Ah, the glorious food truck! A mobile feast for the senses, a culinary adventure on wheels… but also a potential smoke-filled, grease-slicked, fire-hazard-waiting-to-happen. That’s where the unsung hero of the food truck world, the food truck range hood, struts its stuff! This isn’t just some fancy exhaust fan; it’s a life-saver, a lung-protector, and a grease-fighting ninja all rolled into one. Get ready to dive into the nitty-gritty of keeping your food truck smelling like deliciousness (and not like a burning tire fire).
We’ll explore the different types of range hoods, from the wall-mounted workhorses to the island-style showoffs. We’ll calculate CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) like we’re rocket scientists (but with more delicious outcomes). We’ll dissect the materials, ogle the filtration systems, and even peek at the ductwork that keeps the whole operation running smoothly. Plus, we’ll tackle the thrilling world of legal regulations because, let’s be honest, nobody wants a surprise visit from the fire marshal during peak lunch hour.
Prepare for a wild ride, folks!
Introduction to Food Truck Range Hoods
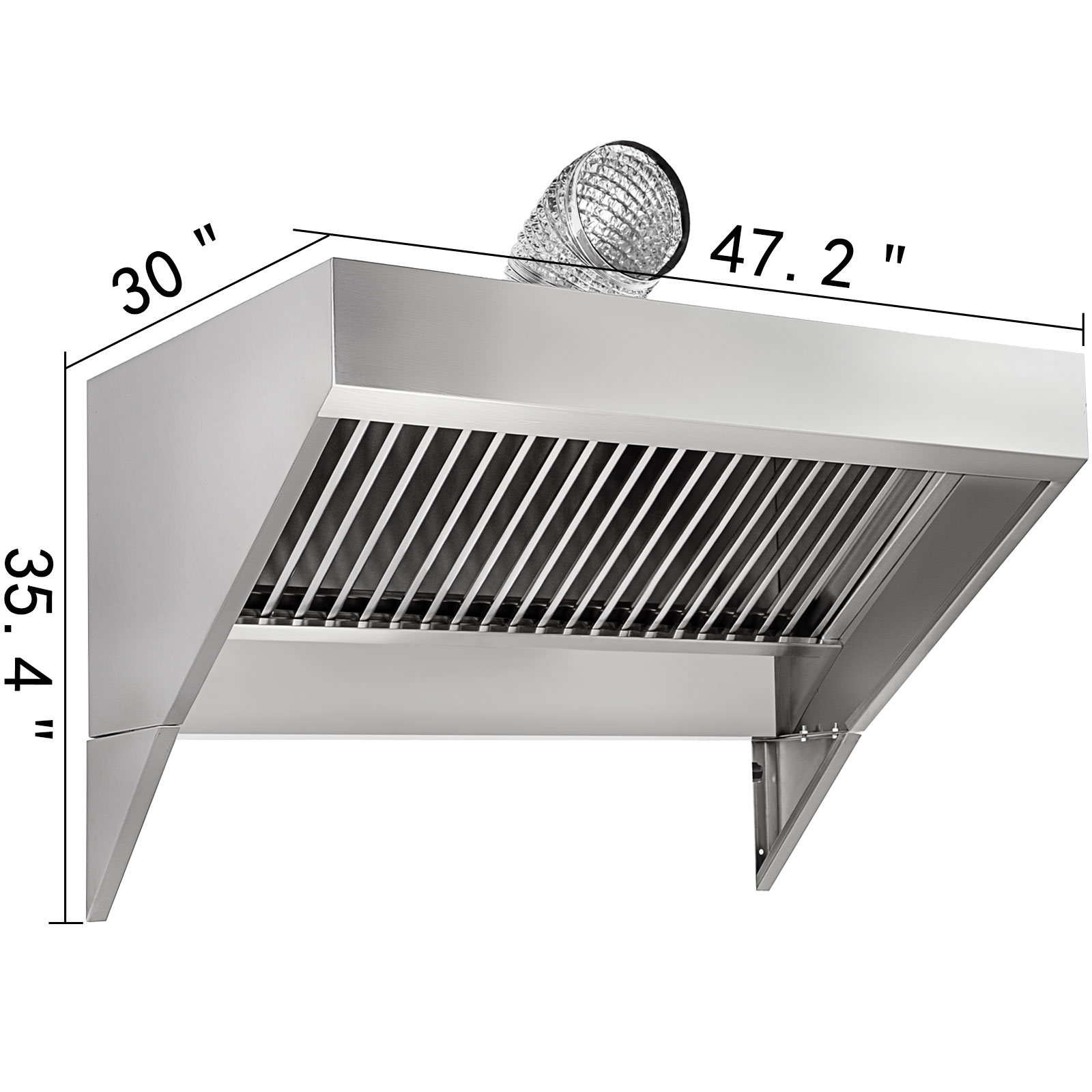
The food truck range hood is a critical piece of equipment in any mobile food unit, serving as the primary line of defense against airborne contaminants and ensuring a safe and comfortable cooking environment. Its effectiveness directly impacts worker safety, regulatory compliance, and the overall success of the food truck operation.
Primary Function of a Food Truck Range Hood
The core function of a food truck range hood is to capture and remove grease, smoke, fumes, and odors produced during cooking. This is achieved through a system that draws air upwards from the cooking surface, filters out particulate matter, and exhausts the cleaned air outside the food truck. This process is essential for maintaining acceptable air quality within the confined space of a mobile kitchen.
Importance of a Range Hood in Maintaining Air Quality and Safety
A properly functioning range hood is paramount for several reasons. Without it, the buildup of grease and smoke can create hazardous conditions.
- Fire Hazard Reduction: Grease buildup on surfaces, including the hood itself and surrounding areas, significantly increases the risk of fire. The hood’s suction and filtration system help to prevent grease accumulation, mitigating this risk.
- Improved Air Quality: Cooking generates a variety of airborne pollutants, including carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The range hood removes these pollutants, ensuring a healthier working environment for food truck staff and reducing the risk of respiratory problems.
- Odor Control: The strong odors produced during cooking can be unpleasant for both staff and customers. The range hood helps to minimize these odors, making the food truck a more inviting place to work and potentially enhancing the customer experience.
- Regulatory Compliance: Most jurisdictions have regulations regarding ventilation in commercial kitchens, including food trucks. A compliant range hood is essential for passing health inspections and avoiding penalties.
Different Types of Range Hoods Available
Food truck range hoods come in various configurations, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of hood depends on factors such as the type of cooking equipment, the volume of food preparation, and the available space within the food truck.
- Type I Hoods: These are designed for capturing grease and are typically used over cooking equipment that produces grease-laden vapors, such as fryers, grills, and griddles. They include grease filters to remove particulate matter.
- Type II Hoods: These hoods are designed for capturing steam, odors, and non-grease-laden vapors. They are commonly used over dishwashers and other equipment that produces steam. They usually have a different filtration system compared to Type I hoods.
- Wall-Mounted Hoods: These hoods are mounted directly to the wall and are a common choice for smaller food trucks or those with limited space. They often have a more compact design.
- Island Hoods: Island hoods are designed to be installed over cooking equipment that is located in the center of the kitchen. This type of hood is less common in food trucks due to space constraints, but can be seen in larger operations.
- Updraft Hoods: These hoods draw air directly upwards, which is a common design in many food truck applications.
- Downdraft Hoods: Downdraft hoods draw air downwards, and are less common in food trucks.
Types of Food Truck Range Hoods
Food truck range hoods are essential for maintaining a clean and safe cooking environment. Selecting the right type of hood is crucial for effective ventilation and smoke removal. Different designs cater to various kitchen layouts and cooking styles, impacting both efficiency and cost. Understanding the available options allows food truck owners to make informed decisions that optimize their operations.
Wall-Mounted Range Hoods
Wall-mounted range hoods are a common choice for food trucks due to their straightforward installation and space-saving design. They are typically mounted directly onto a wall, above the cooking surface. This type of hood effectively captures and removes smoke, grease, and odors generated during cooking.
- Advantages: Wall-mounted hoods offer a relatively simple installation process, making them a cost-effective option. They are readily available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different cooking setups. The direct mounting to a wall provides stable support, and they often incorporate built-in lighting for enhanced visibility.
- Disadvantages: Their placement is limited by the location of the wall, potentially restricting kitchen layout flexibility. They might not be suitable for island cooking stations or open kitchen designs. Cleaning can be challenging, depending on the hood’s design and accessibility.
Island Range Hoods
Island range hoods are designed to be suspended from the ceiling above a cooking island or a central cooking area. They provide ventilation for kitchens where the cooking surface is not against a wall. This type of hood offers a stylish aesthetic, but requires careful planning for installation and maintenance.
- Advantages: Island range hoods offer a design-focused solution for open kitchen layouts, creating a focal point. They provide ventilation from all sides of the cooking surface, capturing smoke and odors efficiently. They are often available in modern and attractive designs that complement the food truck’s interior.
- Disadvantages: Installation is more complex and potentially more expensive than wall-mounted hoods, requiring ceiling support. They typically require a stronger ventilation system to effectively capture and remove fumes from all directions. Cleaning can be difficult due to their suspended position and complex designs.
Downdraft Range Hoods
Downdraft range hoods are integrated into the cooking surface or countertop and draw air downwards. They are less common in food trucks compared to other types due to space limitations and performance considerations. They offer a streamlined appearance, but their effectiveness can be limited.
- Advantages: Downdraft hoods provide a clean and minimalist aesthetic, suitable for modern kitchen designs. They do not obstruct the view, which is beneficial in open spaces.
- Disadvantages: Their performance is generally less effective than other types, especially in capturing rising smoke and grease. Installation can be complex and may require modifications to the cooking surface or countertop. They often have limited airflow capacity and can be noisy during operation. They also need a significant amount of space below the cooktop to house the ventilation system.
Performance Characteristics Comparison
The performance of a range hood is typically measured by its airflow capacity, expressed in cubic feet per minute (CFM), and its capture efficiency. Higher CFM ratings generally indicate a more powerful hood capable of removing larger volumes of air. Capture efficiency refers to the hood’s ability to contain and remove smoke, grease, and odors effectively.
- Airflow: Wall-mounted and island range hoods typically offer higher CFM ratings compared to downdraft models, ensuring effective ventilation. The required CFM depends on the cooking surface size and the intensity of cooking. For example, a food truck using a high-output wok burner might require a range hood with a CFM rating of 1200 or higher.
- Capture Efficiency: Wall-mounted and island hoods generally provide superior capture efficiency due to their proximity to the cooking surface and their ability to contain rising fumes. Downdraft hoods, drawing air downwards, may struggle to capture smoke and grease effectively, especially from high-heat cooking.
Range Hood Type Comparison Table
This table summarizes the key differences between the range hood types.
| Range Hood Type | Size | Installation Requirements | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wall-Mounted | Variable, based on cooking surface size | Simple, mounts directly to a wall | Generally the most affordable |
| Island | Variable, based on cooking surface size | Complex, requires ceiling support and ductwork | Typically more expensive |
| Downdraft | Integrated into cooking surface or countertop | Complex, may require modification of existing equipment | Can be expensive, especially for high-performance models |
Range Hood Sizing and CFM Requirements
Proper range hood sizing and CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) are critical for maintaining a safe, efficient, and comfortable cooking environment within a food truck. A range hood that is too small or has insufficient CFM will fail to effectively remove smoke, grease, and odors, leading to poor air quality, reduced cooking performance, and potential health hazards. This section delves into the factors involved in determining the correct range hood size and calculating the necessary CFM for optimal performance.
Determining Range Hood Size
The size of the range hood must be appropriately matched to the cooking surface area. A general rule of thumb is that the range hood should be at least as wide as the cooking surface below it, and ideally, slightly wider. This ensures that the hood effectively captures all the rising smoke, grease, and fumes generated during cooking. Consider the arrangement of cooking appliances and any potential obstructions.
Calculating Required CFM
Calculating the required CFM involves considering the type and number of cooking appliances, as well as the overall dimensions of the food truck. CFM is a measure of how much air the range hood can move in one minute. A higher CFM rating indicates a more powerful hood, capable of removing larger volumes of smoke and grease.
CFM Calculation Formula:CFM = (BTU of cooking appliances) / 100
This is a simplified calculation and may need adjustment based on the specific setup.
Impact of Insufficient CFM
Insufficient CFM can have several negative consequences. Inadequate ventilation leads to poor air quality, with lingering smoke, grease, and odors. This can create an uncomfortable and potentially unhealthy environment for the food truck operators and customers. The build-up of grease can also create a fire hazard. Furthermore, a lack of proper ventilation can hinder cooking efficiency.
Inefficient smoke removal can obstruct visibility and impede the proper operation of cooking equipment, affecting the taste and quality of the food.
Steps for Calculating Necessary CFM
The following steps provide a systematic approach to calculating the necessary CFM for a food truck range hood:
- Identify Cooking Appliances: Make a detailed inventory of all cooking appliances, including their BTU (British Thermal Units) ratings. The BTU rating indicates the heat output of the appliance and is usually found on a label on the appliance itself. Examples include gas ranges, fryers, charbroilers, and griddles.
- Calculate Total BTU: Sum the BTU ratings of all cooking appliances. This gives the total heat output of the cooking setup. For instance, if you have a 60,000 BTU range and a 40,000 BTU fryer, the total BTU is 100,000.
- Apply the CFM Formula: Use the CFM formula to determine the required CFM. Divide the total BTU by 100. In the example above, with a total BTU of 100,000, the required CFM is 1000.
- Consider Food Truck Dimensions: Evaluate the overall dimensions of the food truck, especially the ceiling height. Higher ceilings may require slightly higher CFM to ensure adequate air exchange. If the truck is unusually large, consider increasing the calculated CFM by 10-20%.
- Factor in Cooking Style: Consider the type of cooking performed. If the cooking involves heavy frying or grilling, which produces more smoke and grease, a higher CFM might be needed. For example, a food truck specializing in fried foods might benefit from a CFM rating slightly above the calculated minimum.
- Select Range Hood: Choose a range hood with a CFM rating equal to or greater than the calculated value. It’s always better to err on the side of a slightly higher CFM to ensure adequate ventilation.
Materials and Construction
The longevity and effectiveness of a food truck range hood are significantly influenced by the materials used in its construction. Choosing the right materials ensures the hood’s durability, resistance to the harsh environment of a mobile kitchen, and ease of maintenance. The construction process itself is a crucial factor, dictating the hood’s structural integrity and its ability to effectively capture and remove grease, smoke, and odors.
Common Materials Used
Food truck range hoods are primarily constructed from a select few materials, each offering a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. These materials are chosen based on their ability to withstand high temperatures, resist corrosion from grease and cleaning agents, and provide a durable and easily cleanable surface.
- Stainless Steel: This is the most prevalent material for food truck range hoods due to its excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Stainless steel is also relatively easy to clean and maintain, making it ideal for a demanding kitchen environment. Different grades of stainless steel are available, with 304 and 430 being the most commonly used.
- Galvanized Steel: Galvanized steel offers a more cost-effective alternative to stainless steel. It is coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. While galvanized steel is less resistant to corrosion than stainless steel, it can still provide adequate protection in certain applications, especially if properly maintained.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is sometimes used for certain components of range hoods, particularly filters and ductwork. It’s lightweight and has good heat transfer properties, making it suitable for these applications. However, it’s generally less durable than stainless or galvanized steel and can be more susceptible to damage.
Pros and Cons of Each Material
The selection of a material involves a careful balancing act between cost, performance, and longevity. Each material presents its own set of advantages and disadvantages that must be considered based on the specific needs and budget of the food truck owner.
- Stainless Steel:
- Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, high durability, easy to clean, aesthetically pleasing, high heat resistance.
- Cons: Higher initial cost compared to galvanized steel.
- Galvanized Steel:
- Pros: Lower initial cost compared to stainless steel.
- Cons: Less corrosion resistance than stainless steel, can be prone to rust if the zinc coating is damaged, may require more frequent maintenance.
- Aluminum:
- Pros: Lightweight, good heat transfer properties.
- Cons: Less durable than steel, can be dented or damaged more easily, may not be suitable for high-heat applications, can corrode in contact with certain cleaning agents.
Construction Process of a Typical Range Hood
The construction of a food truck range hood involves several key steps, from initial design and material selection to fabrication and final assembly. This process ensures the hood’s structural integrity, its ability to effectively capture and remove contaminants, and its overall longevity.
- Design and Planning: The process begins with detailed design specifications, considering the size and layout of the food truck kitchen, the type of cooking equipment, and the required airflow. Engineers and designers use Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to create detailed blueprints, including dimensions, material specifications, and component placement.
- Material Cutting and Shaping: Based on the design, the selected materials (typically stainless steel) are cut to the required dimensions using laser cutters, water jets, or shears. The metal sheets are then shaped using bending machines, rollers, and presses to create the hood’s body, baffles, and other components.
- Welding and Assembly: The various components are joined together through welding, riveting, or bolting. Welding is a common method for creating strong, airtight seams. The seams are often ground and polished to create a smooth, seamless finish.
- Filter and Baffle Installation: Filters and baffles are installed within the hood to capture grease and other contaminants. These components are crucial for the hood’s effectiveness and are typically made of stainless steel or aluminum. The baffles are designed to direct grease away from the exhaust system.
- Motor and Fan Installation: The motor and fan assembly are installed to provide the necessary suction and airflow. The motor is usually enclosed in a protective housing to prevent damage and ensure safety. The fan blades are carefully balanced to minimize noise and vibration.
- Testing and Quality Control: The assembled range hood undergoes rigorous testing to ensure its performance and safety. This includes airflow testing, grease containment testing, and inspection for any leaks or defects. Quality control checks are performed throughout the entire manufacturing process.
- Finishing and Packaging: The hood is cleaned, polished, and sometimes coated with a protective film. It is then carefully packaged to prevent damage during shipping and installation.
Visual Representation of a Range Hood Cross-Section
Here’s a description of a range hood cross-section, including its key components and the materials used:Imagine a horizontal slice through a typical food truck range hood, revealing its internal structure. The outermost layer is the hood’s body, made of a thick sheet of stainless steel (304 grade). The stainless steel provides a durable, corrosion-resistant surface, easy to clean and maintain.Inside, you’ll see a series of angled metal plates, the baffle filters.
These are also made of stainless steel and are designed to capture grease particles. Grease, as it rises with hot air, strikes the angled baffles and condenses, dripping down into a grease collection trough. This trough, located at the bottom of the hood, is made of the same stainless steel as the hood body.Above the baffles, there is an empty space that is the plenum.
Inside this space, is the duct connection that leads to the exhaust fan, typically located on the roof of the food truck. The duct connection is often made of stainless steel or galvanized steel.A light fixture, protected by a glass or polycarbonate cover, is often integrated into the hood’s design, providing illumination over the cooking surface. The electrical wiring for the light is carefully routed and protected within the hood’s structure.The top of the hood has an opening that connects to the exhaust duct.
This duct, often made of galvanized steel or stainless steel, channels the smoke, grease, and odors out of the food truck. The entire structure is supported by a robust frame, providing stability and structural integrity. The cross-section reveals the careful engineering and material selection that go into creating an effective and durable food truck range hood.
Filtration Systems
Food truck range hoods are critical for removing grease, smoke, and odors generated during cooking. Effective filtration systems are essential for maintaining air quality, preventing fire hazards, and complying with health and safety regulations. The choice of filtration system significantly impacts the performance and longevity of the range hood.
Types of Filtration Systems
Different types of filtration systems are employed in food truck range hoods to capture various contaminants. Each filter type targets specific pollutants, working in concert to provide comprehensive air purification.
- Baffle Filters: Baffle filters are typically made of stainless steel and are designed with a series of angled vanes or baffles. As grease-laden air passes through, the baffles redirect the airflow, causing grease particles to collide with the vanes and drain into a collection trough. This design effectively removes a significant amount of grease.
- Mesh Filters: Mesh filters, often constructed from aluminum or stainless steel, consist of a fine mesh that traps grease particles. These filters are generally less effective at grease removal than baffle filters but are useful for capturing smaller particles and providing a final level of filtration.
- Grease Filters: The term “grease filter” is often used generically to describe any filter designed to remove grease. However, in some contexts, it specifically refers to filters that are a combination of baffle and mesh filtration systems. They are designed to capture grease particles, preventing them from entering the exhaust system and posing a fire hazard.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Activated carbon filters are used to remove odors and gases. These filters contain activated carbon, a material with a highly porous structure that adsorbs volatile organic compounds (VOCs) responsible for unpleasant smells. These are often used in conjunction with other filtration methods to improve air quality.
Function of Each Filter Type
Each filter type within a food truck range hood performs a specific function in removing contaminants from the air. The effectiveness of each filter depends on its design and the type of pollutants it is intended to capture.
- Baffle Filters: Baffle filters primarily remove grease. Their design redirects airflow, causing grease particles to separate from the air and collect. This is a crucial first step in preventing grease buildup in the exhaust system and reducing the risk of fire.
- Mesh Filters: Mesh filters capture smaller grease particles and other airborne debris that may pass through the baffle filters. They act as a secondary filter, providing an extra layer of protection for the exhaust system.
- Grease Filters: As a general term, grease filters are designed to capture grease, preventing it from entering the exhaust system. They may incorporate features from both baffle and mesh filters.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Activated carbon filters remove odors and gases. They work through a process called adsorption, where VOCs are trapped within the porous structure of the activated carbon. This process significantly improves air quality and eliminates cooking smells.
Effectiveness Comparison of Different Filtration Systems
The effectiveness of different filtration systems varies depending on the type of pollutants being removed and the design of the filters. Baffle filters are generally the most effective at removing large grease particles, while activated carbon filters excel at removing odors. The best filtration system often combines multiple filter types.
- Grease Removal: Baffle filters are highly effective at removing grease, with efficiency rates often exceeding 90% for large grease particles. Mesh filters provide a lower level of grease removal, typically capturing smaller particles that escape the baffle filters.
- Smoke Removal: Baffle and mesh filters contribute to smoke removal by capturing particulate matter. However, they are not specifically designed for smoke removal.
- Odor Removal: Activated carbon filters are the most effective at removing odors. They can adsorb a wide range of VOCs, resulting in significantly improved air quality.
- Overall Effectiveness: The overall effectiveness of a filtration system depends on the combination of filter types used. A system that combines baffle filters for grease removal, mesh filters for smaller particles, and activated carbon filters for odors will provide the most comprehensive air purification.
Filter Types, Materials, Maintenance, and Replacement
Proper maintenance and timely replacement of filters are essential for the continued effectiveness of a food truck range hood. The following table summarizes the characteristics of different filter types.
Get the entire information you require about 99 cent store food quality on this page.
| Filter Type | Materials | Maintenance Requirements | Replacement Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baffle Filters | Stainless steel | Clean regularly with degreasing detergent; can be washed in a dishwasher | Typically, no replacement is needed, provided they are maintained properly. However, they may need to be replaced if damaged. |
| Mesh Filters | Aluminum, stainless steel | Clean regularly with degreasing detergent; can be washed in a dishwasher | Typically, every 6-12 months, or as needed if damaged. |
| Grease Filters (Combination) | Stainless steel, aluminum | Follow manufacturer’s instructions; clean regularly with degreasing detergent | Typically, every 6-12 months, or as needed if damaged. |
| Activated Carbon Filters | Activated carbon | Do not wash; replace when odors are no longer being removed | Typically, every 3-6 months, or as needed depending on usage. |
Ventilation and Exhaust Systems
A well-designed ventilation and exhaust system is critical for a food truck’s operational safety, air quality, and compliance with health codes. This system removes smoke, grease-laden vapors, and odors produced during cooking, while also providing fresh, clean air for the comfort of the staff and customers. The following sections will Artikel the essential components and considerations for a robust ventilation system.
Components of a Complete Ventilation System, Food truck range hood
A complete ventilation system in a food truck comprises several interconnected components working in harmony. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall effectiveness of the system.
- Range Hood: The range hood captures smoke, grease, and cooking odors directly from the cooking surface. Its design and size are crucial for efficient capture and containment.
- Ductwork: Ductwork transports the contaminated air from the range hood to the exhaust fan and then outside the food truck. Proper design, material selection, and installation are essential to prevent leaks, ensure efficient airflow, and minimize fire hazards.
- Exhaust Fan: The exhaust fan is the heart of the system, providing the necessary suction to pull the contaminated air through the ductwork and out of the truck. The fan’s size and power must be matched to the range hood’s CFM requirements and the ductwork’s resistance.
- Filtration System: Filtration systems, often integrated into the range hood or ductwork, remove grease particles, smoke, and other contaminants from the air before it is exhausted. These systems include baffle filters, grease filters, and sometimes activated carbon filters for odor control.
- Make-up Air System: A make-up air system replaces the air exhausted by the range hood. This system can be as simple as passive vents or as complex as a powered air handler with filtration and heating/cooling capabilities. Properly designed make-up air prevents negative pressure inside the truck, ensuring efficient exhaust and preventing the backdraft of fumes.
- Fire Suppression System: An automatic fire suppression system, typically integrated with the range hood, is a critical safety feature. It detects and suppresses fires that may originate from cooking equipment.
Importance of Proper Ductwork Design and Installation
Ductwork is the circulatory system of the ventilation setup, and its design and installation directly impact the efficiency and safety of the entire system. Improper ductwork can lead to a range of issues, including reduced airflow, increased fire hazards, and health code violations.
- Material Selection: Ductwork must be constructed from durable, fire-resistant materials, typically stainless steel or galvanized steel. The material must withstand high temperatures, grease buildup, and cleaning chemicals.
- Diameter and Shape: The ductwork’s diameter should be sized according to the range hood’s CFM rating and the length and number of bends in the duct run. Rectangular or square ducts are less efficient than round ducts.
- Smooth Interior: The interior surface of the ductwork should be smooth to minimize friction and resistance to airflow.
- Sealing and Insulation: All joints and seams must be tightly sealed to prevent leaks of contaminated air and to maintain the proper airflow. Insulation may be necessary to prevent condensation and heat loss, especially in colder climates.
- Slope and Drainage: The ductwork should be sloped slightly downward towards the exhaust fan to allow grease and condensation to drain properly. Drain plugs or grease traps should be installed at low points in the ductwork.
- Accessibility for Cleaning: The ductwork should be designed to allow easy access for cleaning and maintenance. Access panels or removable sections should be incorporated at regular intervals. Regular cleaning is essential to remove grease buildup, which can significantly reduce airflow and pose a fire hazard.
Calculating Exhaust Fan Size and Power
Determining the appropriate size and power of the exhaust fan is crucial for achieving adequate ventilation. The fan’s capacity must match the range hood’s requirements and the resistance imposed by the ductwork.
- CFM Requirements: The range hood’s CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) rating indicates the volume of air it can exhaust per minute. This rating is determined by the size and type of cooking equipment. As a general guideline, the CFM rating is often calculated by multiplying the hood’s width (in feet) by its length (in feet) and then multiplying the result by 100 for light-duty cooking, 150 for medium-duty, and 200 for heavy-duty cooking.
For example, a 6-foot-wide by 4-foot-long range hood used for medium-duty cooking would require a fan with a minimum CFM of (6 x 4) x 150 = 3600 CFM.
- Ductwork Resistance: The length, diameter, and number of bends in the ductwork system create resistance to airflow. This resistance reduces the effective CFM of the exhaust fan.
- Static Pressure: Static pressure is the measure of resistance in the ductwork. It is usually expressed in inches of water column (in. w.g.). The higher the static pressure, the more powerful the fan needs to be to overcome the resistance.
- Fan Selection: The exhaust fan’s performance curve, provided by the manufacturer, indicates its CFM output at different static pressure levels. Select a fan that can deliver the required CFM at the calculated static pressure.
- Example: A food truck with a 6-foot range hood, a 20-foot-long duct run with two 90-degree bends, and a calculated CFM requirement of 3600, might require a fan with a 3800 CFM rating to account for the resistance in the ductwork. The fan’s performance curve must be consulted to ensure it can deliver the 3600 CFM at the estimated static pressure of the ductwork.
Diagram of a Complete Food Truck Ventilation System
The following diagram illustrates a typical layout of a complete ventilation system for a food truck.
Diagram: Food Truck Ventilation System Layout
The diagram depicts a food truck from a side view, showing the key components of a ventilation system. The range hood is positioned directly above the cooking equipment inside the truck. The range hood is connected to a series of ductwork that runs from the hood, up through the roof of the truck, to the exhaust fan. The exhaust fan is mounted on the roof of the truck and is responsible for exhausting the contaminated air outside. The diagram also shows a make-up air intake, which can be either a passive vent or a powered air handler, positioned on the opposite side of the truck to the exhaust fan. A filtration system is depicted within the range hood, capturing grease particles before the air enters the ductwork. The fire suppression system is shown connected to the range hood, ready to extinguish any potential fires. Arrows illustrate the airflow: contaminated air flows from the cooking equipment up into the range hood, through the ductwork, through the exhaust fan, and out of the truck. Fresh air flows from the make-up air intake into the truck, replacing the exhausted air.
Installation and Maintenance
Maintaining a food truck range hood is crucial for ensuring both the safety and efficiency of your mobile kitchen. Proper installation, coupled with a consistent maintenance schedule, minimizes fire hazards, extends the lifespan of the equipment, and helps maintain optimal air quality. Neglecting these aspects can lead to costly repairs, potential health risks, and operational downtime.
Installation Steps
Installing a food truck range hood requires careful planning and execution. The following steps Artikel the general process, although specific instructions may vary depending on the model and manufacturer’s recommendations:
- Planning and Preparation: This involves assessing the available space, determining the appropriate hood size and type based on your cooking equipment, and gathering all necessary tools and materials. This also includes checking local building codes and obtaining the required permits.
- Mounting the Hood: Securely attaching the range hood to the food truck’s structure. This typically involves using mounting brackets and screws, ensuring the hood is level and properly aligned with the cooking surface.
- Ductwork Connection: Connecting the range hood to the exhaust system, which removes smoke, grease, and odors from the cooking area. This often involves installing ductwork, ensuring proper sealing to prevent leaks, and routing the ductwork to an appropriate exhaust point, such as a roof vent.
- Electrical Connections: Connecting the range hood’s electrical components, including lights and fan motor, to the food truck’s power supply. This should be performed by a qualified electrician to ensure safe and compliant wiring.
- Filter Installation: Installing the appropriate filters, such as baffle filters or mesh filters, to capture grease and other contaminants.
- Testing and Inspection: Testing the range hood to ensure it functions correctly, including the fan speed, lighting, and filter effectiveness. A final inspection should be conducted to verify that all connections are secure and that the system meets local codes and regulations.
Importance of Professional Installation and Code Compliance
Professional installation is highly recommended for food truck range hoods. Qualified technicians possess the expertise and experience to ensure the hood is installed correctly, safely, and in compliance with all applicable codes and regulations. Adhering to these standards is paramount for several reasons:
- Safety: Proper installation minimizes fire hazards and electrical risks. Incorrect wiring or improper ductwork connections can lead to serious accidents.
- Code Compliance: Local building codes and fire regulations dictate specific requirements for range hood installations. Professional installers are familiar with these codes and ensure that the installation meets all necessary standards. Failure to comply can result in fines, operational delays, and even the closure of your food truck.
- Efficiency: A professionally installed hood will operate more efficiently, providing optimal ventilation and removing smoke and grease effectively.
- Warranty: Many range hood manufacturers require professional installation to validate the warranty.
Recommended Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your food truck range hood functioning efficiently and safely. A consistent maintenance schedule, including cleaning and filter replacement, will extend the lifespan of the equipment and prevent potential problems.
- Daily Cleaning: Wipe down the exterior surfaces of the range hood with a mild detergent and water to remove grease and grime.
- Weekly Cleaning: Clean the filters to remove grease buildup. Depending on the filter type, this may involve washing them in a dishwasher or soaking them in a degreasing solution.
- Monthly Inspection: Inspect the ductwork for any signs of leaks, damage, or obstructions. Check the fan motor for proper operation and listen for any unusual noises.
- Regular Duct Cleaning: Professional duct cleaning is recommended at least once a year, or more frequently depending on the volume of cooking and grease accumulation. This removes accumulated grease and reduces the risk of fire.
- Filter Replacement: Replace filters as needed, following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Clogged filters reduce ventilation efficiency and increase fire hazards. The frequency of replacement depends on the filter type and usage. Baffle filters can last longer than mesh filters.
- Fan Maintenance: Lubricate the fan motor bearings as recommended by the manufacturer.
Essential Safety Precautions
Maintaining a food truck range hood involves certain safety precautions to minimize risks. Always prioritize safety when performing any maintenance tasks.
- Disconnect Power: Before performing any maintenance, always disconnect the power supply to the range hood to prevent electrical shocks.
- Wear Protective Gear: Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and eye protection, when cleaning and handling greasy components.
- Use Appropriate Cleaning Solutions: Use only cleaning solutions that are specifically designed for range hoods and are safe for the materials used in the hood’s construction. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners.
- Handle Filters Carefully: Handle filters with care to avoid damaging them. Replace filters promptly when they are worn or damaged.
- Be Aware of Fire Hazards: Be vigilant about fire hazards, such as grease buildup in the ductwork or on the filters. Ensure that the exhaust system is functioning correctly and that there are no leaks.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections by qualified professionals to identify and address potential safety issues.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Operating a food truck range hood is not just about cooking; it’s about adhering to a complex web of legal and regulatory requirements designed to protect public health and safety. Failing to comply can lead to hefty fines, operational shutdowns, and even legal liabilities. This section details the crucial legal and regulatory aspects surrounding food truck range hoods.
Relevant Codes and Regulations
Food truck range hoods are subject to a variety of codes and regulations that vary by location, but generally fall into the categories of fire safety and air quality. These regulations dictate design, installation, and operation.
- Fire Safety Standards: These are paramount, ensuring the hood and ventilation system minimize fire hazards. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) publishes several relevant standards, including NFPA 96, which addresses ventilation control and fire protection of commercial cooking operations. Compliance often includes requirements for fire suppression systems, regular inspections, and proper cleaning procedures. For example, a common requirement is the installation of a fire suppression system that automatically activates in case of a grease fire, spraying a chemical agent to extinguish the flames.
- Air Quality Standards: These standards focus on minimizing the release of pollutants into the atmosphere. They are typically enforced by local air quality management districts or environmental protection agencies. Regulations often mandate the use of grease filters, activated carbon filters (for odor control), and sometimes even electrostatic precipitators to remove grease, smoke, and other contaminants from the exhaust. Failure to meet these standards can result in significant penalties.
- Building Codes: Although food trucks are mobile, local building codes can still apply, especially concerning the installation of the range hood and its venting system. These codes may specify requirements for the size and type of ductwork, the location of exhaust vents, and the overall structural integrity of the installation.
- Health Codes: Local health departments have a vested interest in food safety. They often have specific requirements related to the cleanliness and maintenance of range hoods, as well as the type of filters used to prevent grease buildup and contamination. Regular inspections are conducted to ensure compliance with these health codes.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Inspections
Obtaining the necessary permits and undergoing inspections are essential steps in legally operating a food truck range hood. The process typically involves several stages.
- Permit Application: The first step is to research and apply for the required permits from local authorities. This usually involves submitting detailed plans and specifications for the range hood system, including its size, type, and installation details. You may need to provide information about the fire suppression system, filtration systems, and ventilation plan.
- Plan Review: Local authorities review the submitted plans to ensure they comply with all applicable codes and regulations. This review may take several weeks or months, depending on the jurisdiction. It’s essential to address any comments or revisions requested by the reviewing agency promptly.
- Installation and Inspection: After the plans are approved, the range hood system can be installed. Once the installation is complete, a series of inspections are usually required. These inspections may cover fire safety, air quality, and electrical safety. The inspector will verify that the installation meets all the required standards.
- Ongoing Inspections: After initial approval, periodic inspections are often required to ensure ongoing compliance. These inspections may be conducted annually or more frequently, depending on the local regulations. Failure to pass these inspections can lead to fines or even the suspension of the food truck’s operating permit.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with the regulations related to food truck range hoods can have serious consequences, both financially and operationally.
- Fines and Penalties: Violations of fire safety or air quality regulations can result in significant fines. The amount of the fine can vary depending on the severity of the violation and the jurisdiction. Repeated violations may lead to escalating fines.
- Operational Shutdowns: In severe cases, non-compliance can lead to the shutdown of the food truck’s operations. If a range hood is deemed unsafe or fails to meet air quality standards, the authorities may issue a stop-work order until the issues are corrected. This can result in significant lost revenue.
- Legal Liabilities: If a fire or other incident occurs due to a non-compliant range hood, the food truck owner could face legal liabilities. This could include lawsuits from injured parties or fines for environmental damage.
- Difficulty Obtaining Insurance: Insurance companies may be reluctant to insure food trucks with non-compliant range hood systems. This can make it difficult to operate legally.
- Reputational Damage: Non-compliance can damage the food truck’s reputation, leading to a loss of customers and business. News of violations can spread quickly through social media, impacting customer perception and loyalty.
Finding Local and National Regulations
Locating the specific regulations that apply to a food truck range hood can be a complex process, but is crucial for ensuring compliance.
- Local Authorities: The primary source of information is usually the local government agencies. This includes the local fire department, health department, building department, and air quality management district. Contacting these agencies directly is the most reliable way to obtain the relevant regulations. You can often find contact information and regulatory documents on their websites.
- National Organizations: Several national organizations provide resources and guidelines that can be helpful. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is a key resource for fire safety standards. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides information on air quality regulations.
- Industry Associations: Industry associations, such as food truck associations or restaurant associations, often provide guidance and resources to their members. They may be able to offer information about local regulations or provide templates for permit applications.
- Online Resources: Many online resources can help you find the relevant regulations. Government websites, legal databases, and industry blogs may provide helpful information. Be sure to verify the accuracy of any information found online with the local authorities.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Maintaining a food truck range hood is crucial for ensuring a safe, efficient, and compliant cooking environment. Regular operation, however, can lead to various problems. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly prevents potential hazards, extends the lifespan of the equipment, and minimizes operational downtime. This section Artikels common problems, diagnostic steps, and effective solutions.
Poor Airflow
Inadequate airflow is a primary concern, as it compromises the hood’s ability to effectively remove smoke, grease, and odors. This can lead to an uncomfortable and potentially hazardous work environment, and it can also cause a build-up of grease and smoke inside the food truck.The causes of poor airflow are varied, and a systematic approach to troubleshooting is required.
- Clogged Filters: Grease-laden filters restrict airflow.
- Blocked Ductwork: Accumulation of grease or debris within the ductwork can obstruct airflow.
- Fan Malfunction: A malfunctioning fan motor or impeller can reduce the hood’s suction power.
- Incorrect CFM: If the hood’s CFM (cubic feet per minute) rating is insufficient for the cooking equipment, airflow will be inadequate.
- Obstructions Near the Hood: External factors, like nearby buildings or improperly positioned exhaust outlets, can create backpressure and reduce airflow.
To diagnose poor airflow:
- Check the Filters: Remove and inspect the filters for grease buildup. Clean or replace them as needed.
- Inspect the Ductwork: Examine the ductwork for obstructions. Professional cleaning may be necessary.
- Test the Fan: Ensure the fan is running at the correct speed and is not making unusual noises. Consult a qualified technician if the fan is malfunctioning.
- Assess the CFM: Verify that the hood’s CFM rating is appropriate for the cooking equipment and the size of the food truck.
- Examine the Exhaust: Ensure that the exhaust outlet is clear and unobstructed. Check for any nearby structures that might be causing backpressure.
Potential solutions include:
- Regular Filter Cleaning/Replacement: Implement a regular filter cleaning schedule.
- Professional Duct Cleaning: Schedule professional duct cleaning at least annually, or more frequently depending on cooking volume.
- Fan Repair/Replacement: Replace or repair a faulty fan motor or impeller.
- Hood Replacement: If the CFM rating is insufficient, consider replacing the hood with a more powerful model.
- Exhaust System Modification: Adjust the exhaust outlet location or modify the system to eliminate backpressure.
Excessive Noise
Excessive noise from a range hood can be disruptive and uncomfortable for the food truck operators and customers. This can also indicate underlying mechanical issues.The causes of excessive noise can be diverse, and a detailed examination is crucial.
- Loose Components: Loose fan blades, ductwork connections, or other components can vibrate and generate noise.
- Fan Imbalance: An imbalanced fan impeller can cause vibrations and noise.
- Motor Issues: Worn or damaged motor bearings can produce excessive noise.
- Obstructions in the Fan: Objects caught in the fan blades can create noise.
To diagnose excessive noise:
- Listen Carefully: Identify the source and type of noise (e.g., rattling, humming, grinding).
- Inspect Components: Check for loose screws, bolts, or other components.
- Examine the Fan: Inspect the fan blades for damage or obstructions.
- Check the Motor: Listen for unusual motor sounds, such as squealing or grinding.
Potential solutions include:
- Tighten Loose Components: Secure any loose components.
- Balance the Fan: If the fan is imbalanced, have it professionally balanced.
- Motor Repair/Replacement: Replace or repair the motor if the bearings are worn or damaged.
- Remove Obstructions: Remove any objects caught in the fan blades.
Grease Buildup
Grease buildup is a persistent problem in food truck range hoods. It poses a fire hazard, reduces airflow, and can lead to unsanitary conditions. Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial to manage grease buildup.The primary cause of grease buildup is the condensation of grease-laden vapors from cooking. This buildup occurs on filters, ductwork, and the hood’s interior surfaces.To diagnose grease buildup:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the filters, hood interior, and ductwork for grease accumulation.
- Airflow Assessment: Reduced airflow can indicate grease buildup in the filters or ductwork.
Potential solutions include:
- Regular Cleaning: Establish and adhere to a regular cleaning schedule for filters, hood interior, and ductwork.
- Professional Cleaning: Schedule professional cleaning of the ductwork at least annually, or more frequently depending on cooking volume.
- Filter Replacement: Replace filters when they become heavily saturated with grease.
- Grease Capture Systems: Consider using grease capture systems to minimize grease accumulation in the ductwork.
Common Troubleshooting Tips:
- Always disconnect power before performing any maintenance or troubleshooting.
- Consult the manufacturer’s manual for specific troubleshooting instructions.
- Keep a maintenance log to track cleaning and repairs.
- If you are not comfortable with any troubleshooting steps, consult a qualified technician.
Cost Considerations: Food Truck Range Hood
The cost of a food truck range hood is a significant factor in the overall budget of a mobile food business. Understanding the various cost components, from initial purchase to ongoing operational expenses, is crucial for making informed decisions. Careful consideration of these costs ensures a financially sound investment that contributes to the long-term success of the food truck.
Factors Influencing Range Hood Costs
Several factors significantly impact the price of a food truck range hood. These include the hood’s size, the type of hood (e.g., wall-mounted, island, or downdraft), the materials used in its construction, and the features it offers.
- Size: Larger range hoods, designed to cover more cooking surface, naturally cost more due to increased material requirements and manufacturing complexity. For instance, a 6-foot hood will be more expensive than a 4-foot hood.
- Type: The design of the range hood influences the cost. Wall-mounted hoods are generally less expensive than island hoods, which require more complex installation and aesthetic considerations. Downdraft hoods, while less common in food trucks, often come with a higher price tag due to their specialized design and integrated ventilation systems.
- Materials: The choice of materials affects the price. Stainless steel is a common and durable option, but different grades of stainless steel (e.g., 304 vs. 430) have varying costs. The gauge (thickness) of the steel also plays a role; thicker steel adds to the price but also to the hood’s longevity.
- Features: Additional features, such as built-in lighting, variable speed controls, automatic fire suppression systems, and advanced filtration technologies, increase the cost. While these features enhance performance and safety, they contribute to a higher initial investment.
Comparison of Range Hood Options
The cost of a food truck range hood varies significantly depending on the chosen configuration. Below is a comparison of estimated costs for different range hood options, providing a range based on common configurations and features. These are estimates, and actual prices can fluctuate based on market conditions and vendor pricing.
- Basic Wall-Mounted Hood: This is the most economical option, typically ranging from $1,500 to $3,500. This price usually includes the hood, basic grease filters, and a standard exhaust fan.
- Mid-Range Wall-Mounted Hood with Upgraded Features: This option includes features like higher CFM fans, better filtration, and possibly built-in lighting. The cost generally falls between $3,500 and $6,000.
- Island Hood (Custom): These hoods are designed for applications where the cooking equipment is not against a wall, and the cost can vary significantly depending on the size and complexity of the design. Expect to pay between $4,000 and $8,000 or more, especially if custom finishes or advanced features are requested.
- Downdraft Hood (Less Common in Food Trucks): Downdraft systems are less common in food trucks due to space constraints and ventilation challenges. They are also typically more expensive, with prices starting around $6,000 and potentially exceeding $10,000, including the hood and associated ventilation equipment.
Estimating Long-Term Ownership Costs
Beyond the initial purchase price, it is essential to consider the long-term costs associated with owning a food truck range hood. These costs include maintenance, energy consumption, filter replacements, and potential repairs. Ignoring these ongoing expenses can lead to unexpected financial burdens.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including cleaning the hood and filters, is crucial for optimal performance and fire safety. The cost of professional cleaning services can range from $100 to $500 or more per cleaning, depending on the hood’s size and the frequency of cleaning.
- Energy Consumption: The energy consumption of the exhaust fan contributes to ongoing operational costs. A higher CFM fan will consume more energy. Consider the energy efficiency of the fan when making your selection. For example, a fan rated at 1000 CFM might consume approximately 500-700 watts, while a more powerful 2000 CFM fan could consume 1000-1400 watts.
- Filter Replacements: Grease filters need regular replacement. The cost of replacement filters varies depending on the type and size. Standard baffle filters typically cost between $20 and $50 per filter. Carbon filters, used for odor control, are more expensive and need more frequent replacement.
- Repairs: While range hoods are designed for durability, repairs are sometimes necessary. The cost of repairs can vary widely, depending on the nature of the problem. It is advisable to budget for potential repairs, which can range from minor electrical fixes ($100-$300) to major component replacements ($500-$1,000 or more).
Comparison Table of Estimated Costs
The following table summarizes the estimated costs for different range hood options, including initial purchase, maintenance, and energy consumption. These are average figures, and actual costs will vary.
| Range Hood Option | Initial Purchase Cost | Annual Maintenance Cost | Annual Energy Cost (Estimate) | Filter Replacement Cost (Annual) | Total Estimated Annual Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Wall-Mounted Hood | $1,500 – $3,500 | $200 – $600 | $150 – $300 | $100 – $200 | $450 – $1,100 |
| Mid-Range Wall-Mounted Hood | $3,500 – $6,000 | $300 – $700 | $250 – $450 | $150 – $300 | $700 – $1,450 |
| Island Hood (Custom) | $4,000 – $8,000+ | $400 – $800 | $300 – $600 | $200 – $400 | $900 – $1,800 |
| Downdraft Hood | $6,000 – $10,000+ | $400 – $800 | $400 – $800 | $250 – $500 | $1,050 – $2,100 |
Concluding Remarks
So, there you have it: the lowdown on food truck range hoods. From the basic function of sucking up smoke and grease to the complex calculations of CFM and the thrilling world of filter maintenance, we’ve covered it all. Remember, a well-chosen, properly installed, and diligently maintained range hood is an investment in your health, your customers’ happiness, and your food truck’s long-term success.
Now go forth, conquer the culinary world, and keep those delicious smells where they belong: in your customer’s bellies, not clogging up your lungs! And remember, safety first (and deliciousness always!).


