The snow leopard food web, a complex tapestry of life woven across the high-altitude landscapes of Central Asia, is far more than a simple diagram of who eats whom. It’s a dynamic system, a delicate dance where the apex predator, the snow leopard, exerts a profound influence, shaping the lives of everything from the smallest alpine plants to the largest ungulates.
Understanding this web is crucial, as it reveals the intricate connections that sustain this elusive creature and its environment. We will explore the snow leopard’s role as a keystone species, the critical importance of its prey, the challenges posed by other predators and human impacts, and the vital role of decomposers in maintaining ecosystem health. Each component is vital, and its interconnectedness dictates the fate of the entire ecosystem.
Snow Leopard’s Place in the Ecosystem
Oke, jadi kita ngomongin macan salju nih, si raja puncak di habitatnya. Bayangin aja, dia tuh kayak bos besar yang ngatur semua makhluk hidup di lingkungannya. Gak cuma ngejar mangsa buat makan, tapi juga punya peran penting banget buat keseimbangan alam. Kalo macan salju gak ada, wah, bisa kacau balau deh semuanya.
Apex Predator Role
Macan salju, aliasUncia uncia*, bener-bener predator puncak di habitatnya, kayak di pegunungan Himalaya. Artinya, dia ada di puncak rantai makanan, gak ada predator lain yang ngejar dia. Karena posisinya itu, dia punya pengaruh besar banget ke populasi hewan-hewan lain.* Macan salju ngontrol populasi mangsanya, kayak kambing gunung, argali (domba gunung), dan marmut. Kalo jumlah macan salju sedikit, populasi mangsanya bisa meledak, yang akhirnya bisa ngerusak tumbuhan dan bikin ekosistem gak seimbang.
- Dengan ngejar hewan-hewan yang lemah atau sakit, macan salju juga bantu menjaga kesehatan populasi mangsanya. Ini penting banget buat mencegah penyebaran penyakit.
- Macan salju juga bisa ngaruh ke perilaku hewan-hewan lain. Misalnya, hewan-hewan mangsa jadi lebih waspada dan lebih hati-hati, yang akhirnya bisa ngubah cara mereka cari makan dan berinteraksi.
Influence on Species Populations
Macan salju punya dampak langsung ke populasi hewan-hewan lain di ekosistemnya. Gak cuma soal makan dan dimakan, tapi juga soal gimana caranya hewan-hewan itu hidup dan berkembang biak.* Populasi Mangsa: Kalo macan salju banyak, populasi mangsanya bakal lebih terkontrol. Contohnya, di daerah-daerah yang macan saljunya dilindungi, populasi kambing gunung cenderung stabil. Kalo macan salju berkurang, populasi kambing gunung bisa naik drastis, yang bisa ngerusak padang rumput dan tumbuhan lainnya.
Kompetisi Antar Spesies
Macan salju juga bisa ngaruh ke kompetisi antar spesies. Kalo macan salju ngejar satu jenis mangsa, hewan predator lain yang juga makan mangsa itu bisa kena dampaknya. Misalnya, populasi serigala bisa berkurang kalo macan salju lebih banyak di daerah itu.
Perilaku Hewan
Kehadiran macan salju bikin hewan-hewan mangsa jadi lebih hati-hati. Mereka jadi lebih sering ngumpet, lebih waspada, dan lebih fokus cari makan di tempat yang aman. Perubahan perilaku ini bisa ngaruh ke struktur komunitas hewan secara keseluruhan.
Trophic Cascades and Snow Leopards
Trophic cascade tuh kayak efek domino di ekosistem. Kalo ada perubahan di satu level rantai makanan, dampaknya bisa nyebar ke level-level lainnya. Macan salju, sebagai predator puncak, punya peran penting banget di sini.* Kalo macan salju berkurang, populasi mangsanya bisa naik. Ini bisa bikin tumbuhan di daerah itu rusak, karena mangsa makan tumbuhan lebih banyak. Kalo tumbuhan rusak, hewan-hewan lain yang makan tumbuhan juga kena dampaknya.
Bahkan, bisa ngaruh ke komposisi tanah dan siklus nutrisi di ekosistem.
-
Contoh nyata
Di beberapa daerah, berkurangnya macan salju bikin populasi kambing gunung meledak. Akibatnya, tumbuhan di daerah itu jadi berkurang, yang akhirnya ngaruh ke hewan-hewan lain yang bergantung sama tumbuhan itu. Ini nunjukkin betapa pentingnya peran macan salju buat menjaga keseimbangan ekosistem.
- Intinya, perubahan di populasi macan salju bisa ngasih efek domino ke seluruh ekosistem, mulai dari tumbuhan sampe hewan-hewan kecil.
“The removal of a top predator, like the snow leopard, can trigger a cascade of effects that alter the entire ecosystem.”
Primary Consumers in the Snow Leopard’s Diet
Aight, so we’ve already talked about the snow leopard’s place in the food web, right? Now, let’s get into the
- mangsa* (prey) that these majestic cats
- sikat* (eat). We’re talkin’ about the primary consumers – the herbivores, the veggie eaters, the ones that get their energy directly from plants. These guys are the foundation of the snow leopard’s diet, and their abundance
- ngaruh pisan* (really affects) the big cat’s survival.
Primary Prey Animals of the Snow Leopard, Snow leopard food web
The snow leopard is acarnivora* (carnivore), but they’re picky eaters. Their diet is mainly based on certain herbivorous animals. Understanding these primary consumers is key to understanding the whole ecosystem.Here’s a list of the main
korban* (prey) animals
- Blue Sheep (Pseudois nayaur): This is, like, the snow leopard’s
-langganan* (regular). They’re a medium-sized wild sheep, perfectly suited to the high-altitude life. They’re found all over the snow leopard’s range. - Argali Sheep (Ovis ammon): These are the biggest wild sheep on Earth! They’re a
-gede* (big) meal for a snow leopard, and their presence is a good indicator of a healthy ecosystem. - Ibex (Capra sibirica): These are mountain goats, known for their incredible climbing skills. They’re another staple in the snow leopard’s diet, especially in certain areas.
- Markhor (Capra falconeri): Similar to the ibex, but with distinct spiral horns. Found in the more mountainous regions, they’re a valuable food source.
- Urial (Ovis vignei): Another wild sheep, a bit smaller than the argali, and found in specific parts of the snow leopard’s habitat.
- Bharal or Blue Sheep (Pseudois nayaur): The snow leopard’s most frequent prey, and they are found in the high-altitude regions of the Himalayas.
- Other smaller prey: Sometimes, when bigger prey is scarce, snow leopards
-terpaksa* (are forced) to eat smaller animals like marmots, pikas, and even birds. These are more like
-ngemil* (snacks) compared to the main course.
Table of Primary Consumers
Okay, let’s
- bikin* (make) a table to organize this info. Here’s a breakdown of the primary consumers, including their scientific names and where they’re typically found. Remember, the locations can overlap,
- tapi* (but) this gives you a general idea.
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Geographical Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue Sheep | Pseudois nayaur | Himalayas, Tibet, Pamir Mountains | Most common prey; adapted to high altitudes. |
| Argali Sheep | Ovis ammon | Central Asia, Altai Mountains | Largest wild sheep; indicates a healthy ecosystem. |
| Ibex | Capra sibirica | Mountains of Central Asia, Siberia | Excellent climbers; important food source. |
| Markhor | Capra falconeri | Himalayas, Karakoram | Distinct spiral horns; found in mountainous regions. |
| Urial | Ovis vignei | Himalayas, Pamir Mountains | Smaller wild sheep; regional importance. |
Factors Influencing Abundance of Primary Consumers
The number of these primary consumers is
- krusial* (crucial) for the snow leopard’s survival. So, what
- bikin* (makes) their numbers go up or down?
Here are some key factors:
- Habitat Quality: If the
-tempat tinggal* (habitat) is good – plenty of grass, shrubs, and other plants – the herbivores
-bakal* (will) thrive. This is
-basic* (basic), right? Good food, happy animals. - Climate Change:
-Pemanasan global* (global warming) can change the vegetation, which can affect the herbivores’ food supply. Also, extreme weather events can be
-ngaruh* (affect) survival rates. - Competition: Herbivores compete with each other and with livestock (like goats and sheep) for food. Too much competition means less food for everyone.
- Poaching and Hunting:
-Pemburu* (poachers) and illegal hunting can drastically reduce the numbers of these animals, leading to food scarcity for the snow leopards. This is a
-masalah gede* (big problem). - Disease: Outbreaks of disease can wipe out large numbers of herbivores, which directly impacts the snow leopard.
- Predation: While snow leopards are predators, they are not the only ones. Other predators, like wolves, also hunt these herbivores, impacting their populations.
So, basically,
- banyak banget* (a lot of) things influence the abundance of the primary consumers. It’s a complex
- lingkaran* (cycle) of factors that all affect the snow leopard’s
- kehidupan* (life).
Secondary Consumers and the Snow Leopard
Ayo, kita lanjut ngobrolin soal snow leopard dan para predator lain di lingkungan mereka. Sekarang, kita bakal bahas gimana snow leopard berinteraksi sama “kawan-kawan” karnivora lainnya, cara mereka berburu, dan siapa aja sih yang jadi saingan snow leopard di alam liar. Gak pake basa-basi lagi, langsung gas aja!
Snow Leopard’s Interactions with Other Carnivores
Snow leopard itu bukan cuma jagoan di habitatnya. Mereka juga punya hubungan yang kompleks sama predator lain. Persaingan, kerjasama, bahkan kadang-kadang konflik, semua ada. Ini nih beberapa poin pentingnya:
- Persaingan: Di daerah tempat tinggal snow leopard, ada juga predator lain kayak serigala abu-abu (gray wolf), macan tutul (leopard), dan beruang coklat (brown bear). Mereka semua punya selera makan yang mirip, yaitu hewan-hewan yang jadi mangsa snow leopard. Jadi, sering banget terjadi persaingan buat dapetin makanan. Contohnya, kalau ada snow leopard berhasil ngejerat kambing gunung, predator lain bisa aja datang dan nyolong hasil buruan itu.
- Koeksistensi: Meskipun ada persaingan, snow leopard dan predator lain juga bisa hidup berdampingan. Mereka punya strategi yang beda-beda buat berburu. Misalnya, snow leopard lebih sering berburu di daerah yang tinggi dan terpencil, sementara serigala lebih suka berburu di daerah yang lebih rendah dan terbuka.
- Dominasi: Snow leopard itu predator puncak di banyak habitatnya. Artinya, mereka gak punya predator alami lain selain manusia. Tapi, mereka bisa aja kalah kalau berhadapan sama predator yang lebih besar dan kuat, kayak beruang coklat. Beruang coklat bisa mengancam snow leopard, terutama kalau mereka lagi berburu di wilayah yang sama.
Hunting Strategies: Snow Leopard vs. Other Predators
Gaya berburu snow leopard itu khas banget. Tapi, gimana sih perbandingannya sama predator lain di habitat yang sama? Mari kita bedah:
- Snow Leopard: Snow leopard itu spesialis pemburu di daerah pegunungan yang berbatu-batu. Mereka punya kemampuan lompat yang luar biasa, bisa lompat sampai 15 meter! Mereka biasanya mengintai mangsa dari tempat yang tinggi, lalu menyergap dengan cepat. Mangsa favorit mereka adalah kambing gunung, domba liar, dan marmut.
- Gray Wolf: Serigala itu pemburu yang hebat dalam kelompok. Mereka punya stamina yang kuat dan bisa mengejar mangsa jarak jauh. Strategi berburu mereka adalah mengepung dan mengejar mangsa sampai kelelahan. Serigala lebih sering memburu hewan yang lebih besar, kayak rusa atau kijang.
- Leopard: Macan tutul itu pemburu yang fleksibel. Mereka bisa berburu di berbagai macam lingkungan, dari hutan sampai padang rumput. Mereka punya kemampuan bersembunyi yang hebat dan sering menyergap mangsa dari jarak dekat. Macan tutul juga bisa memanjat pohon buat berburu atau menyimpan hasil buruan.
- Brown Bear: Beruang coklat itu predator yang kuat dan serba bisa. Mereka bisa berburu, memakan bangkai, atau bahkan makan tumbuhan. Beruang coklat punya tenaga yang besar dan bisa mengalahkan mangsa yang lebih besar dari mereka.
Secondary Consumers in the Snow Leopard’s Habitat
Nah, sekarang kita lihat siapa aja sih yang termasuk secondary consumers atau konsumen sekunder di habitat snow leopard. Mereka ini adalah predator yang makan hewan lain yang makan tumbuhan (herbivora).
- Gray Wolf: Seperti yang udah disebutin, serigala juga termasuk predator di lingkungan snow leopard.
- Leopard: Macan tutul juga seringkali menjadi saingan snow leopard.
- Eurasian Lynx: Lynx ini juga pemakan daging, meskipun ukurannya lebih kecil dari snow leopard.
- Birds of Prey: Burung pemangsa seperti elang dan rajawali juga bisa jadi pesaing dalam memburu mangsa.
- Foxes: Rubah juga termasuk dalam kelompok predator kecil di lingkungan snow leopard.
Plants and the Snow Leopard Food Web
Oke, sekarang kita ngomongin peran tumbuhan dalam dunia snow leopard, guys. Meskipun snow leopard itu karnivora alias pemakan daging, tumbuhan tetep punya peran penting banget, malah bisa dibilang krusial buat kelangsungan hidup mereka. Gak langsung sih, tapi dampaknya gede banget. Jadi, simak baik-baik ya!
Indirect Role of Plants
Tumbuhan itu kayak fondasi dari semua makanan di ekosistem. Mereka menghasilkan makanan lewat fotosintesis, kan? Nah, makanan yang dihasilkan ini jadi sumber energi buat hewan herbivora, alias pemakan tumbuhan. Hewan herbivora ini, kayak argali (domba gunung) atau ibex (kambing gunung), adalah makanan utama snow leopard. Jadi, tanpa tumbuhan yang sehat, populasi herbivora bisa anjlok, dan snow leopard bakal kekurangan makanan.
“Kesehatan tumbuhan secara langsung memengaruhi populasi konsumen primer. Kalau tumbuhan gak sehat, konsumen primer kayak herbivora bakal kekurangan makanan, populasi mereka turun, dan akhirnya berdampak ke predator puncak, yaitu snow leopard.”
Impact of Climate Change on Vegetation
Perubahan iklim, beuh, ini sih ancaman serius buat semua makhluk hidup, termasuk snow leopard. Perubahan suhu dan pola curah hujan bisa ngerusak habitat tumbuhan. Misalnya, kalau suhu makin panas, tumbuhan di dataran tinggi bisa mati atau pertumbuhannya terhambat. Hal ini bisa menyebabkan:
- Perubahan Habitat: Tumbuhan gak bisa tumbuh di tempat yang biasanya mereka tumbuh, akibatnya hewan herbivora yang bergantung pada tumbuhan tersebut juga pindah, dan snow leopard harus mencari mangsa di tempat lain.
- Berkurangnya Ketersediaan Makanan: Kalau tumbuhan gak bisa tumbuh dengan baik, populasi herbivora bakal menurun. Akibatnya, snow leopard bakal kesulitan cari makanan, dan bisa jadi populasi mereka juga menurun.
- Perubahan Pola Migrasi: Beberapa jenis herbivora mungkin akan mengubah pola migrasi mereka karena perubahan ketersediaan makanan, yang bisa bikin snow leopard kesulitan buat berburu.
Sebagai contoh nyata, penelitian di wilayah Himalaya menunjukkan bahwa perubahan iklim telah menyebabkan pergeseran vegetasi, dengan beberapa spesies tumbuhan naik ke ketinggian yang lebih tinggi. Hal ini berdampak pada ketersediaan makanan bagi herbivora, yang pada gilirannya memengaruhi populasi snow leopard di wilayah tersebut.
Decomposers and Nutrient Cycling: Snow Leopard Food Web
Aight, so we’ve seen the snow leopard do its thing, huntin’ and eatin’, and we know the plants are gettin’ their grub on too. But what happens when things die? That’s where the real MVPs come in – the decomposers. They’re the clean-up crew of the ecosystem, and they’re super important for keepin’ everything tickin’ over nicely, ya know?
Decomposers’ Role in Breaking Down Organic Matter
Decomposers are basically the ultimate recyclers. They take dead plants and animals, and break ’em down into simpler stuff. Think of it like this: a snow leopard dies, right? Its body is full of complex molecules. Decomposers, like fungi and bacteria, get to work.
They release enzymes that break down those complex molecules into simpler ones, like nutrients. This process is called decomposition, and it’s crucial for the whole ecosystem. Without it, the mountains would be piled high with dead stuff, and there’d be no nutrients for the plants to grow.Here’s the lowdown:
- Fungi: Fungi, like mushrooms and molds, are major decomposers. They secrete enzymes that break down organic matter from the outside. They’re like the secret agents of the ecosystem, workin’ silently to break down dead leaves, wood, and animal carcasses.
- Bacteria: Bacteria are another super important group. They’re microscopic, but they’re everywhere, and they’re amazing at breakin’ down organic matter. They can break down pretty much anything, from plant matter to animal waste.
- Other organisms: Besides fungi and bacteria, other critters like earthworms and insects also help with decomposition. They break down organic matter into smaller pieces, makin’ it easier for the fungi and bacteria to do their job.
Benefits of Nutrient Cycling for Plants and Animals
The whole point of decomposition ain’t just to get rid of dead stuff; it’s to recycle the nutrients. When decomposers break down organic matter, they release nutrients back into the soil. These nutrients, like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are essential for plant growth. Plants then use these nutrients to grow, and animals eat the plants, and so on. It’s a never-ending cycle, and it’s what keeps the ecosystem alive and kickin’.Here’s how it helps everyone:
- Plants: Plants get the nutrients they need to grow strong and healthy. Think of it like fertilizer, but natural and free! They get the essential building blocks for life, allowing them to photosynthesize and produce energy.
- Animals: Animals, like the ibex that the snow leopard munches on, benefit indirectly. Healthy plants mean more food for herbivores, which means more food for carnivores, like the snow leopard.
- Overall ecosystem health: Nutrient cycling keeps the soil fertile and the ecosystem balanced. It ensures that resources are available for all the organisms that live there.
Energy and Matter Flow Through the Food Web with Decomposers
So, let’s see how this all fits together in the snow leopard’s food web. Energy and matter flow through the food web in a pretty predictable way, and the decomposers are a key part of that flow.Here’s the flow:
- Sunlight: Plants, like those tough alpine grasses, capture energy from the sun through photosynthesis.
- Producers: Plants convert sunlight into energy and create their own food.
- Primary Consumers: Herbivores, like the blue sheep, eat the plants and get energy from them.
- Secondary Consumers: Carnivores, like the snow leopard, eat the herbivores and get energy from them.
- Decomposers: When any organism dies (plant or animal), decomposers break down their remains.
- Nutrient Recycling: Decomposers release nutrients back into the soil, which are then used by plants, startin’ the whole cycle all over again.
So, the energy flows from the sun to the plants, to the herbivores, to the carnivores, and then, when everything dies, the decomposers get their turn. Matter, in the form of nutrients, cycles through the whole system, makin’ sure everything keeps goin’. It’s a beautiful and complex system, all working in harmony.
Threats to the Snow Leopard Food Web
Aduh, guys, we’re talkin’ about the snow leopard food web, right? And it’s not all rainbows and sunshine up there in the mountains, sadly. There are some serious threats that are messing with this whole ecosystem. We gotta know what’s going down so we can, you know,
nge-gas* and do something about it!
Main Threats to the Snow Leopard Food Web
The snow leopard’s survival, and the survival of everything in its food web, is under serious pressure. These threats are like, a bunch ofpreman* gangin’ up on the poor snow leopard. They’re all interconnected, making the situation even more complicated.* Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: This is like, the big one. It’s where the snow leopards’ homes are getting smaller and broken up.
Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade
Sadly, snow leopards are sometimes hunted for their fur and bones.
Climate Change
This is changing the weather patterns, and that’s affecting everything, from the plants to the prey animals.
Human-Wildlife Conflict
When snow leopards go after livestock, it can lead to retaliatory killings by humans.
Overgrazing by Livestock
Too many goats and sheep can mess up the habitat and food sources.
Discover more by delving into beef wet dog food further.
Disease
Sometimes, diseases can spread and affect the snow leopards or their prey.
Impact of Habitat Loss on Prey Availability
Okay, so imagine your
- kosan* getting smaller and smaller. That’s kinda what’s happening to the snow leopard’s hunting grounds. Habitat loss is a real
- geblek* problem. It directly impacts how much food is available for the snow leopards.
The main reason is the shrinking of their natural habitat. With less space, there’s less room for wild prey like blue sheep, ibex, and argali to roam and breed. This makes it harder for snow leopards to find food, and the whole food web starts to crumble. For example, in the Himalayas, deforestation and agricultural expansion have led to a decrease in prey populations, directly impacting snow leopard numbers.
This means fewer prey animals, less food for the snow leopards, and a weaker food web overall.
Conservation Efforts for the Snow Leopard Food Web
Alright, so what can we do? There are some solid efforts being made to protect the snow leopard and its food web. It’s like, the
kreatif* people are stepping up!
Here are some things being done:* Protected Areas and Habitat Preservation: Creating national parks and reserves where snow leopards and their prey can thrive, like the Annapurna Conservation Area in Nepal. This protects crucial habitats.
Anti-Poaching Patrols and Law Enforcement
Stopping the illegal hunting of snow leopards and their prey is a must. Increased patrolling and stricter penalties are crucial.
Community-Based Conservation
Involving local communities in conservation efforts. They help protect the snow leopards and their prey. For instance, communities in Mongolia are trained to track and monitor snow leopards.
Reducing Human-Wildlife Conflict
Implementing programs that help protect livestock from snow leopards. This includes livestock insurance programs and predator-proof corrals.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Tackling climate change is essential for protecting the snow leopard’s habitat.
Sustainable Land Management
Promoting sustainable grazing practices and reducing overgrazing to protect the habitat.
Monitoring and Research
Scientists are constantly studying snow leopards and their environment. This helps us understand the threats and find better solutions.
International Collaboration
Working with different countries and organizations to protect snow leopards across their range. This involves sharing knowledge and resources.
Adaptations for Hunting and Survival
Oke, jadi urusan snow leopard mah, mereka tuh jago pisan buat bertahan hidup di tempat yang keras. Adaptasi mereka tuh keren, dari fisik sampe tingkah lakunya, semuanya dirancang buat jadi pemburu ulung. Penasaran kan gimana caranya mereka bisa survive di lingkungan yang ekstrem? Yuk, kita bahas!
Physical Adaptations for Hunting
Snow leopard mah punya beberapa keunggulan fisik yang bikin mereka jadi predator yang mematikan. Tubuh mereka tuh emang didesain buat berburu di medan yang susah.
- Bulu Tebal dan Padat: Ini mah bukan cuma buat gaya, bulu tebal mereka tuh kayak jaket hangat yang melindungi dari suhu dingin ekstrem di pegunungan. Bahkan, bulu di kaki mereka juga tebal, biar bisa jalan di salju tanpa kelelep.
- Ekor Panjang dan Berotot: Ekor panjang ini bukan cuma buat keseimbangan doang pas mereka manjat tebing atau ngejar mangsa. Ekornya juga bisa dipake buat selimut pas tidur, biar anget.
- Kaki Lebar: Kaki mereka lebar kayak sepatu salju, jadi mereka gak gampang kelelep di salju yang dalam. Cengkraman kukunya juga kuat banget buat manjat tebing yang curam.
- Mata yang Tajam: Mata snow leopard tuh adaptasi yang paling penting. Mereka punya penglihatan yang super tajam, bahkan di kegelapan. Ini penting banget buat ngeliat mangsa dari jarak jauh, di tengah medan yang susah.
- Lubang Hidung Besar: Lubang hidung mereka besar buat ngambil oksigen lebih banyak di dataran tinggi yang udaranya tipis.
Behavioral Adaptations for Hunting
Gak cuma fisik, tingkah laku snow leopard juga udah disesuaikan buat berburu. Mereka punya strategi yang jitu banget.
- Penyergapan: Snow leopard tuh pemburu penyergap. Mereka sering ngendap-ngendap deket tebing atau bebatuan, terus nyerang mangsa dari jarak dekat.
- Kemampuan Memanjat: Mereka jago manjat, bisa manjat tebing curam buat nyari mangsa atau ngumpet dari bahaya.
- Berburu Sendirian: Biasanya, snow leopard berburu sendirian, kecuali pas musim kawin atau pas ngurus anak.
- Waktu Berburu: Mereka aktif berburu pas pagi atau sore hari, pas mangsa mereka juga lagi aktif.
Hunting Success Rates in Different Environments
Tingkat keberhasilan berburu snow leopard tuh beda-beda, tergantung lingkungannya. Faktor-faktor kayak ketersediaan mangsa, kondisi medan, dan interaksi sama predator lain, ngaruh banget.
- Dataran Tinggi: Di dataran tinggi Himalaya, tempat tinggal utama mereka, snow leopard berburu mangsa kayak argali, ibex, sama marmut. Tingkat keberhasilan mereka lebih tinggi di daerah yang mangsanya banyak.
- Kawasan Lindung: Di kawasan lindung, di mana aktivitas manusia dibatasi, snow leopard cenderung lebih sukses berburu karena mangsa mereka lebih aman.
- Daerah yang Terganggu: Di daerah yang banyak manusia atau ada perburuan liar, tingkat keberhasilan snow leopard bisa turun drastis karena mangsanya berkurang atau mereka lebih sering menghindari manusia.
Hunting Techniques of Snow Leopards
Snow leopard punya teknik berburu yang spesifik, disesuaikan sama jenis mangsa dan kondisi lingkungannya.
- Pendekatan: Mereka mendekati mangsa secara diam-diam, memanfaatkan medan buat ngumpet. Mereka bisa ngendap-ngendap di balik batu, di semak-semak, atau di balik tebing.
- Penyergapan: Begitu udah deket, mereka nyerang dengan kecepatan tinggi, biasanya dengan sekali terkam.
- Gigitan di Leher: Snow leopard sering menggigit leher mangsa buat langsung bikin lumpuh atau bahkan ngebunuh.
- Memanfaatkan Keunggulan Fisik: Mereka manfaatin kekuatan, kelincahan, dan penglihatan tajam mereka buat ngejar, nyergap, dan ngebunuh mangsa.
Geographic Variations in the Food Web
Ayo, gengs! The snow leopard’s a real traveler, right? They don’t just chill in one spot. Their food web is like a big, diversenasi campur*, changing depending on where they’re located. From the Himalayas to the Altai Mountains, the menu for this majestic cat is never the same. Let’s dive into how the snow leopard’s diet and the whole food web around it switch things up depending on the area.
Prey Species Variations
The snow leopard’s diet is pretty flexible, but what they eat really depends on what’s available. This means the main course changes depending on where the snow leopard hangs out. Some areas have specific prey that are basically the snow leopard’s go-to meal, while in other places, it’s a whole different story.
Here’s a table to show you the different
-lauk pauk* (dishes) the snow leopard enjoys across different regions:
| Region | Common Prey Species | Additional Prey Species | Key Environmental Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Himalayas (Nepal, India, Bhutan) | Blue Sheep (Bharal) | Argali Sheep, Himalayan Tahr, Marmots, Pikas | Steep terrain, high altitude, sparse vegetation |
| Altai Mountains (Russia, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, China) | Siberian Ibex | Argali Sheep, Red Deer, Roe Deer, Marmots | Open grasslands, rocky slopes, colder climate |
| Tian Shan Mountains (Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, China) | Siberian Ibex, Marco Polo Sheep | Argali Sheep, Wild Boar, Marmots | Varied terrain, presence of glaciers, seasonal changes |
| Pamir Mountains (Tajikistan, Afghanistan, China) | Marco Polo Sheep | Argali Sheep, Siberian Ibex, Pikas | High altitude, extreme temperatures, limited resources |
As you can see, the
-isi* (contents) of the snow leopard’s diet really varies! The Blue Sheep is super important in the Himalayas, while the Siberian Ibex is a big deal in the Altai and Tian Shan. The Marco Polo Sheep is a main course in the Pamirs. These differences show how adaptable the snow leopard is and how it can survive in different environments, always hunting the most available prey.
The Impact of Humans
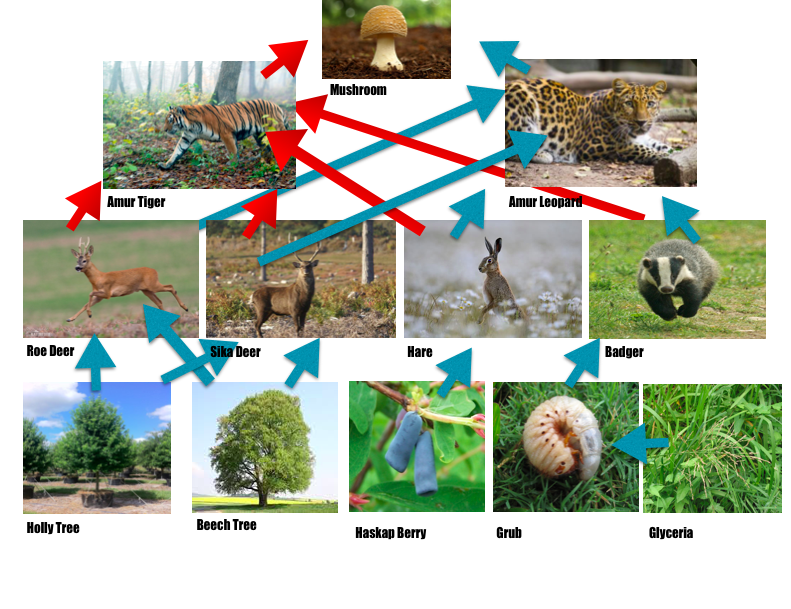
Aduh, manusia emang bisa bikin kacau balau, termasuk urusan makanan macan salju. Aktivitas kita, dari yang kecil sampe yang gede, punya efek domino yang bisa ngerusak ekosistem tempat mereka tinggal. Mari kita bahas satu-satu, ya, biar makin ngarti.
Effects of Poaching on Snow Leopard Populations
Poaching, alias perburuan liar, itu kayak kanker buat populasi macan salju. Gara-gara manusia serakah, macan salju jadi makin langka. Ini bukan cuma soal ngurangin jumlah macan, tapi juga ngerusak keseimbangan alam.
- Penurunan Populasi: Ya iyalah, macan salju ditembak, otomatis jumlahnya berkurang. Ini bisa bikin populasi mereka jadi kecil banget, gampang kena penyakit, dan susah berkembang biak.
- Gangguan Keseimbangan Ekosistem: Macan salju kan predator puncak. Kalo mereka ilang, populasi mangsanya (kayak kambing liar, domba, dll.) bisa meledak. Akibatnya, tumbuhan yang dimakan mangsa juga jadi berkurang, dan seterusnya. Rantai makanan jadi nggak stabil.
- Perubahan Genetik: Kalo populasi macan salju kecil, variasi genetiknya juga berkurang. Ini bikin mereka lebih rentan terhadap penyakit dan perubahan lingkungan. Kayak keluarga, kalau cuma punya sedikit anggota, ya gampang banget kena masalah.
- Perdagangan Gelap: Poaching seringkali terkait sama perdagangan ilegal. Kulit, tulang, dan bagian tubuh macan salju punya harga tinggi di pasar gelap. Ini yang bikin pemburu makin semangat ngejar macan salju.
How Human Activities Like Climate Change Affect the Food Web
Selain poaching, perubahan iklim juga jadi ancaman serius. Aktivitas manusia, terutama yang bikin polusi, memperparah masalah ini. Efeknya, nggak cuma buat macan salju, tapi juga buat semua yang ada di ekosistem mereka.
- Perubahan Habitat: Pemanasan global bikin gunung-gunung mencair, dan pola curah hujan berubah. Ini bisa ngerubah habitat macan salju, bikin mereka susah nyari makanan dan tempat tinggal.
- Perubahan Distribusi Mangsa: Mangsa macan salju (kayak kambing liar) juga terpengaruh sama perubahan iklim. Mereka bisa berpindah tempat, atau jumlahnya berkurang. Akibatnya, macan salju jadi susah nyari makan.
- Penyakit dan Wabah: Perubahan iklim bisa bikin penyakit dan wabah lebih gampang nyebar. Ini bisa nyerang macan salju, mangsanya, atau bahkan tumbuhan yang jadi sumber makanan.
- Dampak Terhadap Tumbuhan: Perubahan iklim juga ngerusak tumbuhan. Kalo tumbuhan nggak tumbuh subur, mangsa macan salju juga nggak punya makanan. Akibatnya, rantai makanan makin terganggu.
“Perubahan iklim itu kayak tsunami buat ekosistem. Semuanya kena dampaknya.”
Summary
In conclusion, the snow leopard food web is a compelling illustration of nature’s interconnectedness and fragility. From the apex predator to the smallest decomposer, each element plays a vital role in the delicate balance of this unique ecosystem. The threats facing the snow leopard food web, largely stemming from human activities, underscore the urgent need for conservation efforts. Protecting the snow leopard and its habitat is not merely about saving a single species; it is about safeguarding the health and resilience of an entire world, a world whose fate is inextricably linked to the survival of the “ghost of the mountains.”


