
- Training: Train all staff members on fire safety procedures, including the use of fire extinguishers, evacuation routes, and the operation of the fire suppression system. Regular fire drills are essential to ensure that staff members are prepared to respond to a fire emergency.
- Fire Extinguishers: Keep a Class K fire extinguisher (specifically designed for kitchen fires) readily accessible in the food truck. Ensure that staff members know how to use it.
- Compliance: Ensure the vent system and all fire safety measures comply with local fire codes and regulations. This may involve inspections and permits.
Energy Efficiency and Venting
Optimizing a food truck’s ventilation system for energy efficiency is crucial for minimizing operational costs and reducing environmental impact. Energy-efficient practices not only save money but also contribute to a more sustainable business model. This section delves into how to achieve this, exploring component comparisons and providing actionable tips for food truck owners.
Optimizing Ventilation System Efficiency
To enhance energy efficiency, food truck owners should consider several key strategies. These include selecting energy-efficient equipment, implementing smart controls, and adopting proper maintenance practices. Regular evaluation of the system’s performance is also important.
Energy Consumption of Vent System Components
The energy consumption of a food truck’s ventilation system varies significantly depending on the components used. Comparing the energy demands of different elements allows for informed decisions during the system’s design and operation.
- Exhaust Fans: Exhaust fans are major energy consumers. Consider fans with variable speed drives (VSDs) that adjust fan speed based on demand. These fans can reduce energy consumption during periods of low cooking activity. For example, a VSD-equipped fan can use up to 50% less energy than a single-speed fan.
- Make-Up Air Units: These units bring in fresh air and often include heating or cooling elements. The energy use of these components can vary significantly. Using heat recovery systems, such as those that transfer heat from exhaust air to incoming air, can reduce energy consumption by up to 70%.
- Lighting: The type of lighting used in the hood and throughout the food truck impacts energy usage. LED lighting is significantly more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent or fluorescent bulbs, reducing energy consumption by up to 75%.
- Grease Filters: While not directly consuming electricity, the type of grease filters can affect airflow and, consequently, fan energy use. Properly maintained and efficient filters ensure optimal airflow, reducing the load on the exhaust fan.
Energy-Saving Tips for Food Truck Owners
Food truck owners can implement various energy-saving practices to minimize energy consumption related to their ventilation systems.
- Use Variable Speed Drives (VSDs): As mentioned earlier, VSDs on exhaust fans adjust fan speed based on cooking needs, reducing energy waste during periods of low activity.
- Implement a Timer System: Install timers to automatically turn off the ventilation system during non-operational hours. This prevents unnecessary energy consumption.
- Optimize Hood Design: Ensure the hood is properly sized for the cooking equipment and cooking volume. Oversized hoods can lead to wasted energy.
- Utilize Heat Recovery Systems: If feasible, integrate a heat recovery system to preheat incoming air, particularly in colder climates.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance on the ventilation system, including cleaning grease filters and ductwork. Clean filters ensure optimal airflow, reducing fan energy use.
- Choose Energy-Efficient Appliances: Select energy-efficient cooking appliances that produce less heat and grease.
- Install LED Lighting: Replace existing lighting with LED fixtures to reduce energy consumption and heat generation.
- Monitor Energy Usage: Regularly monitor energy consumption to identify areas for improvement. Consider using energy monitoring tools.
- Train Staff: Educate staff on energy-saving practices, such as turning off equipment when not in use and properly using the ventilation system controls.
Cost Considerations
Understanding the financial implications of a food truck ventilation system is crucial for any aspiring mobile food vendor. The initial investment, ongoing maintenance, and operational costs can significantly impact profitability. Careful consideration of these factors allows for informed decision-making and helps in choosing a system that aligns with both budgetary constraints and operational needs.
Cost Breakdown of Purchasing, Installing, and Maintaining a Food Truck Ventilation System
The total cost of a ventilation system encompasses several key areas. Each component contributes to the overall expense, requiring a comprehensive approach to budgeting.
- Purchasing Costs: This includes the price of the vent hood, exhaust fan, make-up air unit (if applicable), filters, and any associated hardware like ductwork and mounting brackets. The complexity and size of the system directly influence these costs.
- Installation Costs: Professional installation is often necessary to ensure proper functionality and compliance with local codes. Labor costs for electricians, HVAC technicians, and other specialists will factor into this expense.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity. This includes filter replacements, cleaning, and potential repairs. Frequency and cost vary depending on the system type and usage.
- Operating Costs: Energy consumption is a significant ongoing cost. The exhaust fan and, if present, the make-up air unit consume electricity. These costs fluctuate based on usage and local electricity rates.
- Grease Removal and Cleaning: Professional cleaning of the vent hood and ductwork is required periodically to prevent fire hazards and maintain hygiene standards. These services incur additional costs.
Comparison of Upfront Costs for Different Vent System Types
The initial investment in a ventilation system can vary widely based on the type of system selected. Understanding the differences in upfront costs allows for a more informed choice.
- Type 1 Hoods: These are typically the most expensive due to their robust construction and fire suppression systems. They are designed for high-volume cooking and often required for operations involving open flames. The upfront cost can range from $5,000 to $20,000 or more, depending on size and features.
- Type 2 Hoods: These systems are generally less expensive than Type 1 hoods, as they are designed for lower-volume cooking and do not require fire suppression. They can range from $2,000 to $8,000, based on the system’s dimensions and features.
- Exhaust Fans: Standalone exhaust fans, without a hood, are a cost-effective option for some food trucks. These systems may cost between $500 and $2,000, based on the fan’s CFM (cubic feet per minute) rating and features.
- DIY Systems: Some food truck owners opt for DIY systems to reduce upfront costs. However, this approach may compromise performance, safety, and compliance with regulations. The costs of a DIY system can range from $1,000 to $5,000, based on the components used.
Potential Long-Term Costs Associated with Various Vent Systems
Beyond the initial investment, the long-term costs associated with a ventilation system can significantly impact overall profitability. These costs include maintenance, repairs, and energy consumption.
| Vent System Type | Maintenance Costs (Annual) | Repair Costs (Estimate, over 5 years) | Energy Usage (Annual Estimate) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Hood (High-Volume) | $500 – $2,000 (Filter replacement, cleaning) | $1,000 – $5,000 (Fan motor, fire suppression system) | $1,500 – $3,000 (Based on CFM and usage) | Requires professional cleaning and inspection. Fire suppression system maintenance is critical. |
| Type 2 Hood (Medium-Volume) | $300 – $1,000 (Filter replacement, cleaning) | $500 – $2,500 (Fan motor, minor ductwork repairs) | $800 – $1,800 (Based on CFM and usage) | Less frequent maintenance than Type 1. Cleaning frequency can be adjusted based on cooking style. |
| Exhaust Fan Only | $100 – $500 (Filter replacement, cleaning) | $200 – $1,000 (Fan motor replacement) | $500 – $1,200 (Based on CFM and usage) | Suitable for low-volume cooking. Regular cleaning is crucial to prevent grease buildup. |
| DIY System | $100 – $300 (Filter replacement, cleaning) | $500 – $1,500 (Potential for frequent repairs due to lower quality components) | $400 – $1,000 (Varies significantly based on components used) | Potential for increased maintenance and repair costs. May not meet all regulatory requirements. |
Design Considerations for the Vent
Designing a food truck’s ventilation system isn’t just about removing smoke and grease; it’s about maximizing space, ensuring operational efficiency, and maintaining a safe and aesthetically pleasing environment. Careful planning and execution are crucial, especially given the confined nature of a mobile kitchen. The vent system must be thoughtfully integrated into the overall design to avoid being an afterthought.
Maximizing Space Utilization in a Food Truck
Space is a premium in a food truck. The vent system’s design directly impacts how efficiently that space is used. Strategic placement of components minimizes wasted area and allows for optimal workflow.The following points illustrate how to maximize space:
- Compact Hood Design: Choosing a hood with a low profile and integrated features, such as built-in lighting and fire suppression systems, minimizes the footprint. Consider a wall-mounted hood instead of a large, centrally located island hood to free up valuable counter space.
- Ductwork Routing: Route ductwork strategically. Avoid running ducts through areas that impede movement or obstruct access to equipment. Consider routing them along the ceiling, above equipment, or within wall cavities where possible. Using flexible ductwork in certain sections can allow for easier maneuvering around obstacles.
- Equipment Placement: Coordinate the vent system’s location with the placement of cooking equipment. Position the hood directly above the cooking appliances it serves to minimize ductwork length and optimize capture efficiency. Ensure sufficient clearance around equipment for ventilation and maintenance.
- Component Integration: Integrate the vent system’s components, such as the exhaust fan and grease trap, into existing truck structures or design custom enclosures to house them. This can help to reduce the visual impact of the system and free up additional space.
- Accessibility for Maintenance: Design the system to ensure all components are easily accessible for cleaning, maintenance, and repair. Avoid placing components in locations that require extensive dismantling or restrict access.
Visual Appearance of a Well-Designed Vent System
A well-designed vent system seamlessly blends into the food truck’s interior, enhancing the overall aesthetic rather than detracting from it. The goal is a clean, professional look that complements the truck’s branding and style.Here’s a detailed description of a well-designed system:
- The Hood: The hood itself is constructed from brushed stainless steel, reflecting light and creating a clean, modern appearance. The edges are smoothly finished, and the hood extends slightly beyond the cooking surface to effectively capture smoke and grease. Integrated LED lighting provides bright and efficient illumination of the cooking area. The hood’s design incorporates a baffle filter system, easily accessible for cleaning.
- Ductwork: The ductwork, also constructed from stainless steel, is meticulously routed along the ceiling. The ductwork’s surface is smooth and free of sharp edges, minimizing grease buildup and making cleaning easier. The ducts are securely fastened to the truck’s structure, and any joints are sealed to prevent leaks.
- Exhaust Fan: The exhaust fan is housed in a discreet, insulated enclosure, typically located on the roof of the food truck. The enclosure is designed to minimize noise and vibration. The fan is painted to match the truck’s exterior, creating a cohesive visual appearance.
- Grease Management System: The grease management system, including the grease trap, is located in an easily accessible compartment, possibly behind a panel, and is designed for efficient grease collection and disposal. The compartment is well-ventilated to prevent odors.
- Overall Integration: The vent system’s design complements the food truck’s interior design. The stainless steel components reflect the light, creating a bright and inviting atmosphere. The clean lines and professional finish contribute to a sense of quality and professionalism.
Integrating the Vent System with Overall Food Truck Design
Seamless integration is key to a successful food truck design. The vent system should not appear as an afterthought but rather as an integral part of the overall aesthetic and functionality.Consider these examples:
- Color Coordination: Match the vent hood and ductwork’s color to the truck’s exterior or interior design. For example, if the truck’s exterior is a vibrant red, the hood could be a matching red, or a complementary color, creating a visually unified look.
- Material Consistency: Use consistent materials throughout the food truck. If the countertops are stainless steel, consider using stainless steel for the hood and ductwork. This creates a cohesive and professional appearance.
- Camouflaging Components: Conceal less attractive components, such as the exhaust fan and grease trap, by housing them in custom-designed enclosures. These enclosures can be painted to match the truck’s exterior or interior, or they can be incorporated into the overall design.
- Strategic Lighting: Incorporate lighting into the vent hood and the cooking area. This can enhance the aesthetic appeal of the food truck while providing functional lighting for cooking.
- Branding Integration: Integrate the food truck’s branding into the vent system design. This could involve adding the company logo to the hood, using custom-designed ductwork covers, or incorporating the brand’s colors into the system’s design. For example, a food truck named “Burger Bliss” could have a custom hood with the company logo subtly etched into the stainless steel.
Final Wrap-Up
So there you have it, the lowdown on food truck ventilation. From choosin’ the right system to keepin’ it clean, this is the kit to keep your business runnin’ smooth. Remember, a good vent ain’t just about followin’ the rules, it’s about protectin’ your staff, keepin’ your food tasting top-notch, and makin’ sure your customers keep comin’ back for more.
Get your vent sorted, and your food truck will be the envy of the streets, guaranteed.


