Alright, let’s talk about your amazing uterus! 💖 We’re diving deep into foods good for uterus and how your diet can be a game-changer for your reproductive health. It’s more than just what you eat; it’s about fueling your body with the right nutrients to keep things running smoothly. Think of your uterus as a powerhouse, and food as the fuel. 🚀
From understanding the basics of uterine function to tackling common issues like PMS and hormonal imbalances, we’ll explore a delicious array of foods packed with the nutrients your body craves. Iron, folate, anti-inflammatory heroes, and fiber-rich goodies are all on the menu. Plus, we’ll uncover the sneaky foods that might be hindering your progress and how to create a balanced diet for optimal uterine wellness.
🥗
Understanding Uterine Health and Diet
The uterus, a vital organ in the female reproductive system, plays a crucial role in menstruation, pregnancy, and childbirth. Its health is intrinsically linked to overall well-being, and a balanced diet can significantly contribute to its proper function and resilience. Neglecting uterine health can lead to various complications, emphasizing the importance of proactive care through lifestyle choices, including dietary adjustments.Maintaining a healthy diet is paramount for uterine health, as it provides essential nutrients that support the organ’s functions and protect against potential ailments.
Dietary choices can directly impact hormone balance, inflammation levels, and the overall health of the uterine lining and tissues. By incorporating specific foods and avoiding others, individuals can proactively address common uterine health concerns and improve their reproductive well-being.
Common Uterine Health Concerns Addressed by Diet
Dietary modifications can play a significant role in managing and preventing several uterine health issues. These concerns often stem from hormonal imbalances, inflammation, and nutrient deficiencies. A strategic dietary approach can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall uterine health.
Managing Endometriosis through Dietary Changes
Endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often causes pain, heavy bleeding, and infertility. Diet plays a crucial role in managing its symptoms.
- Reducing the intake of inflammatory foods: This includes processed foods, red meat, and excessive amounts of sugar. These foods can exacerbate inflammation, worsening endometriosis symptoms.
- Increasing the consumption of anti-inflammatory foods: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, and walnuts, can help reduce inflammation.
- Including plenty of fruits and vegetables: These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and reduce inflammation. For example, berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) are packed with antioxidants.
- Considering a gluten-free diet: Some women with endometriosis find that eliminating gluten reduces their symptoms. While not universally effective, it’s a dietary change worth considering.
Addressing Uterine Fibroids with Dietary Adjustments
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths in the uterus. Dietary choices can influence their growth and symptoms.
- Limiting red meat and processed foods: Studies suggest that a high intake of red meat may be linked to an increased risk of fibroids. Processed foods often contain additives that can disrupt hormone balance.
- Consuming a diet rich in fruits and vegetables: These foods provide essential nutrients and antioxidants, supporting overall health and potentially slowing fibroid growth.
- Incorporating cruciferous vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain compounds that can help regulate estrogen levels, which may be beneficial for fibroid management.
- Increasing fiber intake: Fiber helps to eliminate excess estrogen from the body, which may contribute to fibroid growth. Good sources include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Dietary Support for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Uterine Health
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can affect uterine health, often leading to irregular periods and fertility issues. Diet is a key component of PCOS management.
- Following a low-glycemic index (GI) diet: This helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance, a common issue in PCOS. Foods with a low GI include non-starchy vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Prioritizing lean protein: Protein helps stabilize blood sugar levels and promotes satiety. Good sources include fish, poultry, beans, and lentils.
- Limiting processed carbohydrates and sugary drinks: These foods can worsen insulin resistance and contribute to weight gain, which can exacerbate PCOS symptoms.
- Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids: These fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity.
Dietary Considerations for Menstrual Health
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining regular and healthy menstrual cycles.
- Ensuring adequate iron intake: Heavy menstrual bleeding can lead to iron deficiency anemia. Consuming iron-rich foods like red meat, spinach, and lentils is crucial.
- Including calcium and vitamin D: These nutrients are essential for bone health and may help alleviate premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms. Dairy products, fortified foods, and sunlight exposure are good sources.
- Reducing caffeine and alcohol consumption: These substances can worsen PMS symptoms and disrupt hormone balance.
- Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains: This provides essential nutrients that support overall health and menstrual regularity.
Nutrient-Rich Foods for Uterine Wellness
Maintaining a healthy uterus is crucial for overall reproductive health and well-being. A balanced diet plays a significant role in supporting uterine function and preventing potential complications. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods into your daily meals can provide the essential building blocks for a healthy uterus. This section will delve into specific nutrients vital for uterine health and the foods that provide them.
Essential Nutrients for Uterine Health
Certain nutrients are particularly important for supporting the uterus. These nutrients contribute to various aspects of uterine health, from maintaining the uterine lining to preventing oxidative stress. Deficiencies in these nutrients can potentially lead to reproductive health issues.
Iron’s Role in Uterine Function
Iron is a vital mineral for overall health, particularly for women, as it plays a crucial role in blood production. During menstruation, the uterus sheds its lining, leading to blood loss. Adequate iron intake helps replenish this loss, preventing anemia and ensuring the uterus receives sufficient oxygen. Iron deficiency can lead to fatigue, weakness, and irregular menstrual cycles.Foods rich in iron include:
| Food Name | Nutrient | Benefit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spinach | Iron | Supports blood production and prevents anemia, crucial for uterine health during menstruation. | Leafy green vegetable |
| Lentils | Iron | A good source of iron, aiding in the replenishment of blood lost during menstruation. | Legume |
| Red Meat (lean) | Iron | Provides heme iron, which is easily absorbed by the body, supporting red blood cell production. | Beef, lamb |
| Fortified Cereals | Iron | Offers a convenient way to boost iron intake, especially for those with dietary restrictions. | Breakfast cereals |
Folate’s Significance for Uterine Health
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is crucial for cell growth and development, especially during periods of rapid cell division. It is particularly important for women of childbearing age, as it plays a vital role in preventing neural tube defects in developing fetuses. Folate also contributes to maintaining a healthy uterine lining and supports overall reproductive health.Foods rich in folate include:
| Food Name | Nutrient | Benefit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spinach | Folate | Supports cell growth and development, essential for a healthy uterine lining. | Leafy green vegetable |
| Broccoli | Folate | Contributes to cell growth and development, supporting overall reproductive health. | Cruciferous vegetable |
| Avocado | Folate | Supports cell growth and development, contributing to a healthy uterine environment. | Fruit |
| Beans (e.g., black beans, kidney beans) | Folate | Provides a good source of folate, supporting cell division and overall reproductive health. | Legume |
Vitamin C’s Contribution to Uterine Health
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. It plays a role in collagen production, which is essential for maintaining the strength and integrity of tissues throughout the body, including the uterus. Vitamin C also aids in iron absorption, enhancing the benefits of iron-rich foods.Foods rich in vitamin C include:
| Food Name | Nutrient | Benefit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oranges | Vitamin C | Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage and supporting overall uterine health. | Citrus fruit |
| Strawberries | Vitamin C | Aids in collagen production, contributing to the health of uterine tissues. | Berry |
| Bell Peppers (especially red) | Vitamin C | Supports collagen production, vital for the structural integrity of the uterus. | Vegetable |
| Kiwi | Vitamin C | Boosts the immune system and supports overall health, including reproductive health. | Fruit |
Anti-Inflammatory Foods and Their Benefits: Foods Good For Uterus
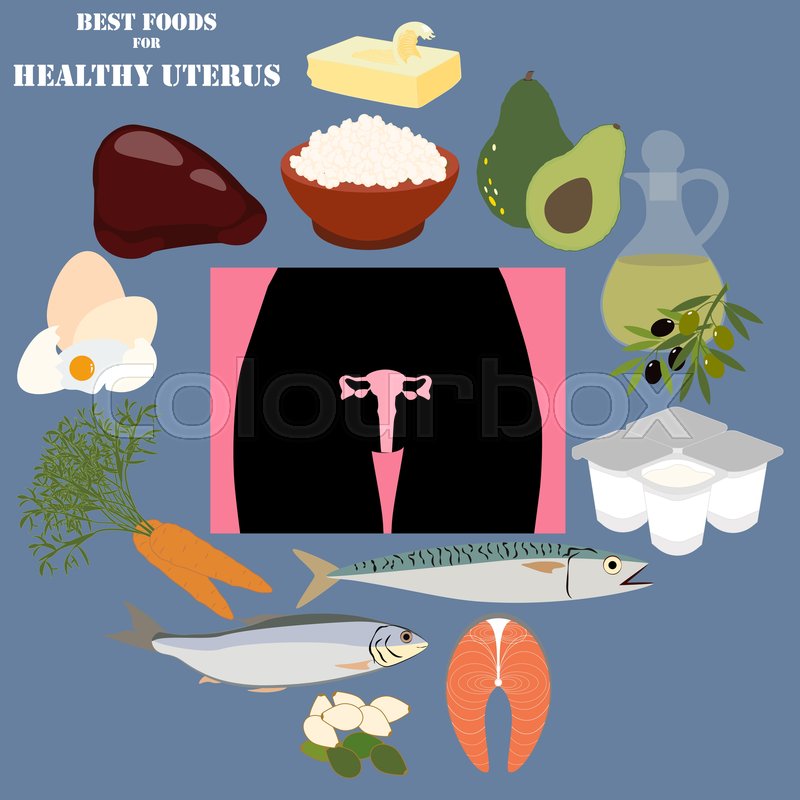
Inflammation plays a significant role in various uterine health issues. Chronic inflammation can exacerbate existing conditions and contribute to the development of new ones. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can be a proactive approach to supporting uterine wellness and mitigating symptoms associated with inflammatory conditions.
The Role of Inflammation in Uterine Health Issues, Foods good for uterus
Inflammation is a natural immune response, but chronic inflammation can damage tissues and organs. In the context of uterine health, chronic inflammation can contribute to various conditions. Endometriosis, for example, is characterized by inflammation as endometrial-like tissue grows outside the uterus. Fibroids, while benign tumors, can also trigger inflammatory responses within the uterus. Furthermore, inflammation can worsen symptoms associated with these and other uterine conditions, including pain, heavy bleeding, and irregular cycles.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods That Reduce Inflammation in the Uterus
Consuming a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce inflammation and support overall uterine health. These foods contain compounds that counteract inflammatory processes within the body. Here are some examples:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA. These fatty acids have potent anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce inflammation throughout the body, including the uterus. For instance, a study published in the “American Journal of Clinical Nutrition” found that increased intake of omega-3 fatty acids was associated with a reduction in pain and inflammation in women with endometriosis.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and other berries are packed with antioxidants, including anthocyanins, which give them their vibrant colors. Antioxidants help combat free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, a key contributor to inflammation. Research has shown that consuming berries can help reduce inflammatory markers in the body.
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They contain compounds like sulforaphane, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. A diet rich in leafy greens can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is a staple of the Mediterranean diet and is rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, including oleocanthal. Oleocanthal has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties similar to ibuprofen. Using olive oil as a primary cooking oil can help reduce inflammation.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are good sources of healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. They can help reduce inflammation and provide essential nutrients for overall health. For example, flaxseeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and can help alleviate inflammation.
- Turmeric: This spice contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound. Curcumin has been shown to reduce inflammation and pain in various studies. Adding turmeric to your diet can be beneficial for overall health and can help manage inflammatory conditions.
How These Foods Help Alleviate Symptoms of Conditions Like Endometriosis or Fibroids
Anti-inflammatory foods can provide significant relief from symptoms associated with uterine conditions like endometriosis and fibroids. By reducing inflammation, these foods can help:
- Reduce Pain: Inflammation is a major contributor to pain in conditions like endometriosis and fibroids. Anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce the inflammatory response, thereby decreasing pain levels.
- Lessen Heavy Bleeding: Inflammation can exacerbate heavy menstrual bleeding. By reducing inflammation, these foods can help regulate bleeding and improve overall menstrual health.
- Improve Cycle Regularity: Inflammation can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to irregular menstrual cycles. An anti-inflammatory diet can help regulate hormonal levels and improve cycle regularity.
- Support Overall Health: Anti-inflammatory foods are rich in essential nutrients that support overall health and well-being. They provide the body with the resources it needs to heal and function optimally.
Foods to Support Hormonal Balance
Maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for overall health, particularly for women. Diet plays a significant role in regulating hormones, influencing everything from menstrual cycles to mood. By incorporating specific foods into your diet, you can support hormonal equilibrium and potentially alleviate related symptoms.
Diet and Hormonal Regulation
The food we consume directly impacts hormone production and function. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone, vital for the female reproductive system, are particularly susceptible to dietary influences. Estrogen, produced primarily in the ovaries, regulates the menstrual cycle and influences secondary sexual characteristics. Progesterone, also produced in the ovaries, prepares the uterine lining for potential pregnancy and maintains it throughout the first trimester.
A diet lacking essential nutrients can disrupt the delicate balance of these hormones, leading to irregular periods, mood swings, and other health issues. Conversely, a diet rich in certain nutrients can help support the production and function of these hormones, promoting a healthier hormonal environment.
Foods that Help Balance Hormone Levels
Certain foods contain nutrients that can support hormone balance. These foods work in various ways, such as providing precursors for hormone synthesis, supporting liver function (which helps metabolize hormones), and reducing inflammation.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and kale are rich in indole-3-carbinol (I3C). I3C helps the liver detoxify excess estrogen, which can lead to hormonal imbalances.
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds are a good source of lignans, which have estrogenic properties. Lignans can help regulate estrogen levels by binding to estrogen receptors, potentially reducing the risk of estrogen-related cancers and alleviating PMS symptoms.
- Avocados: Avocados are packed with healthy fats, which are essential for hormone production. They also contain nutrients that support overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation and support hormone production. Omega-3s can also improve mood and reduce symptoms of PMS.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds are excellent sources of healthy fats, protein, and fiber. They contribute to hormone balance by providing essential nutrients and supporting overall health.
Impact on the Menstrual Cycle and PMS Symptoms
Consuming these foods can have a positive impact on the menstrual cycle and reduce PMS symptoms. For example, the fiber in flaxseeds can help regulate blood sugar levels, which can reduce mood swings and cravings associated with PMS. The anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 fatty acids in fatty fish can alleviate cramps and other inflammatory symptoms.
- Regularity of Cycles: A balanced diet can help regulate the menstrual cycle, leading to more predictable periods. For instance, women who incorporate sufficient amounts of healthy fats and fiber may experience fewer irregularities.
- Reduced PMS Symptoms: Foods that support hormonal balance can significantly reduce the severity of PMS symptoms. For example, magnesium-rich foods, such as nuts and seeds, can help reduce bloating and mood swings.
- Improved Mood: The nutrients in these foods can improve mood and reduce anxiety and depression often associated with hormonal fluctuations. Studies have shown a correlation between omega-3 intake and improved mood in women experiencing PMS.
Fiber-Rich Foods for Uterine Health
Fiber plays a crucial, often underestimated, role in maintaining uterine health. Its impact extends beyond digestive wellness, significantly influencing the body’s detoxification processes and hormonal balance. A diet rich in fiber can be a powerful ally in promoting a healthy uterus and reducing the risk of certain uterine conditions.
The Role of Fiber in Detoxification and Uterine Health
Fiber acts as a natural detoxifier, aiding in the elimination of waste and toxins from the body. This is particularly important for the uterus, as it helps remove excess hormones, such as estrogen, which can contribute to the development of uterine fibroids and other issues if not properly metabolized and excreted. By binding to these hormones in the digestive tract, fiber prevents their reabsorption, facilitating their removal through bowel movements.
This detoxification process supports overall uterine health and reduces the risk of hormone-related imbalances.
Fiber-Rich Foods Beneficial for the Uterus
Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet is a simple yet effective way to support uterine health. Here are some excellent sources of fiber:
- Fruits: Apples, berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), pears, and dried fruits like prunes and figs are excellent sources of fiber and various vitamins and antioxidants that support overall health.
- Vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, artichokes, and leafy greens (spinach, kale) provide substantial fiber along with essential nutrients. For instance, a cup of cooked Brussels sprouts contains approximately 4 grams of fiber.
- Legumes: Lentils, beans (black beans, kidney beans, chickpeas), and peas are packed with fiber and protein, contributing to a feeling of fullness and aiding in digestive regularity. A single cup of cooked lentils can offer around 16 grams of fiber.
- Whole Grains: Oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread offer significant fiber content. Choosing whole grains over refined grains is a crucial step in boosting fiber intake. For example, a cup of cooked quinoa contains about 5 grams of fiber.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, flax seeds, and walnuts are fiber-rich additions to the diet, also providing healthy fats and other essential nutrients. A handful of almonds (approximately 1 ounce) provides about 3.5 grams of fiber.
How Fiber Aids in Eliminating Excess Hormones and Promoting Reproductive Well-being
Fiber’s ability to bind to excess hormones, particularly estrogen, is key to its benefits for uterine health.
By promoting regular bowel movements, fiber ensures that these hormones are efficiently eliminated from the body, preventing their reabsorption and minimizing the risk of hormone-related imbalances.
This process can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce the severity of premenstrual symptoms, and potentially lower the risk of conditions like uterine fibroids and endometriosis. The consistent consumption of fiber-rich foods, combined with other healthy lifestyle choices, contributes significantly to overall reproductive well-being.
Foods to Avoid for Uterine Health
While a nutrient-rich diet is crucial for uterine wellness, certain foods can negatively impact uterine health and potentially exacerbate existing conditions. Understanding which foods to limit or avoid is essential for maintaining optimal reproductive health and minimizing inflammation. Making informed dietary choices is a proactive step towards supporting a healthy uterus.
Foods That Can Negatively Impact Uterine Health
Some foods are associated with increased inflammation, hormonal imbalances, and other factors that can contribute to uterine issues. These foods can worsen symptoms of conditions like endometriosis, fibroids, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). It’s important to note that individual sensitivities can vary, and the impact of these foods may differ from person to person. However, generally, limiting these items can be beneficial.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
The following foods are often associated with negative impacts on uterine health. It’s recommended to reduce their consumption or eliminate them from your diet to promote uterine wellness.
- Processed Foods: These foods often contain high levels of unhealthy fats, added sugars, and sodium, which can contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances. Examples include:
- Fast food
- Packaged snacks (chips, cookies, crackers)
- Processed meats (bacon, sausage, deli meats)
- Sugary Drinks and Added Sugars: Excessive sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance and inflammation, potentially exacerbating uterine conditions.
- Sugary sodas and juices
- Candy and desserts
- Processed foods with added sugars
- Excessive Red Meat: Some studies suggest a link between high red meat consumption and increased risk of certain uterine conditions, such as fibroids.
- Beef
- Pork
- Lamb
- Dairy Products (for some individuals): Dairy products can sometimes worsen inflammation in certain individuals, particularly those with sensitivities or allergies. Some women find that limiting dairy products helps alleviate symptoms related to uterine health.
- Milk
- Cheese
- Yogurt
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt hormonal balance and increase inflammation.
- Beer
- Wine
- Spirits
- Caffeine (in excess): While moderate caffeine intake is generally safe, excessive consumption can potentially worsen symptoms for some women with uterine issues.
- Coffee
- Energy drinks
- Some teas
- Foods High in Trans Fats: Trans fats are known to be highly inflammatory and can negatively impact overall health, including reproductive health.
- Fried foods
- Processed baked goods
- Some margarine and shortening
Recipes and Meal Planning for Uterine Health
A well-planned diet can significantly contribute to uterine health, offering vital nutrients and minimizing inflammation. This section provides a 3-day meal plan, complete with recipes, to support uterine wellness. These meals incorporate the nutrient-rich and anti-inflammatory foods discussed earlier, promoting hormonal balance and overall reproductive health.
3-Day Meal Plan for Uterine Wellness
This meal plan provides a balanced approach, focusing on diverse nutrient intake across three days. It’s designed to be flexible; feel free to adjust portion sizes based on individual needs and preferences. Remember to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Day 1: Focusing on Fiber and Iron
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with Berries and Flaxseeds. Oatmeal provides soluble fiber, crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and supporting hormonal balance. Berries offer antioxidants, while flaxseeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
Recipe: Combine 1/2 cup of rolled oats with 1 cup of water or unsweetened almond milk in a saucepan. Cook over medium heat until the oats are soft, approximately 5-7 minutes. Stir in 1/4 cup of mixed berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) and 1 tablespoon of ground flaxseeds. Sweeten with a touch of honey or maple syrup if desired.
Image Description: A bowl of creamy oatmeal, speckled with vibrant red strawberries, deep blue blueberries, and ruby-red raspberries. The texture is smooth and slightly glossy. The flaxseeds, tiny and brown, are scattered throughout. The presentation is simple, showcasing the natural colors of the ingredients.
- Lunch: Lentil Soup with a Side Salad. Lentils are a powerhouse of iron and fiber, essential for preventing iron-deficiency anemia, which can exacerbate menstrual issues. The salad adds a variety of vitamins and minerals.
Recipe: Sauté 1 chopped onion, 2 cloves of minced garlic, and 1 chopped carrot in olive oil. Add 1 cup of brown lentils, 4 cups of vegetable broth, and spices like cumin and turmeric. Simmer until lentils are tender (about 30 minutes). Serve with a side salad of mixed greens, cucumber, and a light vinaigrette.
Image Description: A hearty, reddish-brown lentil soup fills a bowl. Visible chunks of carrots and onions are scattered throughout. The soup’s texture is thick and slightly chunky. Beside it, a fresh green salad with bright green leaves and colorful vegetables. The presentation is rustic and wholesome.
- Dinner: Baked Salmon with Roasted Broccoli and Quinoa. Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, crucial for reducing inflammation. Broccoli and quinoa provide fiber and various nutrients.
Recipe: Season salmon fillets with salt, pepper, and lemon juice. Bake at 375°F (190°C) for 12-15 minutes, or until cooked through. Toss broccoli florets with olive oil and roast alongside the salmon until tender. Cook quinoa according to package directions. Serve together.
Notice tiki dog food dry for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Image Description: A flaky, light pink salmon fillet sits on a plate. Alongside it are bright green roasted broccoli florets, slightly charred around the edges. A bed of fluffy, white quinoa provides a neutral base. The presentation is elegant, highlighting the natural colors of the ingredients.
Day 2: Emphasizing Anti-Inflammatory Foods
- Breakfast: Smoothie with Spinach, Banana, and Almond Butter. This smoothie incorporates leafy greens, which are nutrient-dense, along with healthy fats from almond butter.
Recipe: Blend 1 cup of spinach, 1 banana, 1 tablespoon of almond butter, and 1/2 cup of unsweetened almond milk until smooth. Add ice for a thicker consistency.
Image Description: A tall, vibrant green smoothie in a glass. The texture is smooth and slightly opaque. Hints of the banana’s creamy yellow are visible. The glass is filled to the brim, with a few drips of the smoothie visible on the outside. The presentation is refreshing and inviting.
- Lunch: Chicken Salad with Avocado on Whole-Wheat Bread. Avocado provides healthy fats and chicken provides lean protein, both contributing to overall health. Whole-wheat bread offers fiber.
Recipe: Combine cooked chicken (shredded or diced) with diced avocado, a squeeze of lemon juice, and a pinch of salt and pepper. Serve on whole-wheat bread. Add a side of sliced tomatoes and cucumbers.
Image Description: Two slices of whole-wheat bread sandwich a creamy, green chicken salad. Visible pieces of avocado and chicken are mixed within the salad. Beside the sandwich, sliced red tomatoes and green cucumbers create a colorful contrast. The presentation is simple and appealing.
- Dinner: Stir-fry with Tofu, Vegetables, and Brown Rice. Tofu is a good source of plant-based protein, and the vegetables provide essential vitamins and minerals. Brown rice adds fiber.
Recipe: Stir-fry cubed tofu with a variety of colorful vegetables (broccoli, bell peppers, carrots, snap peas) in a wok or large pan with a little sesame oil. Season with soy sauce or tamari. Serve over cooked brown rice.
Image Description: A vibrant stir-fry with a variety of colorful vegetables (green broccoli florets, red bell pepper slices, orange carrot sticks, and green snap peas) and tofu cubes, coated in a light brown sauce. The presentation is on a bed of fluffy brown rice. The presentation is visually appealing, showcasing the freshness of the ingredients.
Day 3: Prioritizing Hormonal Balance
- Breakfast: Greek Yogurt with Berries and Walnuts. Greek yogurt provides protein, berries offer antioxidants, and walnuts provide healthy fats.
Recipe: Combine 1 cup of plain Greek yogurt with 1/4 cup of mixed berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) and a handful of walnuts.
Image Description: A bowl of creamy white Greek yogurt, speckled with red strawberries, deep blue blueberries, and ruby-red raspberries. The walnuts are scattered on top, adding a touch of brown and texture. The presentation is clean and fresh, highlighting the natural colors of the ingredients.
- Lunch: Salad with Chickpeas, Cucumber, and Lemon Vinaigrette. Chickpeas are a good source of fiber and protein, supporting hormonal balance.
Recipe: Combine chickpeas, chopped cucumber, red onion, and fresh parsley. Dress with a simple lemon vinaigrette (olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper).
Image Description: A refreshing salad featuring light-colored chickpeas, green cucumber slices, and red onion slivers. The presentation is tossed in a light dressing. The overall look is clean and inviting.
- Dinner: Turkey Meatloaf with Roasted Sweet Potatoes and Green Beans. Turkey is a lean protein source, sweet potatoes provide vitamins and fiber, and green beans offer essential nutrients.
Recipe: Prepare turkey meatloaf using lean ground turkey, breadcrumbs, onion, garlic, and spices. Bake at 350°F (175°C). Roast sweet potato cubes and green beans with olive oil and seasonings. Serve together.
Image Description: A slice of a golden-brown turkey meatloaf sits next to roasted orange sweet potato cubes and vibrant green beans. The meatloaf has a slightly crusty exterior and a moist interior. The sweet potatoes are slightly caramelized, and the green beans are tender-crisp. The presentation is hearty and comforting.
Hydration and Uterine Health
Maintaining optimal uterine health involves a holistic approach, and a crucial element often overlooked is adequate hydration. Water plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, and its significance extends to the well-being of the uterus. Proper hydration supports cellular function, hormonal balance, and the overall health of the reproductive system. Dehydration can exacerbate existing issues and hinder the body’s ability to function optimally.
Importance of Adequate Hydration for Uterine Function
Hydration is essential for various physiological processes that directly impact uterine health. The uterus, like all organs, requires sufficient fluids to function efficiently. Water aids in nutrient transport, waste removal, and maintaining the delicate balance of fluids within the reproductive system.Water helps in:
- Supporting Cellular Function: The uterus is composed of cells that require water to function properly. Hydration ensures these cells receive the necessary nutrients and can efficiently remove waste products.
- Maintaining Hormonal Balance: Water plays a role in the production and regulation of hormones, including those crucial for the menstrual cycle. Dehydration can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to irregular periods or other hormonal imbalances.
- Facilitating Waste Removal: Adequate hydration supports the kidneys and liver in removing toxins and waste products from the body. This detoxification process is essential for overall health, including the health of the uterus.
- Preventing Constipation: Constipation can put pressure on the uterus. Proper hydration softens stools and promotes regular bowel movements, alleviating this pressure.
- Reducing Inflammation: Water can help reduce inflammation throughout the body, including in the uterus. Chronic inflammation is linked to various reproductive health issues.
Benefits of Water and Herbal Teas for Uterine Health
Water is the primary and most essential source of hydration, but incorporating herbal teas can offer additional benefits for uterine health. Certain herbs possess properties that may support reproductive health, reduce inflammation, and promote hormonal balance.
- Water: Plain water is the cornerstone of hydration. It delivers essential nutrients to cells, aids in waste removal, and supports optimal uterine function. Consuming sufficient water throughout the day is the most fundamental step in maintaining uterine health.
- Herbal Teas: Several herbal teas are known for their potential benefits to the reproductive system. Examples include:
- Raspberry Leaf Tea: Traditionally used to strengthen the uterine muscles and prepare the body for childbirth. It can also help regulate menstrual cycles.
- Ginger Tea: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger can help reduce menstrual cramps and alleviate other symptoms associated with the menstrual cycle.
- Chamomile Tea: Known for its calming and relaxing effects, chamomile tea can help reduce stress, which can negatively impact hormonal balance and uterine health.
- Peppermint Tea: Can help with bloating and digestive issues that can sometimes affect uterine comfort.
Guidelines on How Much Water to Drink Daily and How to Incorporate Herbal Teas
Determining the appropriate amount of water intake depends on individual factors such as activity level, climate, and overall health. However, general guidelines can help ensure adequate hydration.The general recommendation is to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day, equivalent to about 2 liters. However, individuals engaging in strenuous physical activity or living in hot climates may require more.Here are some tips for incorporating herbal teas and staying hydrated:
- Start Your Day with Water: Drink a glass of water first thing in the morning to rehydrate after sleep and kickstart your metabolism.
- Carry a Water Bottle: Keep a reusable water bottle with you throughout the day to encourage frequent sips.
- Set Reminders: Use phone apps or set alarms to remind yourself to drink water regularly.
- Flavor Your Water: Add slices of lemon, cucumber, or berries to your water to make it more appealing.
- Choose Herbal Teas Wisely: Research the benefits and potential side effects of different herbal teas before incorporating them into your routine. Consult with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body’s signals. Thirst is a clear indication that you need to drink more water. Other signs of dehydration include dry mouth, fatigue, and dark-colored urine.
Proper hydration, through the consistent intake of water and the thoughtful inclusion of herbal teas, is a fundamental aspect of supporting uterine health and promoting overall well-being.
Supplements and Their Role (with caution)
While a nutrient-rich diet forms the cornerstone of uterine health, certain supplements may offer additional support. It’s crucial to approach supplementation with caution and always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new regimen. Supplements are not a substitute for a healthy lifestyle and should be viewed as a potential complement to dietary and lifestyle modifications, not a standalone solution.
Individual needs vary significantly, and what benefits one person might not benefit another, or could even pose risks.
Understanding the Risks and Benefits
The use of supplements for uterine health involves a careful balancing act. While some supplements may address specific deficiencies or provide targeted support, they can also interact with medications, cause side effects, or be ineffective if taken improperly. Dosage, quality of the supplement, and individual health conditions all play crucial roles in determining the safety and efficacy of any supplement.
The potential benefits should always be weighed against the possible risks.
Common Supplements for Uterine Health
Several supplements are often discussed in the context of uterine health. However, it is crucial to reiterate that this information is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential before considering any supplement.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays a vital role in overall health, including potential benefits for uterine health. Some studies suggest a link between vitamin D deficiency and conditions like uterine fibroids and endometriosis.
- Potential Benefits: May support immune function, reduce inflammation, and potentially improve fertility outcomes.
- Potential Risks: Excessive intake can lead to hypercalcemia (high calcium levels in the blood), kidney problems, and other complications. The appropriate dosage varies significantly based on individual needs and vitamin D levels, as determined through blood tests.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA found in fish oil, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
- Potential Benefits: May help reduce inflammation associated with conditions like endometriosis, potentially alleviating pain and discomfort.
- Potential Risks: Can thin the blood, increasing the risk of bleeding, especially if taken with blood-thinning medications. May also cause gastrointestinal side effects like nausea or diarrhea. The quality of fish oil supplements varies significantly, so choosing a reputable brand is important.
- Iron: Iron is crucial for red blood cell production and oxygen transport.
- Potential Benefits: Addressing iron deficiency anemia, which can be common in women with heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Potential Risks: Iron can cause constipation, nausea, and other gastrointestinal issues. Excessive iron intake can lead to iron overload, which can damage organs. Iron supplementation should only be considered if iron deficiency is confirmed through blood tests.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is involved in numerous bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function.
- Potential Benefits: May help reduce menstrual cramps and improve mood.
- Potential Risks: Can cause diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. High doses can interfere with the absorption of other nutrients. Magnesium citrate is a common form and is known for its laxative effect.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support gut health.
- Potential Benefits: May help reduce inflammation and improve gut health, which can indirectly benefit overall health, including the reproductive system. Some studies suggest a link between gut health and endometriosis.
- Potential Risks: Generally considered safe, but can cause mild gastrointestinal symptoms in some individuals. The specific strains of probiotics and their effectiveness can vary.
- Turmeric/Curcumin: Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Potential Benefits: May help reduce inflammation associated with endometriosis and other inflammatory conditions.
- Potential Risks: Can interact with blood-thinning medications. May cause gastrointestinal issues in some individuals. The bioavailability of curcumin is often low, so choosing a formulation with enhanced absorption, such as those containing piperine (black pepper extract), may be beneficial.
Lifestyle Factors Complementing Diet
Maintaining uterine health requires a holistic approach, with diet being just one crucial component. Alongside a nutrient-rich diet, incorporating specific lifestyle factors can significantly enhance uterine function and overall well-being. These factors work synergistically with dietary choices to promote hormonal balance, reduce inflammation, and support the reproductive system.
The Role of Exercise in Uterine Health
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for uterine health. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for hormonal balance. Obesity can lead to increased estrogen production, potentially increasing the risk of uterine fibroids and other conditions. Exercise also improves blood circulation, ensuring adequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the uterus.
- Types of Exercise: A combination of aerobic and strength training exercises is recommended.
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like brisk walking, running, swimming, and cycling improve cardiovascular health and can aid in weight management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Strength Training: Lifting weights or using resistance bands helps build muscle mass, which can boost metabolism and improve insulin sensitivity, further supporting hormonal balance. Include strength training exercises at least two times per week, focusing on major muscle groups.
- Benefits of Exercise:
- Hormonal Regulation: Exercise helps regulate hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, which are vital for uterine health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of hormonal imbalances and related uterine issues.
- Improved Circulation: Increased blood flow to the uterus promotes its optimal function.
- Stress Reduction: Exercise is a natural stress reliever, which can positively impact uterine health.
Stress Management Techniques and Uterine Function
Chronic stress can negatively impact uterine health by disrupting hormonal balance and increasing inflammation. Effective stress management techniques are essential for supporting the reproductive system. High cortisol levels, a stress hormone, can interfere with the production of other hormones necessary for uterine health.
- Stress Reduction Methods:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Regular meditation can reduce stress levels, promoting relaxation and hormonal balance. Practicing mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment and observing thoughts and feelings without judgment.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These practices combine physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation to reduce stress and improve overall well-being. They can help lower cortisol levels and improve blood flow.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple deep breathing exercises can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing stress. Inhale deeply through the nose, hold the breath for a few seconds, and exhale slowly through the mouth.
- Spending Time in Nature: Exposure to nature has been shown to lower stress levels and improve mood. Take walks in parks, gardens, or forests to experience the calming effects of nature.
- Impact of Stress:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Stress can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones, potentially leading to irregular periods, worsened PMS symptoms, and other uterine issues.
- Increased Inflammation: Chronic stress can contribute to systemic inflammation, which can negatively affect uterine health.
- Reduced Fertility: High stress levels can make it more difficult to conceive.
The Importance of Sleep for Uterine Health
Adequate sleep is critical for overall health, including the health of the uterus. During sleep, the body repairs and rejuvenates itself, including the reproductive system. Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal balance, increase inflammation, and negatively impact uterine function.
- Sleep Recommendations: Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Establish a Regular Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends, to regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Wind down before bed with calming activities such as reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to soothing music.
- Optimize the Sleep Environment: Ensure the bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool to promote restful sleep.
- Effects of Sleep on Uterine Health:
- Hormonal Regulation: Sleep is essential for the production and regulation of hormones, including those that govern the menstrual cycle.
- Reduced Inflammation: Adequate sleep helps reduce inflammation throughout the body.
- Improved Mood: Sleep deprivation can lead to mood swings and increased stress, which can negatively impact uterine health.
- Enhanced Fertility: Sufficient sleep supports overall reproductive health and can improve fertility.
Last Point
So, there you have it! We’ve explored the incredible world of foods good for uterus, from essential nutrients to delicious meal plans. Remember, what you eat can significantly impact your uterine health, hormonal balance, and overall well-being. By making informed choices and embracing a balanced diet, you can empower your body and support a healthy reproductive system. Here’s to a happy, healthy uterus! ✨ Cheers to your health! 🥂


